* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploration and Exploitation in the Americas
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
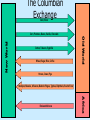
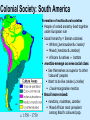
Exploration & Conquest in the “New World” Or Voyage Across, Young Man Outline • Periods of Exploration • Reasons for Exploration • The Columbian – Commerce Exchange – – – – Mercantilism Imperial Expansion Religion Adventure European Global Exploration Periods of European Expansion Portuguese port city of Calicut, India • 15th-17th centuries • 18th –early 19th centuries • 19th –early 20th centuries – Spain & Portugal Asia, S. America & Caribbean – Britain, France & Netherlands North America & Asia – Spain vs. France vs. Britain, esp. W. Hemisphere & Asia – Race for colonies in Africa, Middle East & Oceania Why Expansion? • Commercial Wealth – Trade w/o Muslim middle man • Asia & Africa • Imperial Expansion – Portugal - need for resources – Spain – control spice routes • Religion – 'infidel' muslims – ‘save souls’ • Adventure – Esp. sons of younger nobles • Opportunity for fame & riches Commerce • Exploration – new markets – resources – faster access markets in the Orient • Trade rivalries between European powers need for naval power – protect trade routes – Coastal waters • Mercantilism – – Gov’t encouraged expansion trade • gov’t treasuries • merchant class political influence Mercantilism • Govt supplied resources and protection to aid trade – Supported piracy agst other nations ex. Drake – Disrupt competition & avoid war • Royal charters to individuals for regions, goods, etc. – – – – Dutch East India Co. (VOC) Hudson Bay Company British East India Co. Cadbury, Lipton • Govt rec'd royalties (ie. Tax) on goods produced and traded. Map – The Columbian Exchange The Columbian Exchange Gold, Silver Cotton, Tobacco, Syphillis Wheat, Sugar, Rice, Coffee Old World New World Corn, Potatoes, Beans, Vanilla, Chocolate Horses, Cows, Pigs Smallpox, Measles, Influenza, Bubonic Plague, Typhus, Diphtheria, Scarlet Fever Africa Enslaved Africans Imperial expansion Euro. claims in W. Hemi - 1750 • Europe worn down by war – Religious wars – Regional wars • Discovery of W. Hemisphere vast land, few people, lots of resources • Discovery of gold, silver, etc. frenzy for control of entire region war – Spain vs. Portugal – Britain vs. France • Seven Years War (1756-63) Religion • Reformation Catholic Church in search for new souls to save. • Missionaries accompany all explorations • Immediately begin to seek converts among the native people – Often force conversion at sword or gunpoint • Establish missions in military bases Adventure • Some motivated by adventure, greed & search for fame • Often younger sons of nobles – Little/no inheritance – Military, clergy, exploration • Exploration opportunity for wealth, fame, honour Fransisco Pisarro Exploration & Colonization of The Americas Or I found you, now you’re mine The Spanish Caribbean Indigenous = Taino Columbus builds fort @ Santo Domingo Taino conscripted to mine gold No gold Encomiendas: land grants to Spanish settlers Crown needs to make $$$ on exploration Brutality & smallpox population Taino Indians, Dominican Rep., 1500 CE Conquest of Mexico & Peru Hernan Cortés Aztec & Incawealthier, more complex than Caribbean societies Conquers Aztecs 1519-1521 Francisco Pizarro Conquers the Inca, 1532-1533 1540 Spanish control Inca empire Both aided by internal strife & epidemic disease amongst native pop. Politics W/in the Iberian Empires 1570 - Spanish colonial govt. formalized Governed by viceroys reviewed by audiencias Similar to missi dominici Held vast power w/in jurisdictions Treaty of Tordesillas grants Brazil to Portugal Mediated by Pope to prevent war East of Line – Portuguese exploit West of Line – Spanish Brazil ÷ nobles, w/ governor to oversee Politics W/in the Iberian Empires Colonial American society European-style society in cities indigenous culture persisted in rural areas More exploitation than settlement Still, many Iberians settled btw. 1500-1800 Opportunities in new land Free of social constraints Colonization—Spanish Style Colonization of North America France & England Colonization on east coast, exploration of west coast Sought fur, fish, trade routes early 17th century Suffered from isolation & food shortages Jamestown & Roanoke colonies fail Colonial govt. Private investors, royal governors, & institutions of self-government Jamestown Colony 1607 Colonization of North America Relations w/ indigenous people Settlers interrupt migrations of indigenous peoples Seized lands justified w/ treaties Natives raided farms & villages Attacks reprisals by settlers 1500 - 1800, native pop. 90% Colonial Justice Colonial Society: South America Formation of multicultural societies c. 