* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Networks..
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
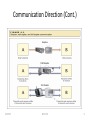
Foundations of information systems : BIS 1202 Lecture3 Telecommunications, Networks, and the Internet BIS1202 1 Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture students should; Identify and describe the fundamental components of a telecommunications system including media and hardware devices Identify several network types and describe the uses and limitations of each Name three basic processing alternatives for organizations that require two or more computer systems and discuss their fundamental features BIS1202 2 Learning Objectives Understand how telecommunication has improved business Factors affecting communication in telecommunications Understand computer networks and protocols Understand network hardware and how the internet works BIS1202 3 Telecommunications The communication of information by electronic means, usually over a distance. Telecommunications has improved business in three main ways: Better communication Higher efficiency Better distribution of data BIS1100 4 Telecommunications system A telecommunication system is a collection of compatible hardware and software arranged to communicate from one location to another. Essential components of a telecommunication system •Computers-to process information •Terminals or any input/output devices that send or receive data. •Communication channels-links by which data or voice are transmitted between sending and receiving devices in a network BIS1100 5 Telecommunications system Essential components of a telecommunication system End processors which provide support functions for data transmission and reception E.g. modem and decoders •Communications software, which controls input and output activities and manages other functions of the communications network BIS1202 6 Telecommunications in Daily Use • Cellular Phones • Videoconferences • Voice Mail • fax • Web-Based Electronic Commerce • Worldwide Peer-to-Peer File Sharing – Napster, Gnutella, Morpheus BIS1202 7 Communication Direction • Simplex – One-way in one direction e.g. antenna • Half-Duplex • Systems that provide communications in both directions, but only one direction at a time. E.g. walkie talkies • Full-Duplex-allows communication in both directions and allows this to happen simultaneously e.g. telephones BIS1202 8 Communication Direction (Cont.) 5/8/2017 BIS1100 9 Factors affecting Telecommunications • Communications medium – Physical medium through which data can be communicated – Telephone lines, television cables • Capacity – Speed at which data are communicated – Also called the transmission rate – It is often called “bandwidth”(the rate at which electronic signals can travel through a medium) • Bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps) – The greater the capacity, the faster the transmission BIS1202 10 Bandwidth and Media (Cont.) • Bandwidth – Narrowband is low speed – Broadband has greater capacity • Media – A medium is any means by which data can be transmitted BIS1202 11 Telecommunications Media Twisted Pair – Telephone line made of a pair of copper wires twisted to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) Coaxial Cable Commonly used for cable television transmission – More expensive than twisted pair – Greater transmission rate than twisted pair – Much less susceptible to EMI BIS1202 12 Telecommunications Media conts.. Microwaves : High-frequency, short radiofrequency (RF) waves – Terrestrial microwave – Satellite microwave Optical Fiber: – Fiber-optic technology uses light instead of electricity to transmit data BIS1202 13 Digital and Analog Data • Analog data is represented as continuous waveforms – Example: audio tape • Digital data is computer data – sequence of binary 0s and 1s: – Example: data stored on the hard drive BIS1202 14 Modulation (Cont.) BIS1202 15 Computer networks A computer network can be defined as: a communications system that links two or more computers and peripheral devices and enables transfer of data between the components’. Telecommunications: the communication of information by electronic means, usually over some distance. BIS1202 16 What is a Computer Network? Two or more computers or communications devices connected by transmission media and channels and guided by a set of rules for communication purposes that allow users to communicate with each other and share applications and data. Hardware: Computer Network card Routers Modem … Software: Network OS Utilities … 5/8/2017 Media: Cable Wire Microwave … Network Design: Logical layout Physical layout … Components of aBIS1100 Computer Network 17 Categorization of Networks.. A number of different ways exist to organize telecommunications components to form a network and hence provide multiple ways of classifying/categorizing a network By size: • Local Area Networks (LANs) • Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) By capability: • Client/Server Networks (Server-Based Networks)-Resources are shared with the help of a centralized computer • Peer-to-Peer Networks –computers share equally with out having to rely on a server BIS1202 18 Client/Server Pros: Very secure Centralized servers easy to manage Physically centralized Secure OS Better performance Centralized backups Reliability Cons: Require professional administration More hardware intensive BIS1202 19 19 Peer-to-Peer (p2p) Computers on the network communicate with each others as equals and each computer is responsible for making its own resources available to other computers on the network. Pros: Uses less expensive computer networks Easy to administer No NOS (network operating system) required Shared resources – some machine will have what you need BIS1202 20 20 Peer-to-Peer (p2p)Conts.. Cons: Not very secure Individual user performance easily affected Tragedy of the commons – no guarantee others will administer their resources properly. Hard to back up. BIS1202 21 Categories of Networks LANs (Local Area Networks) Networks within a building, or within a group of adjacent buildings(the interconnection of different network devices with in a small geographical area) WANs (Wide Area Networks) Networks that cross organizational boundaries or reach outside the company (The interconnection of different network devices with in a wide geographical area) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Covers a geographic area the size of a city or suburb. The purpose of a MAN is often to bypass local telephone companies when accessing long-distance service. BIS1202 22 Network Topologies • One way of describing networks is by the way their components are connected, or topology. Physical layout of the nodes in a network – Star-consists of a central host computer connected to a number of smaller computers or terminals – Ring-each computer on a network can communicate directly with another computer-does not rely on a central host computer. – Bus-links a number of computers by a single circuit made of twisted wire, coaxial cable, or fiber optic cable – Tree-very many star networks interconnected together. BIS1202 23 Network Topology BIS1202 24 Network Selection Criteria Size of the organization Level of required security Level of available administrative support Amount of network traffic Needs of the network users Budget for building the network BIS1202 25 Networking Hardware Hub. device for connecting multiple twisted pair or fiber optic Ethernet devices together and making them act as a single network segment Switch. Interconnects different network devices together. Router .Interconnects networks based on different rules or protocols Network Interface Card (NIC). computer hardware component designed to allow computers to communicate over a computer network Bridge. A device that interconnects different network segments. BIS1202 26 Networks: Pros and Cons Pros • Resource sharing – Printers, CD-ROMs, computers .Software. • Data and information sharing • Communications- email. -voice and video. -E-learning. –VOIP. • Reduced Cost • On-line services • Groupware Cons • Security risks increase with networks • Complexity is associated with networks • Investment is high and return on it may not happen – Software that supports group efforts over a network • Electronic data interchange BIS1202 27 The Internet 5/8/2017 BIS1100 28 The Internet • A network of networks (interconnection of different networks for the purpose of sharing information and data) • Popular uses –E-mail –Instant messaging –Browsing the World Wide Web –Newsgroups and chat rooms BIS1202 29 Internet Service Providers • Any company that provides individuals or organizations with access to the Internet • Most charge a monthly fee • Many ISPs and online services – Offer broadband Internet access through digital subscriber lines (DSLs), cable, or satellite transmission BIS1202 30 Network Protocols • Communication protocols – Rules governing the communication between computers or between computers and other computer-related devices • Network protocols-Rules governing a network of devices BIS1202 31 Protocols (Cont.) LAN Protocols Ethernet Token passing WAN Protocols OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Standard protocol model Seven layers BIS1202 32 Summary • Telecommunications concepts and terminology • Communication within a computer system and among computers • Telecommunications media and devices • Network layouts and protocols • Telecommunications impact on operations • Telecommunications developments and speed BIS1202 33 Review questions List major components of a computer and explain their functions Explain how computers communicate Classify computers into major categories, and identify their strengths and weaknesses With examples, Define the most commonly used hardware terminology. Input devices Output devices Memory Cache memory EPROM BIS1202 34 questions (Cont.) Identify and evaluate key criteria when deciding what computers or related devices to purchase Explain the controversy regarding the health hazards of computers Evaluate hardware so that you can harness it to improve managerial processes Explain why successful managers must be familiar with telecommunications concepts and terminology Describe the principles of communication within a computer system and among computers Identify the major media and devices used in telecommunications differentiate between logical control unit and Arithmetic Logic Units BIS1202 35 questions (Cont.) How are networks used to solve business problems? List the main components of a network? Explain three main Network Topologies? Why do businesses use networks to share hardware? List and explain the functions of different network layouts and the concept of protocols Explain how telecommunications can improve operations in organizations List the types of transmission media that are available? 36