* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry - Asbury Park School District
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Asbury Park
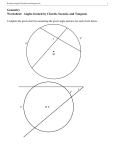
Name of Unit: Circles With and Without Coordinates
Content Area: HS Math - Geometry
Big Idea:
All circles are similar
School District
Unit #/Duration: Unit 5 / 25 days
Grade Level: 10th
An angle drawn from a diameter of a circle to a point on the circle is sure to be a right angle (Thales’
Theorem)
A central angles is equal to its intercepted arc whereas an inscribed angle equals half of its intercepted arc
Pythagorean Theorem can be used to derive the equation of a circle
A tangent to a circle and the radius of the circle are perpendicular at the point of intersection
Essential Questions:
● If 2 chord are equidistant from the center of a circle,
what do we know? Explain why.
● What is Thales’ Theorem? It’s converse?
● How can we construct a rectangle with vertices on a
circle? Is there more than 1 unique way to do this?
● What is an inscribed polygon? Can you sketch a few
examples?
● Is it possible to inscribe a parallelogram that is not a
I Can Statements:
● Apply Thales’ Theorem ( if triangle ABC has vertices on the
circumference of a circle and it is a right triangle, one side
is the diameter of the circle}
● Prove Thales’ Theorem
● identify the relationships between the diameters of a
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
rectangle in a circle? Explain why or why not.
How do minor and major arcs compare?
How are minor and major arcs denoted? Explain
why one of them uses 3 points and the other 2 ?
What is an auxiliary segment and why might you
draw one?
How would you describe the secant angle theorem? Can
you sketch a diagram to show which arcs are needed to
use this theorem?
Why do we use different forms of equations for circles?
Can you support your answer with an example?
How can we convert a general formula circle into a
center-radius form? Why would we do this?
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
circle and other chords of the circle
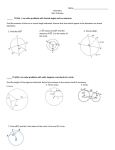
Inscribe a rectangle in a circle
Understand the symmetries of inscribed rectangles
across a diameter
describe relationships between inscribed angles and
central angles and their intercepted arcs
prove the inscribed angle theorem
understand that inscribed angles that intersect the
same arc are equal in measure and use that
relationship to solve problems
compare and contrast central angles and inscribed angles
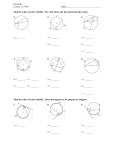
identify minor and major arcs
utilize inscribed angle theorem to find the measures
of unknown angles
prove relationships between inscribed angles and
central angles
Understand and explain why all circles are similar
Utilize the arc angle measurement formula to solve
problems
Demonstrate arcs between parallel chords are
congruent
Show that congruent chords have congruent arcs
construct tangents to a circle through a given point
prove that tangent segments from the same point
are equal in length
use the fact if a circle is tangent to both rays of an
angle, then its center lies on the angle bisector
utilize tangent segments and radii of circles to
conjecture and prove geometric statements
use the inscribed angle theorem to prove other
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
geometric theorems
utilize the inscribed angle theorem to solve for
missing “unknown” angles
understand that the measure of an angle whose
vertex lies in the interior of a circle is equal to half
the sum of the angle measures of the arcs
intercepted by it and its vertical angle
find the measures of angles, arcs, and chords in
figures that include two secant lines meeting outside
a circle ( inference is required )
find missing lengths in circle-secant or circle-secanttangent diagrams
write the equation for a circle in center-radius form,
( − h)2 + ( – k)2 = r2 and use it to solve problems
identify the center and radius of a circle given the
equation
determine the distance between the centers of 2
tangent circles
complete the square in order to write the equation
of a circle in center-radius form
factor perfect square trinomials
use standard form of a circle x2 + y2 + Cx + Dy + E =0
to solve problems
find the equations of two lines tangent to the circle
with specified slopes, given a circle
given a circle and a point outside the circle, students
find the equation of the line tangent to the circle
from that point
●
Common Core State Standards:
● G.C.2 ; G.C.1 ; G.C.3 ; G.C.4 ; G.C.5
● G.GPE.1 ; G.GPE.4
● G.SRT.9
Pre-requisite standards:
G.CO.10 ; G.CO.11 ; G.CO.12 ; G.CO.3 ;G.CO.5 ; G.CO.9
G.SRT.5
8.G.7 ; 8.G.8
Mathematical standards highlighted:
● MP 1; MP 3 ; MP 7
Interdisciplinary Connections:
Symbol: **IC
Technology Integration: (Standards included only if students will be demonstrating knowledge/understanding/skill.)
