* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.6 Rate of reaction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
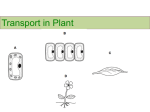
Calculating Rate of Reaction (RoR) Units for RoR g/s cm3/s Model answer e.g. Small particles Larger particles Large surface area, therefore a higher frequency of collisions happen between reactants, more successful collisions, meaning a faster rate of reaction Smaller surface area, therefore a lower frequency of collisions happen between reactants, there will be fewer successful collisions, meaning a slower rate of reaction. 4.6 Rate of reaction Key words: Rate of reaction – the rate at which a reactant is used up, or the rate at which a product is formed Collision theory- An explanation of chemical reactions in terms of reacting particles colliding with enough energy for a reaction to take place. Activation energy – The minimum energy needed for a reaction to start off. Concentration – The amount of a substance in a given volume of solution Catalyst – A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but remains chemically unchanged itself at the end of the reaction. Using tangents to work out RoR Enzymes carry out the chemical reactions in our body; these reactions are known as METABOLISM. Digestive enzymes break large food molecules into small molecules so they can be absorbed. Cells are the building blocks of living organisms Tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function Organs are lots of tissues performing specific functions. Organs are organised into organs systems, which work together to form organisms. Plasma: Yellow liquid; transports blood cells, waste CO2 to lungs, urea from liver to kidneys, digested food. Red blood cells: Carry oxygen; are biconcave to increase surface area, haemoglobin which carries oxygen and they have no nucleus to carry more oxygen. White blood cell: involved in immunity; fewer in number that red blood cells, much bigger, nucleus, produce antibodies, antitoxins and engulf pathogens) Platelets: small fragments of cells, no nucleus involved in blood clotting. Enzyme action is affected by temperature and pH. Adaptations of the lungs for gas exchange. Organisation: Digestive system, heart and lungs. enzyme amylase Protease lipase reaction catalysed starch → sugars proteins → amino acids lipids → fatty acids + glycerol enzyme amylase protease lipase where produced salivary glands, pancreas, small intestine stomach, pancreas, small intestine pancreas, small intestine Adaptations of the digestive system: Bile: produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder; emulsifies fat (smaller droplets) and neutralises stomach acid. This increases fat digestion. LOCK AND KEY MODEL Heart rate is controlled by group of cells located in the right atrium that act as a pacemaker. Artificial pacemakers are electrical machines that correct an irregular heartbeat. Food test Food type Start - Positive result Iodine Starch Orange – blue/black Biuret test Protein Blue – Purple Benedicts Some sugars Blue – red/green orange Fat Sudan III Orange layer Plants Roots, stem and leaves form plant organ system for transport. Transpiration: The loss of water vapour from the leaves. Epidermis: covers and protects the leaf. Palisade mesophyll: contains lots of chloroplasts. Spongy mesophyll: a few chloroplasts but has air spaces to increase surface area for diffusion. Xylem and phloem: transport tissues Meristem: growing tips in roots and shoots, made up of rapidly dividing plants cells that grow and differentiate into different types of cells. Translocation: Movement of dissolved sugars from the leaves to the rest of plant. Phloem tissue transports the sugars. Composed of tubes of elongated cells. Cell sap can move from one phloem cell to next through pores in the end walls. Root hair cells increase surface area to uptake more water by osmosis and mineral ions by active transport. Xylem tissue transports water and mineral ions from roots to stems and leaves. Hollow strengthened tubes to transport water in transpiration stream. Stomata in leaves are open and closed by the guard cells to allow water and carbon dioxide to diffuse in and out. Transpiration rate increases in high temperatures as molecules move faster in high temperatures and photosynthesis is increased opening up guard cells. High humidity reduces transpiration as the is a lower concentration gradient for osmosis at the stomata. High air movement increases transpiration by maintaining steep concentration gradient. Light intensity increases photosynthesis which opens stomata increasing water loss. Cancer : uncontrolled cell division and growth. Benign tumours: growth of abnormal cells in one area within membrane – DO NOT SPREAD. Malignant tumour cells are cancer. Invade