* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download myogenesis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
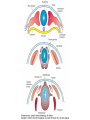
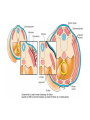
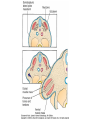
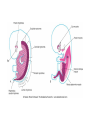
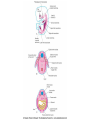
• Somites are transient segmented structures derived from paraxial mesoderm. • contain the progenitors of the axial skeleton, trunk musculature and associated tendons, trunk dermis, endothelial cells, and meninges of the spinal cord • ventromedial part of the somite forms the sclerotome • the remainder of the somite consists of a dorsal epithelial layer called the dermomyotome • dermomyotome quickly separates into two structures: a dermatome and a myotome The dermatomes contribute to the dermis (including fat and connective tissue) of the neck and the back. • The myotomes differentiate into myogenic (muscle-producing) cells • Each myotome splits into two structures: a dorsal epimere and a ventral hypomere • The epimeres give rise to the deep epaxial muscles of the back, including the erector spinae and transversospinalis groups. • The hypomeres form the hypaxial muscles of the lateral and ventral body wall in the thorax and abdomen [intercostal muscles,external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis, and the rectus abdominis] • Cervical region:hypaxial myoblasts form the strap muscles of the neck, including the scalene and infrahyoid muscles. • Lumbar region, the hypomeres form the quadratus lumborum muscles. • At limb-forming levels, hypaxial myoblasts invade the developing limb buds and give rise to the limb musculature.