* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The vertebral column is 33 vertebrae held together by ligaments and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
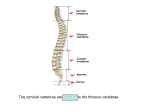
The vertebral column is 33 vertebrae held together by ligaments and muscles, with intervertebral discs in between. The vertebral column provides support and upright posture (attenuates loads) for the body. It is also a site for many muscle attachments. There are natural curves in the spine to help with the support and posture, as well as increasing the flexibility of the spine. The 33 vertebrae are divided into 5 sections, with each group having unique features designed for specific purposes. The groups are: cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacrum (5), and coccyx (4). All vertebrae have a body, 2 transverse processes, a spinous process, superior/inferior articulating facets, lamina, pedicle, and a vertebral foramen. 1 There are anterior convex curves in the cervical and lumbar spines. Posterior concave curves occur in the thoracic and sacral-coccygeal spines. The curves of the spine may increase/decrease as the body’s center of gravity shifts (ex: pregnancy, weight gain/loss, trauma)—this is a result of trying to maintain in the upright position, the brain over the body’s center of gravity. 2 Scoliosis—excessive lateral curvature; side to side Kyphosis—hunchback; excessive curvature of thoracic Lordosis—swayback ; excessive curvature of lumbar 3 C1 and C2 are shaped differently than the other 5 cervical vertebrae to permit the head to rotate. C1 (atlas) = holds up the world (head) and is missing a body; it articulates with the occipital bone as well as rotating around the odontoid process (dens) of the C2 vertebrae (atlantoaxial joint). The atlantoaxial joint is what type of joint?? C2 (axis) = odontoid process projects up C3-C7 = the body is small and all the processes are short and blunted. Their spinous processes are bifircated (split) to provide passage of blood vessels and the transverse processes have holes in it (transverse foramen) where spinal nerves exit. 4 Be able to identify these landmarks Pedicle = connects the body to the transverse process Lamina = connects the transverse process to the spinous process Vertebral Foramen = where the spinal cord goes 5 *Identify which vertebrae is the atlas and which vertebrae is the axis* The bottom 2 vertebrae are C3 (smaller one) and C7 (the bigger one). Intervertebral Foramen = hole in between 2 vertebrae that allows nerves to leave the spine and go to other parts of the body Superior Articulating Facet = facet that projects upward Inferior Articulating Facet = facet that projects downwards *What type of joint are facets???? 6 Atlantoccipital joint is a condyloid joint. Atlantoaxial joint is what kind of joint again??? 7 Thoracic vertebrae are thicker and bigger than cervical vertebrae. They have a bigger body and the spinous process is longer and projects downward at a sharp angle. The facets are grooved out more and easier to see and there is also a groove on the transverse processes. Why would there be a groove there??? The groove is for the ribs. It’s where the ribs come around and articulate with the vertebral column. These notches provide the articulation of the 12 pairs of ribs with the 12 thoracic vertebrae. 8 The lumbar vertebrae are the largest vertebrae. Lumbar vertebrae are different from the thoracic by the body being even thicker. The reason for that is the lumbar region is in the lower back and so it has to bear a lot more of the weight from the body. Therefore, the body is thicker to deal with that extra load. The lumbar vertebrae also has a short and stubby spinous process. 9 Be sure to identify all of the landmarks and to know the differences between the 3 vertebrae regions: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. 10 This website can be a good review as you learn the different landmarks. It will also be helpful when we go over all of the bones. 11 Ligamentum nuchae helps sustain the weight of the head in animals and helps restore the head to its normal position. The longitudinal ligaments are also known as the interbody ligaments. The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament runs along the anterior aspect of the body of all 33 vertebrae. It is structurally the weakest of all the spinal column ligaments and it limits hyperextension of the head/neck. So if you get bad whiplash from a car accident, you probably severely stretched or tore your anterior longitudinal ligament during the hyperextension of the neck as your head whipped back. The Posterior Longitudinal Ligament runs along the posterior aspect of the bodies of all 33 vertebrae. It helps form the anterior wall of the spinal canal and it limits flexion of the head/neck. 12 More movement is allowed in the cervical and lumbar regions, whereas movement is more restricted in the thoracic region due to the ribs. 13 Intervertebral discs are cartilaginous and help absorb shock in between the vertebrae as well as separating them to allow nerve roots to pass from the spinal canal to other parts in the body. You have a herniated disc when the inner nucleus pulposus bulges out through the outer layer (annulus fibrosus). Low back pain and motion restriction is usually associated with a herniated intervertebral disc. In your lumbar region, about L4-L5, you have a big important nerve called the sciatic nerve. If a herniated disc bulges out in that region and hits the sciatic nerve, an acute lower back pain radiates down the posterolateral aspect of the thigh. 14 15 16 Spinal nerves innervating the musculature are formed into plexuses, or a network of nerves. Nerves that innervate the head and cervical spine come from the cervical plexus. The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm and allows us to breathe. The brachial plexus innervates the upper extremities and the lumbar, etc. innervate the lower extremities. 17 18 The thorax creates a large compartment called the thoracic cavity (chest cavity), which houses the lungs and heart. The manubrium is the top upside-down shaped triangle of the sternum. The top notch of the top part of the manubrium is called the suprasternal notch (also called the jugular notch) and the palpable horizontal ridge connecting the manubrium to the body is called the sternal angle. The sternal angle is a reference point for locating the 2nd rib and for listening to heart valve sounds with a stethoscope. The xiphoid process is the bottom point of the sternum and is a reference point for CPR compressions. 19 Costochondral Joint = where the rib and cartilage come together Costosternal Joint= where the ribs/cartilage meet the sternum **The ribs are connected to the sternum by cartilage which helps make the ribs more flexible for breathing. True ribs have a direct connection to the sternum. False ribs have an indirect connection because they attach jointly with the cartilage to the sternum. The floating ribs don’t attach to the sternum at all. 20 The inner walls of the chest cavity and linings of the lungs create a vacuum, and movement of the thorax creates changes in pressure within the chest cavity, which causes air to enter into and be expelled from the lungs. Movement at the joints of the thorax allows for the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, and muscles attached to these bones create that movement, which will be discussed in Unit 2. 21 The head articulates with the bodies of 2 thoracic vertebrae. Remember there are 12 thoracic vertebrae and 12 pairs of ribs…The tubercle on the rib articulates on the groove of the transverse process of the vertebrae. And the anterior end is where the costal cartilage connects. Therefore, the ribs articulate posteriorly with the thoracic vertebrae and anteriorly with the sternum. The rib cage is important because it is made up of 12 vertebrae, 24 ribs, and a breastbone (made up of 3 parts) that all helps to protect the heart and lungs from knocks and bumps. 22 The head articulates with the thoracic vertebrae. 23 24 Adequate pain control is important so you can breathe deeply and avoid lung complications. If you don’t breathe deep enough because it hurts, mucus and moisture build up in the lungs and lead to infections such as pneumonia. Pneumothorax can result as well which is when your lungs collapse. Fracture of the last 2 ribs (your floating ribs) can cause damage to your kidneys, liver, and spleen. 25