* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Organismal Ecology Ways the individual meets
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
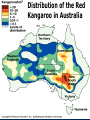
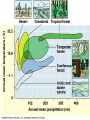
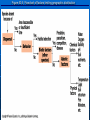
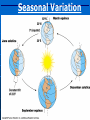
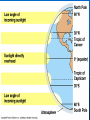
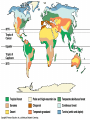
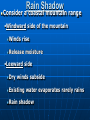
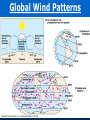
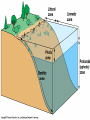
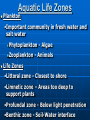
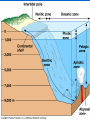
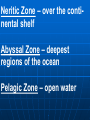
AN INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGY AND THE BIOSPHERE •Ecology is the Study of Interactions Between Organisms and the Environment Distribution of the Red Kangaroo in Australia What are the different subfields of ecology or levels of organization? Biosphere Biome Ecosystem Community Population Species A View of the Biosphere From Space Subfields of Ecology: 1. Organismal Ecology Ways the individual meets challenges posed by the environment 2. Population Ecology Factors that affect population size and composition. 3. Community Ecology Involves predator/prey relationships, competition and disease. 4. Ecosystem Ecology Energy flow, chemical cycling, primary productivity. Rachel Carson Most Famous Book: Silent Spring •Interactions Between Organisms Limit the Distribution of Species •Abiotic and Biotic Factors Influence the Structure And Dynamics of Aquatic Biomes What types of abiotic factors affect the biosphere? Abiotic Factors of the Biosphere: temperature water sunlight wind rocks and soil periodic disturbances (e.g. tornadoes, hurricanes…) Figure 50.5 Flowchart of factors limiting geographic distribution Seasonal Variation •Climate Largely Determines the Distribution and Structure of Terrestrial Biomes Deciduous Forest Grassland Savanna Chaparral/Temperate Woodland and Shrubland Tundra Tropical Rain Forest Coniferous Forest/Taiga Desert What mountain ranges would be in the same locations in S. California? Rain Shadow Consider a coastal mountain range •Windward side of the mountain Winds rise Release moisture •Leeward side Dry winds subside Existing water evaporates rarely rains Rain shadow Global Wind Patterns Aquatic Biomes Aquatic Life Zones Plankton •Important community in fresh water and salt water Phytoplankton - Algae Zooplankton - Animals Life Zones •Littoral zone - Closest to shore •Limnetic zone – Areas too deep to support plants •Profundal zone - Below light penetration •Benthic zone - Soil-Water interface Oligotrophic Eutrophic Lake Lake Neritic Zone – over the continental shelf Abyssal Zone – deepest regions of the ocean Pelagic Zone – open water