1550 - 1750 People of varied ancestry lived together under European rule Social hierarchy Iberian colonies: Whites (peninsulares & creoles) Mixed (mestizos & zambos) Africans & natives = bottom mestizo emerge as new social class See themselves as superior to other ‘coloured’ peoples Want to be like creoles (criolles) Creole marginalise mestizo Brazil more mixed: mestizos, mulattoes, zambos Mixed African most prevalent among Brazil’s coloured pop. Colonial Society: North America French & English more focused on settlement than Spanish Greater gender balance among settlers More families & couples Allowed marriage w/in own groups English frowned on interracial marriages Relations w/ French traders & native women métis (Euro + native) Cultural borrowing: plants, crops, deerskin clothes Spanish Colonial Economy: Mining Silver & gold basis of Spanish wealth Two major sites of silver mining: Zacatecas (Mexico) & Potosi (Peru) Global significance of silver 20% of silver went to royal treasury (the quinto) Funded military & bureaucracy Went to European, then to Asian markets for luxury goods Potosi Silver Mine Manila Galleons Spanish Colonial Economy: Agriculture Haciendas basis of Spanish Am. production Produced foodstuffs for local use Encomiendarepartimiento Encomienda system seen as abusive Repartimiento replaces conscript & slave w/contract labour free laborers by mid-17th century Native Resistance Rebellion, indolence, retreat Difficult to register complaints Portuguese Colonial Economy Originally harvested Brazilwood Hard, rot resistant, ideal for ship-building Over-harvesting need for new crop Sugar and slavery in Brazil Economy relies on sugar production Brazilian life revolved around the sugar mill, or engenho Combined agricultural & industrial enterprises sugar processing on site Sugar planters landed nobility Brazilian Sugar Plantation Portuguese Colonial Economy Growth of slavery in Brazil Natives were not cultivators resisted farm labor Disease indigenous pop. Imported African slaves for cane & sugar production after 1530 deaths births demand for slaves 1 ton of sugar = 1 human life Slaves Harvesting Sugarcane North Am. Colonial Economy Fur traders Fur trade extremely profitable Natives trapped for & traded w/ Europeans Blankets, iron tools (knives, axes, pots), cloth Fur Traders Impact of fur trade Environmental conflicts among native tribes competing for resources Rapid decline of fur animals North Am. Colonial Economy European settlement encroaches on natives Threatens hunting, fishing & tribal lands Develpment of Plantation Cash crops tobacco, rice, indigo, & cotton Indentured labor in 17th & 18th centuries Replaced by Slaves in late 17th century New England merchants participate in slave trade, distillation of rum from Caribbean sugar Triangular or Atlantic Trade network Tobacco Plantation British Mfr goods – African slaves – American Cotton & Rum Colonial Religion: Christianity Spanish missionaries Est. mission schools & churches Some record native languages & traditions Attracted many proselytes French & English missionaries English not interested in native conversion French moderate success Indians @ Mission Ventura Labour systems Spanish America Brazil mita & encomienda systems dominate mine & agricultural economies. in native populations shift to the repartimiento system. immigration from Europe plantation society based on sugar mills (engenhos). Little reliance on slavery, except in Caribbean mortality rate among native 1st to import African slaves 1888 - last to abolish slavery Caribbean North America sugar plantation economy Fur trade & subsistence farming. Absence of native labour Plantations worked by indentured servants from Europe African slave labour (contrast 17th Late c. African slaves. Tobacco, Rice, Indigo Late 18th c. #slaves cotton gin 19th c. immigration from Europe & indentured labour from Asia (esp. West) Slavery in Canada eliminated @start of 19th c. 1865 -- 13th Amend abolished slavery in U.S.A Hawai’i). Hawai’ian islands sugar plantation economy Native resistance to labour introduction of indentured labour from Asia China, Philippines, Japan The Pacific: Australia 1770 British captain James Cook explored east Australia 1788, England est. 1st settlement in Australia as a penal colony Penal Colony: Australia Replaced Georgia after U.S. independence Free settlers outnumbered convicted criminal migrants after 1830s The Pacific Islands Spanish voyages after Magellan Indigenous Chamorro resisted decimated by smallpox Philippines become major entrepot for silk from China in exchange for silver from New Spain Chamorro Church Village Manila Galleons: Acapulco Manila Impact: Huge transfers of silver to China Occasional skirmishes w/natives Whalers visit after 18th century Missionaries, merchants, planters & disease follow