* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 3.4
Survey
Document related concepts
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
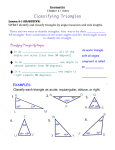
Applying Parallel Lines to Polygons Lesson 3.4 Pre-AP Geometry Objectives 1. Classify triangles according to sides and to angles. 2. State and apply the theorem and the corollaries about the sum of the measure of the angles of a triangle. 3. State and apply the theorem about the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle. Triangle A figure formed by three segments joining three non-collinear points. Each of the three points is called a vertex of the triangle. The segments are the sides of the triangle. B A C Classifying Triangles There are two ways of classifying triangles • by their sides • by their angles Equilateral Triangle All sides are the same length. Isosceles Triangles At least two sides are the same length Scalene Triangles • No sides are the same length Acute Triangles Acute triangles have three acute angles Right Triangles Right triangles have one right angle Obtuse Triangles Obtuse triangles have one obtuse angle Equiangular Triangle Equiangular triangles have all congruent angles. Auxiliary Line A line, not originally a part of a diagram, that is added to more clearly show a relationship. Auxiliary lines are usually shown as dashed lines. Theorem 3-11 The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180º. Definition: Corollary A corollary is a statement which follows readily from a previously proven statement, typically a mathematical theorem. Corollary 1 If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the third angles are congruent. Corollary 2 Each angle of an equiangular triangle has a measure of 60º. Corollary 3 In a triangle, there can be at most one right angle or obtuse angle. Corollary 4 The acute angles of a right triangle are complementary. Definitions Exterior Angle An angle that forms a linear pair with one of the interior angles of the triangle. Remote Interior Angles In a triangle, the two angles that are nonadjacent to the exterior angle of interest. Theorem 3-12 The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles. B C A