* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction - Madera Unified School District
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Freedmen's Colony of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction & The New
South
Key Questions of Reconstruction
1. How do we
bring the South
back into the
Union?
2. How do we
rebuild the
South after its
destruction
during the war?
4. What branch
of government
should control
the process of
Reconstruction?
3. How do we
integrate and
protect newlyemancipated
black freedmen?
Phases of Reconstruction
A.
B.
C.
Phase One: Presidential
Reconstruction (1863 – 1866)
Phase Two: Congressional (Radical)
Reconstruction (1866 – 1873)
Phase Three: Redeemer
Reconstruction (1873 – 1877)
The Defeated South
• Land & Cities in ruins
• Wealth (cotton & slaves) gone
• Major psychological effects
President Lincoln’s Plan
• Proclamation of Amnesty and
Reconstruction (December 1863)
– a.k.a. 10% Plan
• 10% of the 1860 voting population
taking an oath of loyalty and
establishing a government
– the state would be recognized &
representatives seated
Radical Republicans
• Republicans who took a tougher stance
• Wanted to fundamentally change Southern society
• Proposed Wade-Davis Bill (1864)
– Required 50% of 1860 voters to take an “iron clad” oath
of allegiance
– Required a state constitutional convention before the
election of state officials
– Enacted specific safeguards of freedmen’s liberties
• Pocket vetoed by Lincoln
Freedmen’s Bureau (1865)
• Established to aid the
emancipated slaves
• Provided social, economic, &
educational services
• Many northern abolitionists
went to the South to help the
freedmen
• Called “carpetbaggers” by
white southerners
President Andrew Johnson
• Like Lincoln, never believed
the states legally left the Union
• Believed it was “Restoration”
not “Reconstruction”
Johnson’s Plan (10%+)
• State constitutions had to repudiate slavery & secession
• Granted amnesty to all who pledged loyalty to the
Union
• Not granted to major Confederate officials or wealthy
landowners
– Had to apply directly to Johnson
– 90% granted pardons
• Fall 1865, 10 of 11 southern states “restored”
• Planter elite back in power
• State constitutions fell short of recognizing
emancipation
Black Codes
• Laws passed (in the South) denying rights of
citizenship to the freedmen
• Purpose:
– Guarantee stable labor
supply
– Restore pre-emancipation
system of race relations
13th Amendment
• Concern that the Emancipation Proclamation was
not Constitutional
• 13th Amendment ratified December 1865
• Ended slavery in the U.S.
Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude,
except as punishment for crime whereof the
party shall have been duly convicted, shall
exist within the United States or any place
subject to their jurisdiction.
Congress Breaks with the President
• Dec 1865, Republicans worried about the South
• Prevented the seating of Southern representatives in
Congress
• Spring 1866 passed 2 bills to aid
freedmen
– Civil Rights bill
– Expansion of Freedmen’s Bureau
• Both vetoed by Johnson
• Congress passed both bills over
Johnson’s vetoes 1st time in
U. S. history
th
14
Amendment
• Proposed to protect Civil Rights Act (1866)
• Ratified in July 1868
– Defined citizenship to include former slaves
– Prohibited states from violating the rights of citizens
– Gave Congress the power to reduce representation of any
state that denied suffrage to males over the age of 21
• Southern states would be punished for denying
the right to vote to black citizens
1866 Elections
• Referendum on reconstruction
– Democrat or Republican?
– Presidential or Congressional?
• Republicans “Waved the Bloody Shirt”
• Republicans
(Congress) won
Johnson’s “Swing around
the Circle”
Congressional Plan for
Reconstruction
• Constitutional conventions elected by universal
manhood suffrage
• New constitutions had to protect black suffrage
rights and ratify the 13th and 14th Amendments
• Congress began passing laws to oversee
Reconstruction in early 1867 all over Johnson’s veto
Military Reconstruction Act
• Restarted Reconstruction in the 10 Southern states
(no TN) that refused to ratify the 14th Amendment
• Divided the 10 “unreconstructed states” into 5
military districts
• Military now
oversaw state
governments & voter
registration
Tenure of Office Act
• President couldn’t remove any officials
without the Senate’s consent, if the position
originally required Senate approval
• Designed to protect radical Republican
members of Lincoln’s cabinet (esp. Edwin
Stanton, Sec of War)
• Johnson removed him anyways Feb 1868
• Fired generals who were in favor of Radical
Republican plan
Edwin Stanton
Impeachment of a President
• Feb 24, 1868 HOR votes to impeach Johnson (12647)
– 11 counts of “high crimes and misdemeanors”
• Goes on trial in the Senate
• Lasts 11 weeks
• Acquitted
– 35 to convict, 19 to
acquit
– 1 vote shy of 2/3 vote
needed
Reason for Acquittal
• Moderate Republicans feared Johnson’s removal
– Radical Rep Benjamin Wade would become President
• Met with Johnson who agreed to stop challenging
Reconstruction
• Congress’ plans move forward
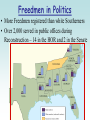
Freedmen in Politics
• Black men could register and vote in states since
1867
– Military protected them
Freedmen in Politics
• More Freedmen registered than white Southerners
• Over 2,000 served in public offices during
Reconstruction – 14 in the HOR and 2 in the Senate
Growing Republican Support
• Freedmen voted Republican
• Carpetbaggers voted Republican
• White Southern Republicans were Scalawags
– Seen as traitors to their race & region
• Southern governments were Republican
• By 1868 8 states fully “Reconstructed”
– But do these governments represent the
Southerners?
