* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cultural diversity pp
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
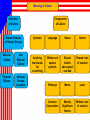
CULTURAL DIVERSITY The Meaning of Culture Cultural Diversity Identify as many culture universals as possible. These are features that exist in all societies. THE MEANING OF CULTURE • Culture- consists of all the shared products of human groups. • Material Culture- physical objects that people create. Examples: automobiles, clothing, books, buildings, computers, etc • Nonmaterial Culture- abstract human creations Examples: language, ideas, beliefs, rules, skills, family patterns, economic systems, etc • Society- a group of mutually interdependent people who have organized in such a way as to share a common culture and feeling of unity. MEANING OF CULTURE CONT. • Symbol- anything that stand for something else. • Language- organization of written or spoken symbols into a standardized system. • Values- shared beliefs about what is good or bad, right or wrong, desirable or undesirable. • Norms- shared rules of conduct that tell people how to act in specific situations. • Law- written rule of conduct that is enacted and enforced by the government EXAMINING CULTURE • Culture is continually changing. • Sociologists examine a culture by breaking it down into levels and studying each level separately. • New material objects are constantly being introduced, as are new words, expressions, and ideas. CULTURE TRAITS • Culture Trait- an individual tool, act, or belief that is related to a particular situation or need. • Our use of forks, knives, and spoons when eating is an example. • The manner in which we greet people is also a culture trait. CULTURAL COMPLEXES • Culture Complex- a cluster of interrelated traits • Example: The game of football -Material traits are football, cleats, helmets, etc. -Specific acts include kicking, passing, catching, tackling, etc. -Beliefs related are to be a good sport, certain rules to the game, penalties given for violations, etc. CULTURE PATTERNS • Culture Patterns- the combination of a number of culture complexes into an interrelated whole. • For example, the complexes of sports such as basketball, softball, swimming, tennis, and soccer combine to form American athletics. CULTURAL VARIATION • The cultures of the world are very different. • For example, there are approximately 240 different languages in the world today. • In addition, the same language may have several variations. -British English, American English, Canadian English, and Australian English. WHAT DO WE HAVE IN COMMON? • Cultural Universalsfeatures common to all cultures • Among these universals are cooking, feasting, tool making, religion, myths, sports, forms of greeting, medicine, dancing, family, housing, music, funeral ceremonies, gift giving, language, etc. VARIATIONS AMONG SOCIETIES • In the 1930’s, Margaret Mead conducted a study of cultural variation among several small societies in New Guinea. The Arapesh The Mundugumor Case Study Page 33 Define these key terms in your own words: •Material Culture •Nonmaterial Culture •Language •Culture Universals DEALING WITH VARIATION • Variations in cultural practices have both positive and negative consequences. • Ethnocentrism- the tendency to view one’s own culture and group as superior • Cultural Relativism- the belief that cultures should be judged by their own standards. VARIATION WITHIN SOCIETIES • Subculturesunique cultural characteristics of societies. • Counterculturewhen a group rejects the values, norms, and practices of the larger society and replaces them with a new set of cultural patterns. San Francisco’s Chinatown share many broad American culture traits but also have their own customs. Meaning of Culture Definition of Culture Shared Products of Human Groups Material Culture Non Material Culture Physical Objects Abstract Human Creations Components of Culture Symbols Language Values Norms Anything that stands for something Written and spoken symbols Shared beliefs about good and bad Shared rules of conduct Folkways Mores Laws Common Conventions Morally Significant Norms Written rules of conduct