* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide - page under construction
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
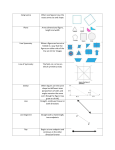
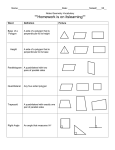
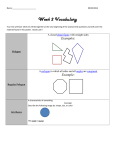
Geometry Chapter 6 Study Guide (6.1-6.6) Polygons and Quadrilaterals Vocabulary side of a polygon - each segment that forms a polygon vertex of a polygon - endpoint of two sides diagonal - a segment that connects any two nonconsecutive vertices regular polygon - a polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular concave - a polygon with a diagonal containing points exterior to the polygon convex - a polygon in which no diagonal contains points exterior to the polygon parallelogram - a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides kite - a quadrilateral with exactly two pairs of congruent consecutive sides trapezoid - a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides • base - a parallel side in a trapezoid • base angles - two consecutive angles whose common side is the base of a trapezoid • leg - a nonparallel side in a trapezoid Theorems, Postulates, and Properties • Polygon Angle Sum Theorem - The sum of the interior angle measures of a convex polygon with n sides is (n-2)180˚. • Polygon Exterior Angle Sum Theorem - The sum of the exterior angle measures, one angle at each vertex, of a convex polygon is 360˚. • Properties of a parallelogram: • opposite sides are congruent. • opposite angles are congruent. • consecutive angles are supplementary. • diagonals bisect each other. • Conditions for parallelograms: a quadrilateral in which • one pair of opposite sides are parallel and congruent. • both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. • both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. • both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. • an angle is supplementary to both of its consecutive angles. • the diagonals bisect each other. • Properties of a kite: a quadrilateral in which • its diagonals are perpendicular • exactly one pair of opposite angles are congruent • If a quadrilateral is an isosceles trapezoid, then each pair of base angles are congruent. • If a trapezoid has one pair of congruent base angles, then it is an isosceles triangle. • A trapezoid is isosceles if and only if its diagonals are congruent. • Trapezoid Midsegment Theorem - The midsegment of a trapezoid is parallel to each base, and its length is one half the sum of the lengths of the bases. Geometry Chapter 6 Practice Problems 1) Any regular polygon can be inscribed in a circle. Find the length of a side of the regular octagon in terms of r. Name: ______________________________________ Date: ____________________ Period: ____________ 2) A campground site is in the shape of a convex quadrilateral. Three sides of the campground form two right angles. The third interior angle measures 10˚ less than the fourth angle. Find the measure of each interior angle. ! side length of regular octagon = __________________ Interior angles = _____________________________ 3) Quadrilateral ABCD has midpoints E, F, G, and H. Show that the area of EFGH is half the area of ABCD. 4) In parallelogram EFGH, FH = 5x inches, EG = (2x+4) inches, and JG = 8 inches. What is the length of JH? ! JH = _________________________ 5) The graphs of y = 2x, y = 2x - 5, and y = -x in the coordinate plane contain three sides of a quadrilateral. Find the equation of the line whose graph contains a segment that can complete the quadrilateral and form a parallelogram. 6) Show that the quadrilateral with vertices E(-1, 5), F(2, 4), G(0, -3), and H(-3, -2) is a parallelogram. 7) What is the length of the midsegment of trapezoid ADEB in inches? 8) Construct a kite such that AC is the segment that connects the congruent angles. ! A midsegment length = __________ C