* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hearing loss
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Hearing aid wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
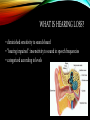
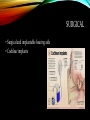
HEARING LOSS By: Hunter Weatherbee WHAT IS HEARING LOSS? • diminished sensitivity to sounds heard • "hearing impaired": insensitivity to sound in speech frequencies • categorized according to levels WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF HEARING LOSS? • • • • • • • • • Age Noise Perinatal problems Congenital problems Medications Chemicals Physical Trauma Genetics Disorders AGE • Progressive loss of ability to hear high frequencies • Men: as early as 25 • Women: as early as 30 • Common conditions: high blood pressure, diabetes or medications NOISE • 50% of all cases • causes some degree of problems in 5% of the population globally • may be temporary or permanent PERINATAL PROBLEMS • Fetal alcohol disorders • Premature Birth CONGENITAL PROBLEMS • Superior semicircular canal dehiscence • Recurring ear infections MEDICATIONS • Ototoxic medications may reversibly affect hearing, including: • Loop diuretics • Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) CHEMICALS • Metals, such as lead • Solvents, such as toluene • Asphyxiants • Starts in the high frequency range and is irreversible PHYSICAL TRAUMA • To the ear itself • To the brain centers • Either temporary or permanent GENETICS • 75–80% of cases are inherited by recessive genes • 20–25% are inherited by dominant genes • 1–2% are inherited by X-linked patterns • Less than 1% are inherited by mitochondrial inheritance • Syndromic = 30% • Nonsyndromic = 70% DISORDERS • • • • • • • • • • • Strokes Multiple sclerosis Viral infections Measles Mumps Congenital rubella (also called German measles) Several varieties of herpes viruses People with HIV/AIDS West Nile virus Meningitis Syphilis WHAT TREATMENT IS THERE? • Hearing Aids • Assistive Devices • Surgical HEARING AIDS • Devices that work to improve the hearing and speech • Works by magnifying the sound vibrations in the ear ASSISTIVE DEVICES • Telephone typewriters (TTY) or telecommunications for the deaf (TDD) • Instant messaging software (IM) • Videophones and similar video technologies • Hearing dogs • Internet and closed captioning • Signaling transmitters SURGICAL • Surgical and implantable hearing aids • Cochlear implants END By: Hunter Weatherbee