* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Effects of genocide on youth wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
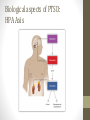
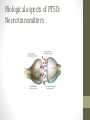
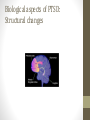
POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER CHARITY HAMMOND, PH.D. PSYCHOLOGIST MICHAEL E. DEBAKEY VA MEDICAL CENTER OBJECTIVES • Describe the history of PTSD • Define the diagnostic criteria of PTSD • Identify risk factors for developing PTSD • Give a brief overview of biological aspects of PTSD • Review evidence based treatment approaches for treating PTSD • Provide resources for learning more about PTSD History of PTSD Shakespeare in Henry IV: Tell me, sweet lord, what is’t that takes from thee Thy stomach, pleasure, and thy golden sleep? Why dost thou bend thine eyes upon the earth, And start so often when thou sit’st alone? Why hast thou lost the fresh blood in thy cheeks, And given my treasures and my rights of thee To thick-eyed musing and cursed melancholy? History of PTSD • • • • • • • • • • • Soldiers heart Da Costa’s syndrome Traumatic neurosis Shell shock Combat fatigue Neurocirculatory asthenia Railway spine Rape trauma syndrome Concentration camp syndrome Battered woman’s syndrome Child abuse syndrome History of PTSD • DSM I (1952): Gross stress reaction • DSM II (1968): Situational reaction • DSM III (1980): Posttraumatic stress disorder • DSM IV (1994): Posttraumatic stress disorder • DSM V (2013): Posttraumatic stress disorder 6 What is traumatic stress? 7 Trauma exposure is common. 8 How common is PTSD? Diagnostic criteria for PTSD Person exposed to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence in one of the following ways: • A) Direct exposure • B) Witnessing in person • C) Indirectly, by learning of a close friend or relative exposed to trauma. • D) Repeated or extreme indirect exposure to aversive details of events, usually in the course of professional duties. Diagnostic criteria for PTSD • Intrusion symptoms: • Recurrent, involuntary, and intrusive memories • Traumatic nightmares • Dissociative reactions (flashbacks) ranging from brief to prolonged • Intense or prolonged distress after exposure to traumatic reminders • Physiological reactivity after exposure to trauma related stimuli Diagnostic criteria for PTSD http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/andrewreeves/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd.html http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/guillermosanchez/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd.html Diagnostic criteria for PTSD • Avoidance symptoms • Avoidance or efforts to avoid distressing memories, thoughts, or feelings about the trauma • Avoidance or efforts to avoid external reminders that lead to thoughts of trauma Diagnostic criteria for PTSD http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/tiachristopher/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd.html http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/wandapegues/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd.html Diagnostic criteria for PTSD • Changes in mood and beliefs • Inability to remember parts of the event • Exaggerated negative beliefs about oneself, others, and the world • Persistent, distorted cognitions about the cause and consequences of event leading to self-blame • Persistent negative emotional state • Diminished interest in participating in significant activities • Feeling detached or estranged from others • Inability to experience positive emotions Diagnostic criteria for PTSD http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/rickcollier/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd.html http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/andrewreeves/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd/2.html Diagnostic criteria for PTSD • Changes in arousal and reactivity: • • • • • • Irritable behavior and angry outbursts Reckless or self-destructive behavior Hypervigilance Exaggerated startle response Problems with concentration Sleep disturbance Diagnostic criteria for PTSD • http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/josesanchez/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd/2.html • http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/veterans/johnangell-jr/how-i-knew-i-had-ptsd.html Diagnostic criteria for PTSD • Symptoms last for more than 1 month • Symptoms cause distress and impairment in functioning • Subtypes: • With dissociative symptoms • With delayed expression (more than 6 months after the event) 19 Why do some people get PTSD while others do not? 20 Personal Factors 21 Traumatic Event 22 Recovery Environment 23 Other Co-occurring Problems Biological aspects of PTSD: HPA Axis Biological aspects of PTSD: Neurotransmitters Biological aspects of PTSD: Structural changes Treatments for PTSD • Cochrane review (2013) • VA/DoD guidelines (2010) • International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies guidelines (2005) • Institute of Medicine (2007) Evidence-based Psychotherapy Treatments Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): build new cognitive skills and engage in new behaviors, or change existing ones • Prolonged Exposure (PE): In PE you confront situations you have been avoiding until distress decreases. • Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT): In CPT you examine and challenge thoughts about the trauma until you can change the way you feel. 28 • First line psychotherapies Evidence-based Psychotherapy Treatments • Stress Inoculation Training (SIT): By teaching coping skills, SIT can help you find new ways to deal with PTSD symptoms. These skills can also help you manage other stressful situations or event in your life. • Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR helps you process upsetting memories, thoughts, and feelings related to trauma. In EMDR, you’ll pay attention to a back-and-forth movement or sound while you think about the upsetting memory long enough for it to become less distressing. 29 • Other VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline first line psychotherapies include: Treatments for PTSD: Psychotherapy • Exposure therapy http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/questions--whattreatment-was-like-for-me--2.html http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/questions--whattreatment-was-like-for-me--3.html http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/questions--whattreatment-was-like-for-me--8.html • Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT/CPT) http://www.ptsd.va.gov/apps/AboutFace/therapies/cpt.html Evidence-based Pharmacological Treatments • First line medications • Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) • E.g., paroxetine (Paxil), sertraline (Zoloft) • Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) • E.g., venlafaxine (Effexor) • Warning: Benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium, Klonopin) • Limited efficacy • Increased safety concerns • Not recommended for PTSD Resources National Center for PTSD www.ptsd.va.gov International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies www.istss.org National Child Traumatic Stress Network www.nctsnet.org Center for Deployment Psychology www.deploymentpsych.org • NCPTSD developed toolkits for various professionals who have contact with Veterans or those with PTSD in their line of work. • Toolkits offer information and networking resources. 33 Toolkits PTSD Basics • Understanding PTSD and PTSD Treatment is a booklet that explains basic information about: • What can cause PTSD? • What are the symptoms of PTSD? • What do I do if I have symptoms? • How do I know if I have PTSD? • Why get treatment for PTSD? • Common questions about treatment • What happens during PTSD treatment? • How do I choose a mental health provider? • Where can I go to get help? 34 • What is PTSD? Animated Whiteboard Videos • NCPTSD created a series of whiteboards, including one for professionals about PTSD and effective treatments. • Short (~3 minute), engaging videos that are easily shared via email or Facebook. 36 AboutFace • NCPTSD has partnered with a number of organizations to develop a variety of mobile apps. • Apps are focused on PTSD, related health problems (e.g., insomnia, alcohol use, etc.), or general well-being. • There are apps for patients, providers, and for use with patient-provider dyads. 37 Mobile Apps Thank you. Questions? Contact information: Charity Hammond, Ph.D. [email protected]