tissues and spread to different parts of the body and form secondary tumours. There are genetic and lifestyle factors that increase risk. Other causal factors (lifestyle behaviours that cause certain diseases). Obesity linked to Type 2 diabetes Alcohol on liver (liver tissue scarring which do not work as well and liver cancer) and brain (becomes soft and pulpy and can not longer function properly). Smoking on lung disease and cancer: Bronchitis, COPD and lung cancer. Smoking and alcohol during pregnancy. Smoking causes lack of oxygen to foetus (premature births, low birthweight and even stillbirths). Alcohol can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, premature births and low birth weight. Babies can have facial deformities, kidney, liver, heart and learning problems (foetal alcohol syndrome). Coronary Heart Disease CHD: a non-communicable disease. CHD formed from a build up of fatty material builds up inside of coronary arteries, narrowing them. This reduces oxygen to the heart muscle – lead to heart attack or death. Treatment of CHD Stents Statins Given to reduce the cholesterol which slows down fatty deposits. artery. Transplants Heart bypass surgery can take place using veins f from other parts of the body to replace the blocked A donor heart or heart and lungs can be transplanted. An artificial heart can be used to keep patients alive whilst waiting for a transplant or allow the heart to rest. Faulty heart valves: In some people valves become faulty, preventing the valve opening or it may develop a leak. People become breathless or may die. They can replaced using biological or mechanical valves. Health: state of physical and mental well-being. Disease, both communicable and non-communicable cause ill health. Factors such as diet, stress, and life situations have an effect on health. Different types of disease may interact: • Defects in immune system means someone more likely to suffer from infectious disease. • Viruses living in cells can trigger some cancer. • Immune reactions first caused by pathogens can trigger allergies. • Severe physical ill health can lead to depression and other mental illness. Cardiovascular disease: Diet: Too much fat (needed for energy and organ protection) can cause obesity and heart disease. Exercise: Too little exercise can cause obesity and heart disease. Smoking: Can lead to arteries narrowing, clot formation, increase in blood pressure can cause heart disease. Organisation revision questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Describe the journey of food through the digestive system. What are the role of enzymes in our body? What is this called? 15. How do enzymes speed up the 16. process of digestion What is the name of the model given to explain how enzymes work? Describe how amylase breaks 17. down starch and where it does 18. it. What is the effect of temperature on how enzymes 19. work? Name the four main chambers of the heart. Describe how heart rate is regulated. What can be given to 20. regulate an irregular heart beat? 21. How are arteries and veins adapted to do their job? Give three ways the lungs are 22. adapted to have efficient gas exchange. a. Name the two cells carried in 23. the blood. b. State their job (function) 24. c. How are they adapted to 25. carry out this function? 26. Why is coronary heart disease 27. described as noncommunicable? Give three ways coronary heart 28. disease can be treated Describe the advantages and 29. disadvantages of using a stent to improve blood flow to the heart. • Give a definition of health. Explain how the following effect the risk of cardiovascular disease: Smoking, Exercise and • Diet Name the diseases that the following lifestyle behaviours • are CAUSAL factors for (including during pregnancy): Smoking, Alcohol What is cancer? • Describe a malignant tumour and it’s effect on the body. Look at the graph; what is the relationship between obesity and Type 2 diabetes Explain the role of the palisade and spongy mesophyll layer in the leaf What is translocation? Where does it take place? What is transpiration? What organs in the plant move water from the root to the leaves? How are these organs adapted to do this? How do the following factors affect the rate of transpiration? High temperatures: Increased light intensity: High humidity: Increased air movement (windy): What are the properties of reflection, refraction and diffraction? Task 1: Copy and fill out the table below Definition Reflection Refraction Diffraction Properties Examples e.g. the law of reflection states that … The change in _________ of ________ when they travel across a b_______ S_______ pool appearing s_______than it is • The n_______ a gap is, the g_________ the diffraction • The w_______ a gap is, the _________ the diffraction