* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LIGHT - Coosa High School
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
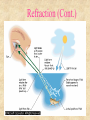
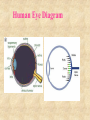
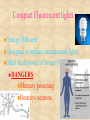
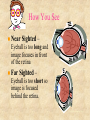
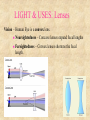
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery WAVES: SOUND & LIGHT Waves carry energy from one place to another NATURE OF WAVES © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Waves (Def.) – A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy. Medium – Substance or region through which a wave is transmitted. Speed of Waves – Depends on the properties of the medium. LIGHT: What Is It? © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Light Energy Atoms As atoms absorb energy, electrons jump out to a higher energy level. Electrons release light when falling down to the lower energy level. Photons - bundles/packets of energy released when the electrons fall. Light: Stream of Photons © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Transverse Waves © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Energy motion is perpendicular to direction of Compression or Longitudinal Waves Electromagnetic Spectrum © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Electromagnetic Spectrum Spectrum – Light we can see Roy G. Biv – Acronym for Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, & Violet. Largest to Smallest Wavelength. Visible Radio Waves Invisible Spectrum Longest wavelength & lowest frequency. Also emitted by Stars and gases Dangers: Radio wave sickness Cancers leukemia © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Modulating Radio Waves © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery AM – Carries audio for T.V. Broadcasts Longer wavelength so can bend around hills FM – Carries video for T.V. Broadcasts Infrared Rays Invisible Spectrum (Cont.) Light rays with longer wavelength than red light. Our skin emits infrared rays Far infrared = hot ; Shorter infrared = cool Uses: Cooking, Medicine, T.V. remote controls, military – thermal imaging, astronomy and weather forecasts, heat lamps for sports medicine Dangers Too much exposure = overheating Infrared: Thermal Imaging Microwave Basically high frequency radio waves Used in satellite communication and transmission, radar systems and microwave cooking/microwave oven travels in straight line without losing much of its energy Dangers: Prolonged exposure causes cataracts Cell phones may cause Brain damage (tumors) satellite station speed-monitoring radar Ultraviolet Rays Invisible spectrum (cont.). Humans can’t see, but some insects can EM waves with frequencies slightly higher than visible light USES: tanning beds, astronomy, food processing & hospitals to kill germs, attracts insects (kills them), detecting counterfeit money, whitening teeth, hardening dental fillings,black light, helps your body produce Vitamin D Ozone layer blocks most UV from getting to earth DANGERS: UV-B CHANGES DNA IN CELLS CANCER SKIN AND EYE DAMAGE, SUNBURN X-RAYS Invisible Spectrum .High frequency waves An X-ray machine works by firing a beam of electrons at a "target". If we fire the electrons with enough energy, X-rays will be produced. Uses: Medicine – Bones absorb x-rays; soft tissue does not., airport security, astronomy Lead absorbs X-rays Dangers: Cancer, Cell damage esp. in first trimester for fetus AIRPORT X-RAY MACHINE GAMMA RAYS Invisible spectrum (cont.) Highest frequency EM waves; Shortest wavelength. They come from outer space. Uses: cancer treatment, radioactive tracers, sterilize foods through irradiation. Dangers: Kills all living cells Causes cancer Only lead or concrete will block Visible light Seen by the human eye Uses: fiber optics, medical procedures, telecommunications, chemical spectral analysis and photosynthesis, endoscopy. Lasers for medical, industrial and surveying use. CD's and DVD's, Laser printers, Dangers: Too much light can damage retina laser surgery Visible Light cont’d LIGHT: Refraction of Light Refraction – Bending of light due to a change in speed. Index of Refraction – Amount by which a material refracts light. Prisms – Glass that bends light. Different frequencies are bent different amounts & light is broken out into different colors. Refraction (Cont.) Color of Light © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Transparent Objects: Light transmitted because of no scattering Color transmitted is color you see. All other colors are absorbed. Translucent: Light is scattered and transmitted some. Opaque: Light is either reflected or absorbed. Color of opaque objects is color it reflects. OPAQUE Color of Light (Cont.) Color of Objects White light is the presence of ALL the colors of the visible spectrum. Black objects absorb ALL the colors and no light is reflected back. © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery How You See © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Retina – Lens refracts light to converge on the retina. Nerves transmit the image Rods – Nerve cells in the retina. Very sensitive to light & dark Cones – Nerve cells help to see color Human Eye Diagram LIGHT & ITS USES © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Sources of Light Incandescent light – light produced by heating an object until it glows. © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery LIGHT & ITS USES © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Fluorescent Light – Light produced by electron bombardment of gas molecules Phosphor coating absorb photons that are created when mercury gas gets zapped with electrons. The phosphors glow & produce light. LIGHT & ITS USES - Neon light – neon inside glass tubes makes red light. Other gases make other colors. Neon © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Compact Fluorescent lights Energy Efficient Designed to replace incandescent lights Must be disposed of properly DANGERS: Mercury poisoning Destroys neurons LIGHT & ITS USES - Reflection Reflection waves – Bouncing back of light LIGHT & ITS USES: Reflection Vocabulary Image – Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears Always inverted Real LIGHT & ITS USES: Reflection Vocabulary Virtual Image– “Not Real” because it cannot be projected Formed in locations where light does NOT reach Image only seems to be there! Light & Its Uses: Mirrors Reflection Vocabulary Optical Axis – Base line through the center of a mirror or lens Focal Point – Point where reflected or refracted rays meet & image is formed Focal Length – Distance between center of mirror/lens and focal point © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery LIGHT & ITS USES: Mirrors Plane Mirrors – Perfectly flat Actually a Virtual Image Erect – Image is right side up © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery LIGHT & ITS USES: Mirrors Reflection & Mirrors (Cont.) Convex Mirror Curves outward Reduces images. Uses: Rear view mirrors, store security… CAUTION! Objects are closer than they appear! © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery LIGHT & ITS USES: Lenses Convex Lenses Thicker in the center than edges. Lens that converges (brings together) light rays. LIGHT & ITS USES: Lenses © 2000 D. L. Power Lenses – Lens that is thicker at the edges and thinner in the center. Diverges light rays All images are erect and enlarged. Concave CONVEX CONCAVE How You See Near Sighted – Eyeball is too long and image focuses in front of the retina Far Sighted – © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery Eyeball is too short so image is focused behind the retina. © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery LIGHT & USES: Lenses Vision – Human Eye is a convex lens. Nearsightedness – Concave lenses expand focal lengths Farsightedness – Convex lenses shortens the focal length. LIGHT & USES: Optical Instruments Cameras Telescopes Microscopes © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery © 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery LIGHT & USES: Optical Instruments LASERS Holography – Use of Lasers to create 3-D images Fiber Optics – Light energy transferred through long, flexible fibers of glass/plastic Uses – Communications, medicine, t.v. transmission, data processing. LIGHT & USES: Diffraction Diffraction – Bending of waves around the edge of a barrier. Breaks images into bands of light & dark and colors. Each element has it's own unique 'fingerprint' of color Scientist identify stars based on the color emitted