* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stats and Probability Journal
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
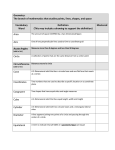
Statistics and Probability Math Journal Curricular Outcomes: SP 7.1 SP 7.2 SP 7.3 I can find and give an example of a central tendency including mean, median and mode. I can give an example and state the range of a set of values. I can create, compare and label circle graphs to show 360° and sum of % to 100. I can use 2 independent events, such as tossing 2 dice to compare theoretical and experimental probabilities. I can interchange a probability expressed as a fraction, a decimal and a percent. Unit Assignment Outline Section Outcome Covered Page # Assignment 7.1 7.1 258-261 1 (a and c – don`t use linking cubes), 2 (a), 3 (only for a), 4, 5, 6, 7 7.2 7.1 262-266 1, 2, 3, 4 7.3 7.1 267-270 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 7.4 7.1 271-275 1, 3, 5, 6 Check In 7.5 7.3 279-283 1, 3, 5, 6, 7 7.6 7.3 284-288 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 Probability Assessment 4.6 7.2 156-160 1, 3, 4, 5 4.7 7.2 161-164 1, 2, 3 Check In Unit Assessment PVSD Post Assessment Your Mark Assessment 7.1 Rubric: Measures of Central Tendency Demonstrate an understanding of the measures of central tendency Fully meeting expectations, with enriched understanding (EU) Confidently selects the appropriate measure of central tendency based on a data set and explains the strategy chosen based on the information required. Is also able to explain how other measures could be used based on other information required. Fully meeting grade level expectations (FM) Mostly meeting grade level expectations (MM) Not yet meeting grade level expectations (NY) Independently and accurately selects an appropriate measure of central tendency (mean, median and mode) for a data set and explains the strategies used to do so. Still working on consistently determining the values for measures of central tendency, or chooses one method of measurement. What other strategies could you use to measure central tendency? What is central tendency? (mean, median, mode) How does our choice of central tendency determine the information we receive and how we deal with it? 7.2 Rubric: Circle Graphs Demonstrate an understanding of circle graphs Fully meeting expectations, with enriched understanding (EU) Fully meeting grade level expectations (FM) Mostly meeting grade level expectations (MM) Not yet meeting grade level expectations (NY) Able to confidently create problems where circle graphs are an appropriate method to represent data and be able to explain why circle graphs are best suited for this situation. Able to independently and accurately identify the characteristics of a circle graph, explain why a circle graph will or will not work in different contexts and read and apply the information given on a circle graph to solve problems and is able to explain the reasoning and strategies used. With assistance is able to identify some characteristics of a circle graph, and able to apply some information from a graph. Why can’t we use circle graphs to represent any context and any data? What do circle graphs tell us? Why are circle graphs not always effective in representing data pictorially? 7.3 Rubric: Theoretical and Experimental Probabilities SP7.3 Demonstrate an understanding of theoretical and experimental probabilities for two independent events where the combined sample space has 36 or fewer elements Fully meeting expectations, with enriched understanding (EU) You show a deep understanding of probability by designing and carrying out a detailed experiment containing two or more independent events to determine sample space, theoretical and experimental probability. You express probability in a variety of formats and you are able to explain, with insight, why your results may or may not be similar. Fully meeting grade level expectations (FM) Mostly meeting grade level expectations (MM) Not yet meeting grade level expectations (NY) You show your understanding of probability by designing and carrying out an experiment containing two independent events to determine sample space, theoretical and experimental probability. You express probability in a variety of formats and can explain your reasoning. With help, you show a basic understanding of probability by designing and carrying out an experiment containing two independent events. You are having some difficulty determining sample space, theoretical and experimental probability, or expressing probability in a variety of formats. Explore and practice each requirement enough that you can do it well on your own. You are having difficulty creating an experiment to determine probability. What are independent events? How can a tree diagram show sample space? What is the difference between experimental and theoretical probability? How can we change fractions to percents and ratios? 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 4.6 4.7 Inside this booklet you will staple all of your marked assignments. To ensure this I would like to hear from your parents as well. I will accept this booklet once your parents, and you, have signed it and, if they wish, have commented below. This booklet will be valuable when it comes time to study for cumulative assessments. Student signature ________________________________________________________ Parent Signature _________________________________________________________