The Invisible Empire of the South
• The Ku Klux Klan was established
in 1866 to combat Reconstruction
• Conducted a “Reign of Terror”
against Republicans
Election of 1868
• Republicans nominated
U.S. Grant
• Democrats nominate
Horatio Seymour
Strategy of the Republicans
• “Wave the bloody
shirt”
• Associate the
Democrats with
treason and war
Results
th
15
Amendment
• Northern states did not all have black suffrage
• 15th amendment proposed to allow suffrage rights to
all men
– The right of citizens of the United States to vote
shall not be denied or abridged by the United States
or by any state on account of race, color, or
previous condition of servitude.
• Ratified 1870
• Women’s right groups furious they were overlooked
• Final 3 Southern states forced to amend & brought
back into the Union in 1870
Dealing with the KKK
• Reconstruction complete, but still major problems in
the South
• Enforcement Acts of 1870 & 1871 [also known as
the KKK Act]
– Outlawed terrorist societies
– Allowed the President to
use the military to put down
any terrorist societies
• Effectively ended the
Reign of Terror, but not southern resentment
Northern Support Wanes
• Problems for the North:
– Grant administration’s Corruption
– Republicans lose control of HOR
in 1874 election
– Resurgence of Northern Racism
– Concern over westward
expansion and Indian wars
– Monetary issues remaining from the War
– Panic of 1873
Who are the Redeemers?
• Redeemers: Democrats who did not oppose
Reconstruction but wanted it to end
• Wanted to oust the Radical Republican from
control & restore or redeem the South back to
Democratic control
Effects of the Redeemers
• By 1876, 8 Southern states are under
Democratic control
• African Americans lose gains made during
Reconstruction
• North tired of interfering
Civil Rights Act of 1875
• Passed before Republicans lost control of HOR
• Outlawed racial discrimination in theaters,
hotels, RRs, and other public places
• Lacked enforcement
• Found unconstitutional in 1883
• No new Civil Rights laws passed until the
1960s
1876 Election
• Republicans nominate
Hayes
• Democrats nominate
Tilden
Results
• Who wins?
Political Crisis of 1877
• Contested results – both sides claimed to have
won FL, LA, & SC
– Not a tie, so it doesn’t go to HOR
• Special Electoral Commission established
– 5 HOR, 5 Senators, 5 SC judges
– 8 Rep, 7 Dem
• Election went to Hayes
Compromise of 1877
• Democrats &
Republicans made a
deal
• If Hayes won:
– Gov’t would pursue a
policy of noninterference
in the South
– Reconstruction is OVER
African American Migration
• 1st instinct after emancipation was to move
• Significant shift toward the cities
– 10 largest Southern cities saw the black population
double
• Most stayed or returned to their former
plantations
Effects on African-American
Culture
• Freedom strengthened family ties
– Many reunions
– Legal Marriages
• Changes in Gender Roles
– Men took on a more typical head of household role
– Women were the more subservient spouse, but still
worked outside of the home
• Rapid spread of churches and schools
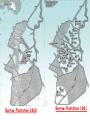
Sharecropping
• Most Freedmen hoped to become self-sufficient
farmers but couldn’t afford to buy land
• Blacks rented land and paid their rent by dividing
their crop with their landlord (former owner)
Barrow Plantation 1860
Barrow Plantation 1881
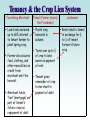
Tenancy & the Crop Lien System
Furnishing Merchant
Loan tools and seed
up to 60% interest
to tenant farmer to
plant spring crop.
Farmer also secures
food, clothing, and
other necessities on
credit from
merchant until the
harvest.
Merchant holds
“lien” {mortgage} on
part of tenant’s
future crops as
repayment of debt.
Tenant Farmer (mainly
the Freedmen)
Plants crop,
harvests in
autumn.
Turns over up to ½
of crop to land
owner as payment
of rent.
Tenant gives
remainder of crop
to merchant in
payment of debt.
Landowner
Rents land to tenant
in exchange for ¼
to ½ of tenant
farmer’s future
crop.
Jim Crow Laws
• Discriminatory and segregationist legislation passed
in the South beginning in the 1880’s
• Meant to forestall racial/social equality in the South
• Beginning of the “White Only” and “Colored” signs
across the South
Plessy v. Ferguson (1896)
• Homer Plessy (1/8 black) boarded a white only
train in LA to challenge Jim Crow laws
• Supreme Court ruled that segregation was
legal as long as there were “separate and equal
facilities” provided
• Segregation sanctioned by the federal
government
Loss of voting rights
• Literacy tests, Poll taxes & Property qualifications
enacted to restrict Black voting
• Grandfather clauses: used to get the poor whites
exempt from qualifications
• 1898 Supreme Court ruled these were a proper
means of restricting the ballot to “Qualified” voters
• Only 5% of the Southern blacks eligible voted
In the End..
• Slavery was over, but not much changed in the
South