Symbol: ***TI
Texts
●
Primary Text:
Eureka Math – 10 [ Engage NY – Geometry mod 5]
●
●
Secondary/Supplemental Texts:
Pearson Geometry
HMH Geometry
Suggested Instructional Activities/Strategies
Topic A – Central and inscribed angles:
Lesson 1: Thales’ Theorem
Lesson 2: Circles, Chords, Diameters, and Their Relationships
Lesson 3: Rectangles Inscribed in Circles
Lesson 4: Experiments with Inscribed Angles
Lesson 5: Inscribed Angle Theorem and Its Applications
Lesson 6: Unknown Angle Problems with Inscribed Angles in Circles
Topic B – Arcs and sectors :
Lesson 7: The Angle Measure of an Arc
Lesson 8: Arcs and Chords
Lesson 9: Arc Length and Areas of Sectors
Lesson 10: Unknown Length and Area Problems
Mid-module assessment
Topic C – Secants and tangents:
Lesson 11: Properties of Tangents
Lesson 12: Tangent Segments
Lesson 13: The Inscribed Angle Alternate—A Tangent Angle
Lesson 14: Secant Lines; Secant Lines That Meet Inside a Circle
Lesson 15: Secant Angle Theorem, Exterior Case
Lesson 16: Similar Triangles in Circle-Secant (or Circle-Secant-Tangent) Diagrams
Topic D – Equations for circles and their tangents:
Lesson 17: Writing the Equation for a Circle
Lesson 18: Recognizing Equations of Circles
Lesson 19: Equations for Tangent Lines to Circles
Topic E – Cyclic quadrilaterals:
Lesson 20: Cyclic Quadrilaterals
Lesson 21: Ptolemy’s Theorem
End – of-module assessment
Teacher Resources
●
●
●
●
●
●
Document Camera
Epson Brite-board ( interactive)
Ti-84’s
Communicators
Geometer’s Sketchpad
Geogebra
Vocabulary
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Domain Specific Academic Vocabulary (Tier 3)
Arc length
Central angle
Chord
Inscribed angle
Sector secant
Tangent line
Inscribed polygon
Cyclic Quadrilateral
Diameter
Minor arc
Major Arc
Radius
Thales Theorem
●
●
●
●
General Academic Vocabulary (Tier 2)
circle
line
adjacent
center
Assessments
Summative Assessment:
● Mid-module assessment
● End-of-module assessment
● Teacher-prepared quizzes
Formative Assessments:
● Do now’s
● Class work
● Homework
● Exit Tickets
● Reflections
Type
Differentiation/Scaffolding
(for example ELL, students who are classified, struggling learners, etc.)
Visual
Auditory
Kinesthetic
●
●
●
Language Development
●
Poster of perpendicular bisector construction;
Reread all instructions aloud; listen to video clips
Hands-on , cut out activity for Thales’ Theorem ; cut out trapezoids (then cut 2 consecutive
angles and place in a line to show they will always be supplementary)
Vocabulary development with pictures and graphs to assist ELL students
Appendix 1
(graphic organizers, rubrics, websites, activities, manipulatives, sample assessments, etc.)
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Kutasoftware.com
Purplemath.com
Mathisfun.com
Coolmath.com
Mathworksheets4kids
Khanacademy.com
him: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thales%27 Theorem
Graphic organizer { chords of a circle ) p. 27, 33 Eureka Math
Mid-module rubric & assessment p. 128-144 Eureka Math
Appendix 2
(Quad D Exemplar Lesson Plan)
http://map.mathshell.org/lessons.php?unit=9335&collection=8 [ Solving problems with circles and triangles]
http://map.mathshell.org/lessons.php?unit=9350&collection=8
[ sorting equations of circles 1]
map.mathshell.org/lessons.php?unit=9355&collection=8 [ sorting equations of circles 2 ]