* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensory System Note Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
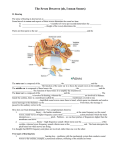
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers SENSORY SYSTEM • Define at least 10 terms relating to the sensory system. • Describe the function of the sensory system. • Identify at least 10 sensory system structures and the function of each. • Describe at least five disorders of the sensory system. Key Terms • • • • • • Accommodation Auditory Cutaneous Equilibrium Gustatory Intraocular • • • • • Olfactory Receptor Refraction Stimulus Vision What are the senses? Sight Eyes Structure and Function • Sensory system consists of receptors in specialized cells and organs that perceive changes in the internal and external environment • The stimuli cause nerve impulses that are sent to the brain for interpretation • Environmental stimuli are perceived with the senses of vision, hearing, touch, taste, position, and balance Smell Hearing Nose Ears Taste Touch Skin Tongue Eye • Considered the most important sensory organ • 60-90% of all information to the brain is via the eyes • 20% of the structure is exposed • Structure - 3 parts External Eye Ball Internal 1 Eye ball Sclera (i) Sclera- white part, supports and gives structure (e) Cornea- focuses images (outer) (b) Iris- colored part, dilates and contracts to let light in (d) Pupil- black dot, allows light in (f) Lens- focuses images (inner) (k) Optic nerve- transmits info to the brain Optic N. Iris Pupil Cornea Lens Internal External Skeletal cavity Eye lid & lashes Mucous membrane Vision Rods 100 million, sensitive to dim light Cones 7 million, see bright light and color (red, green, blue) (m) Retina back part of the eye that contains the rods/cones Retina Figure 20-2 Eye Functions Like A Camera • When we see something, light refracts from object -> cornea, where the rays are bent (and turned upside down), to the lens where the rays are focused onto the retina. • The retina then turns the image into nerve impulses and sends to the brain via the optic nerve 2 Ear Hearing • Used for hearing • Maintains equilibrium • Structure external middle inner How Hearing Works • Middle Ear – Contains the Tympanic Membrane (ear drum) • Moves according to the type of sound waves that vibrate it, transmits sounds to the inner ear. • Can also protect the inner ear from sounds which may damage it. • Pressure is equalized between the ear and the mouth with the Eustachian Tube. How Hearing Works • Inner Ear – Cochlea • Contains fluid which transmits sound vibrations to the hairs in the organ of Corti. How Hearing Works • Outer Ear (Pinna) – Collects sound, channels to the middle ear. – The sound at this point is mechanical sound waves How Hearing Works • At this point, the sound waves are vibrating the ear drum, and these waves have to be passed through the ossicles – Malleus – Incus – Stapes Equilibrium • Semicircular Canals – Contain fluid that moves around when we move, telling our brain where we are positioned. – Organ of Corti • Hairs collect sound and send it to the Cochlear nerves, which carry the sound vibrations to the brain. 3 Tongue Taste taste is perceived by specialized cells called taste buds (papillae) Over 10,000 of these, each with 50-150 receptor cells Nose Smell smell originates in receptors in the nose and travels to the brain via nerves sense of smell is 10,000x more sensitive than taste 5,000 different smells can be perceived 30 primary “pure” odors (peppermint, floral, etc) Skin Touch 5 specialized cells in the skin sensitive to: touch pressure temp pain Also sensitive to knowing where you are in space. 4 Acorcnidg to a sutdy at cimadbrgie uirstneiy, it dsenot mtaetr waht odrer lterets are, olny that the fisrt and lsat are rgiht A BIRD IN THE THE BUSH 5 Assessment Techniques • Sight – Ophthalmoscope examines inner structure of the eye – Visual acuity with Snellen Test Assessment Techniques (Continued) • Hearing – Otoscope is used to view the structures of ear – Impedance testing measures flexibility of the tympanic membrane 6 Disorders of the Sensory System • Achromatism – Called color blindness, is a common inherited defect • Amblyopia – Also called “lazy eye,” is poor vision in one eye often resulting from better vision in the other eye during infancy or early childhood Disorders of the Sensory System (Continued) • Astigmatism – A congenital defect causing imperfect curvature of the cornea resulting in blurred vision • Cataract – Clouding of the lens that causes blurred or partial vision • Conjunctivitis – Also called pink eye, is a bacterial or viral inflammation of the eyelid Disorders of the Sensory System (Continued) • Diplopia – Or double vision, results from muscle imbalance or paralysis of an extraocular muscle • Epistaxis – Nosebleed resulting from disease, trauma, or other conditions such as hypertension, leukemia, or rheumatic fever Disorders of the Sensory System (Continued) • Glaucoma – An increase in the pressure inside the eye, caused by trauma or hereditary factors • Hyperopia – Farsightedness resulting from a congenital deformity in the eye • Macular degeneration – A slow or sudden painless loss of central vision 7 Disorders of the Sensory System (Continued) • Myopia – Nearsightedness resulting from a congenital deformity in the eye Disorders of the Sensory System (Continued) • Otitis media – A middle ear bacterial or viral infection common in young children • Night blindness – Poor vision in dim light that results from a deficiency in the rods of the retina Disorders of the Sensory System (Continued) • Rhinitis – Inflammation of the lining of the nose caused by allergic reaction, viral infection, sinusitis, or chemical irritants • Ruptured eardrum – Results from infection, an explosion, a blow to the head, or a sharp object inserted into the ear Disorders of the Sensory System (Continued) • Sinusitis – A chronic or acute inflammation of the cranium • Stye – Bacterial infection of the sebaceous glands of the eyelid 8 9 10











![[SENSORY LANGUAGE WRITING TOOL]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014348242_1-6458abd974b03da267bcaa1c7b2177cc-150x150.png)