* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solving Equations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
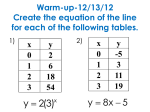
Solving Equations By: Marinda, Ashley, Trevor, and Ti’Shawn Mrs. Sawyer 1st block Essential Question Why is it important to be fair? Unit Questions How do you justify the steps necessary to solve equations? How does the understanding of balances and equality relate to solving equations? Content Questions How do you define a variable? What are the steps for solving equations? 1.02 Use formulas and algebraic expressions, including iterative and recursive forms, to model and solve problems. Student Objectives/Learning Outcomes The learner will: properly use equality formulas to evaluate for the given variable solve equations using addition, subtraction, multiplication and division solve two-step equations using addition, subtraction, multiplication and division use the distributive property to combine like terms and solve problems solve equations with variables on both sides identify equations as identity or no solution model distance-rate-time problems use a graphing calculator to check solutions of equations by graphing a=b Addition Property of Equality a+c=b+c Substitution Property of Equality a–c=b–c Multiplication Property of Equality a∙c=b∙c Division Property of Equality a = b c c Distributive Property a(b + c) = ab + ac a(b – c) = ab – ac Addition Property of Equality a+c=b+c If 10 = 6 + 4, then 10 + 2 = 6 + 4 + 2 Substitution Property of Equality a–c=b–c If 10 = 6 + 4, then 10 – 2 = 6 + 4 – 2 Multiplication Property of Equality a∙c=b∙c If 2 ∙ 6 = 12, then 2 ∙ 6 ∙ 5 = 12 ∙ 5 Division Property of Equality a = b c c If 5 + 1 = 6, then 5 + 1 = 6 2 2 Distributive Property a(b + c) = ab + ac a(b – c) = ab – ac If 3(4 + 1), then 3(4) + 3(1) Example: Solve each equation. Check your answer. ONE STEP a. x – 8 = 0 x–8+8=0+8 x=8 b. 4c = -96 4c = -96 4 4 c = -24 n/ =5 n/ (6) = 5(6) 6 n = 30 3/ 6 4x =9 (4/3)3/4x = 9(4/3) x = 12