* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download continuous time
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
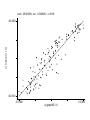
coef = 29.981268, se = 1.0345626, t = 28.98 e( hdiscore | X) 96.4363 -90.3541 -3.01368 3.21655 e( lgnppc95 | X ) Exponential Growth 6 4 5000 2 0 Year 21 00 20 50 0 Ln(GNP) 10 8 10000 20 01 GNP 15000 GNP ln(GNP) On a graph with a log scale, if a country has GDP with a constant growth rate its level of GDP lies on a straight line. Imagine a growth rate for income given by g. This means that if GDP in time 0 is Y0, then income in time 1 is Y1 =Y0(1+g) But then income in time 2 is Y2 =(Y0(1+g))(1+g) =Y0(1+g)2 More generally, income in time t is written: Yt = Y0 (1 + g ) t This type of growth is called “Geometric Growth.” If we take logs of both sides we find the following linear function: lnYt = lnY0 + tln(1 + g ) The slope of the function, ln(1 + g ), is approximately equal to g. A Note on Growth in Continuous Time In the last slide we treated time as if it was divided into chunks and we considered growth from year to year. Time, however is continuous and we may wish to take account of that fact. In the last slide we said that we could write Yt as: Yt = Y0 (1 + g ) t The continuous time version of this equation is: Yt = Y0 eg t If we take logs of this equation we find: Yt = lnY0 + g t Which is again a linear equation with slope of t (no approximation!) Also, have a look here: http://www.ugrad.math.ubc.ca/coursedoc/math100/notes/zoo/andromed.html Doubling Time: 70 is the magic number! Say we want to know how long it will take for something to double when it is growing at growth rate g. How do we work it out? This is the same as asking for what t does Yt = 2 Y0? Using the equation Yt = Y0 eg t we can answer the question by solving the following equation for t: 2 Y0 = Y0 eg t The answer is t=ln(2)/g = .693/g Hence we can find the answer by dividing .693 by the growth rate (or approximately by dividing 70 by the percentage growth rate) MAIN QUESTIONS: 1. 2. 3. Why did modern economic growth emerge only in the 19th Century? What is the relationship between population growth and economic growth? Why is economic growth so concentrated in Europe and European offshoots? Is this the result of historical accident, first-mover advantage, geography, culture, social institutions, other factors? 4. Is economic growth now spreading to all regions of the world? 5. What are the engines of economic growth? Accumulation, division of labor, scale, innovation and diffusion. 6. What are the roles of culture and social stratification in economic development? Religion and economic organization; Gender roles and inequalities; Ethnicity and social divisions. 7. What is the role of politics and political institutions in Economic Development? 8. What is the role of economic institutions in economic development? Is modern economic growth a phenomenon of modern capitalism? 9. Do the rich countries exploit the poor, or do the poor benefit from the rich through diffusion of technology and inflows of capital? 10. Are there special policies for "catching up growth" for laggard economies? (e.g. infant-industry protection, or special policies for technological diffusion, etc.). Alternative Viewpoints: Importance of economic institutions, political institutions, and incentives: Mancur Olson Yours truly Importance of “culture” of modernization Max Weber David Landes Importance of international environment (geopolitical and economic) Karl Marx and followers (exploitation, colonialism, dependency) Moses Abramovitz Importance of geography (ecology, connectivity) Jared Diamond Yours Truly Need for a Comprehensive Social Theory Our Approach Mechanisms of Economic Growth resource exploitation and depletion accumulation of capital division of labor innovation Social, Physical, and Geopolitical Context and the effects on mechanisms of growth Kinds of Social Institutions Economic Political Cultural (norms, religious beliefs, governed by sanction) Scientific Physical Geography: Proximity Ecology Mineral and energy resource Geopolitical Relations: Conquest Imitation Threat Social institutions: Economic Political Cultural Technology: Science Belief systems Innovation and diffusion Demography: Age structure Mortality Morbidity Fertility Economic and Social outcomes: Economic growth Distribution of income