* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
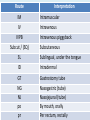
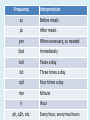
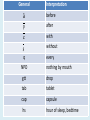
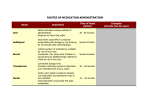
Interpreting Drug Orders Chapter 7 MAT 119 Objectives • Read and write correct medical notation. • Write the standard medical abbreviation from a list of common terminology. • Classify the notation that specifies the dosage, route, and frequency of the medication to be administered. • Interpret physician and other prescribing practitioner orders. Nursing Responsibilities • • • • Interpret order Prepare exact dosage of prescribed drug Identify the patient Administer dosage by prescribed route at prescribed time intervals • Record the administration of the prescribed drug • Monitor the patient’s response for desired and possible adverse effects Route Interpretation IM Intramuscular IV Intravenous IVPB Subcut / (SQ) Intravenous piggyback Subcutaneous SL Sublingual, under the tongue ID Intradermal GT Gastrostomy tube NG NJ po pr Nasogastric (tube) Nasojejunal (tube) By mouth, orally Per rectum, rectally Frequency Interpretation ac Before meals pc After meals prn When necessary, as needed Stat Immediately bid Twice a day tid Three times a day qid Four times a day min Minute h qh, q2h, etc. Hour Every hour, every two hours General Interpretation ā before p after c with s without q every NPO nothing by mouth gtt drop tab tablet cap capsule hs hour of sleep, bedtime Seven Parts of a Drug Order 1. Date and time of order 2. Patient name 3. Drug name 4. Dosage 5. Route of administration 6. Frequency / time and any special instructions 7. Signature and licensure of person writing the order Examining Drug Orders • Drug order must be written clearly – If any part(s) is missing, it is incomplete – If ever in doubt, you MUST ask the prescribing practitioner to clarify Six Rights of Medication Administration 1. Right patient 2. Right drug 3. Right dosage/amount 4. Right route 5. Right time/frequency 6. Right documentation What’s Missing?? • Heparin 5,000 units IV – frequency • Lasix bid – Dosage and route • Depakene 250 mg po – frequency • Demerol 50 mg IV, prn for pain - frequency What’s Missing?? • Amoxocillin 250 mg po – frequency • Xanax 0.1 mg bid – route • Gentamicin sulfate po q 12 h – dosage Preventing Medication Errors • Clarify incomplete orders • Identify scheduling of doses • Read entire medication administration record (MAR) at beginning of each shift – Verify times scheduled with ordered frequency – Review all medications to identify any potential drug interactions or inconsistencies Critical Thinking • What are the legal implications related to medication administration? • What are some potential outcomes of unsafe medication administration? Example of a Written Drug Order • Patient: Ben Jackson MRN 0651325 • 01/23/12 0730 - Amoxil 500 mg po qid pc & hs J. Physician, M.D. • Interpretation: • Give Amoxil 500 milligrams by mouth four times a day after meals and at bedtime. How to interpret… • Ancef 1 g IVPB q 6 h – Give Ancef 1 gram by intravenous piggyback every 6 hours • Humulin R Regular U-100 insulin 5 units subcut stat – Give Humulin R Regular U-100 insulin 5 units subcutaneous immediately How to interpret… • Potassium chloride 10 mEq po bid pc – Give Potassium chloride 10 milliequivalents orally two times a day after meals • Keflex 500 mg po qid – Give Keflex 500 milligrams by mouth four times a day • Atarax 100 mg po hs prn – Give Atarax 100 milligrams orally at bedtime, as necessary How to interpret… • Decadron 0.5 mg po q 12 h – Give Decadron 0.5 milligrams orally every 12 hours • Tegretol 0.2 g po tid – Give Tegretol 0.2 grams orally three times a day Drug Orders To convert to abbreviations: • Give Cortisporin otic suspension two drops each ear three times a day and bedtime: – Cortisporin otic suspension 2 gtt each ear tid & hs • Give Digoxin 0.25 milligrams by mouth daily – Digoxin 0.25 mg po daily • Give Humulin R Regular U-100 insulin 10 units subcutaneously 30 minutes before meals – Humulin R Regular U-100 insulin 10 units subcut 30 min ac Practice • Prescriber’s order: Digoxin 0.25 mg po daily • The frequency of administration in this order is: ____________________ daily • What is the route? _______________ orally Practice • Prescriber’s order: Heparin 8000 units subcut bid • The route of administration in this order is: _________________ subcutaneous • What is the frequency of administration? _______________ Two times a day