* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Auditory Alterations
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
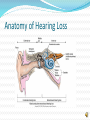
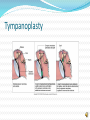
Pediatric Problems Otitis Media Foreign bodies -beads, pencil erasers, insects Treatment -carefully remove foreign body (if able) -seek medical care Ménière's Disease • Ménière's Disease: entire inner ear canal system affected • Population at risk: - usually first occurs in people aged 20 – 50 yrs old -more common in men and in white people • S & S: three main features -Tinnitus - one-sided sensorineural hearing loss - vertigo Treatment for Ménière's Disease Nonsurgical management includes: -slow head movements -diet and lifestyle changes -smoking cessation. Drug Therapy • Nicotinic Acid • Antihistamines: -diphenhydramine hydrochloride (Benadryl) • Antiemetics: -chlorpromazine hydrochloride (Thorazine) • Intratympanic therapy: gentamicin & steroids • Other Measures: Meniett device Meniett’s Device Treatment with Meniett’s device -tympanostomy tube inserted into eardrum -pulses of pressure delivered to inner ear -self directed for 5 mins. TID -studies shown effective in reducing vertigo * *Gates,G., Verrall,A., Green,J.D., Tucci, D.L., & Telian, S.A.(2006). Meniett clinical trial:Long –term follow-up. Archives of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, 132(12), 1311-1316. Ménière’s Disease: Surgical Management Endolymphatic decompression. Surgical management: last resort because hearing in the affected ear is often lost from the procedure Labyrinthectomy Hearing Loss Types of hearing loss Conductive r/t inflammation or obstruction of external or middle ear Sensorineural r/t loud noise, drugs, medical problem Population at risk: older adult Anatomy of Hearing Loss Treatment for Hearing Loss Non-surgical -hearing aids -assistive devices using amplifiers Surgical Interventions -tympanoplasty -stapedectomy Tympanoplasty Nursing Interventions: Pre-op Free of infection Ear flushes Pt. Education: post op expectations -hearing diminished initially -medications Nursing Interventions Post-op Monitor dressings Avoid increased pressure on ear Medications Positioning -Tympanoplasty: lie flat with operative ear face up Potential complication for stapedectomy -Assess for facial nerve damage or muscle weakness Community-Based Care Home care management Health teaching Health care resources Worldwide http://www.wfdeaf.org/ NURSING DIAGNOSES FOR ALTERED HEARING Risk for injury related to altered auditory perception Social Isolation related to decreased hearing Anxiety related to loss of hearing