* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 2 Unit 2 Notebook Guide
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic reciprocity wikipedia , lookup
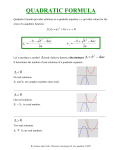
Name:________________________ Algebra 2 Unit 2 Notebook Guide Unit Topic: Quadratic Functions and Factoring—Part 2 (Chapter 4) Date Lesson Textbook Section Homework Assignment / 1. Perform Operations with Complex Numbers 4.6 HW #1 (p. 279) 3, 7, 13, 17, 25, 33, 35, 43, [53, 59] / 2. Complete the Square 4.7 HW #2 (p. 288) 3, 7, 13, 19, 23, 27, 45, 47, [55, 60] / 3. Use the Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant 4.8 HW #3 (p. 296) 3, 5, 7, 19, 23, 27, 31, 39, [45, 63] / 4. Quadratic Problem Solving / 5. Graph and Solve Quadratic Inequalities / 6. Write Quadratic Functions and Models / 7. Unit 2 Review / 8. Problem Solving / 9. Unit 2 Test HW #4 (Handout) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 4.9 HW #5 (p. 304) 7, 9, 11, 17, 21, 25, 47, 49, [69] 4.10 HW #6 (p. 312) 3, 9, 11, 17, 21, 25, 31, 37, [41, 45] Unit 2 Review 4.6-4.10 Problem Solving (p. 316) 1, 2, 3, 8 - Note: Please label your homework assignment as shown above along with your name. Grade Tracking Homework Quiz #1 _____ Homework Quiz #2 _____ Homework Quiz #3 _____ Problem Solving _____ Unit 2 Test _____ Unit 2 Points Earned _____ Unit 2 Possible Points _____ Unit 2 Average _____ Unit 2 Grade _____ Cumulative Average _____ Cumulative Grade _____ Algebra 2 Concepts - Unit 2 (textbook sections 4.6 – 4.10) A complex number is of the form a + bi, in which the a term is a real number and the bi term is an imaginary number. By definition, i equals the square root of negative one, a non-real value. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and the vertical axis to plot the imaginary part. In this way the complex numbers include the ordinary real numbers while extending them in order to solve problems that would be impossible with only real numbers. A perfect square trinomial is what results from squaring a binomial. Start with a binomial, for example x + 5. Square it and you will have a perfect square trinomial, in this case (x + 5)2 or equivalently (x + 5)( x + 5) produces the perfect square trinomial x2 + 10x + 25. Completing the square is a process in which a perfect square trinomial is created and then factored in order to rewrite or solve a quadratic equation. In fact, the quadratic formula, the general solution to all quadratic equations, can be derived using this process. The discriminant of a quadratic equation written in the standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0 is the expression b2 − 4ac. You find this expression in the quadratic formula under the square root sign. The discriminant determines the number and type of solutions. A quadratic equation with real coefficients can have either one or two real solutions, or two imaginary solutions. If the discriminant is positive, then there are two distinct real roots. If the discriminant is zero, then there is one distinct real root. If the discriminant is negative, then there are two distinct complex roots. A best-fitting regression model is a mathematical equation used to approximate the relationship between variables observed in the real world. Depending on the data, the model may be a linear function, a quadratic function, or from some other family of functions. How close the equation comes to matching the data is referred to as the “goodness-of-fit”, and the chosen function is typically the one that fits the best, as measured by the correlation coefficient.