* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - VarsityField
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
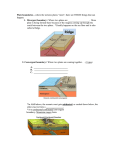
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER • JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics The Unifying Theory © 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Interactions at plate boundaries depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Key Figure 2.6 (pages 26-27) Go to next slide to begin Divergent Boundaries Oceanic Plate Separation MidAtlantic Ridge an c i r e m A th r o e N P la t E ur asia n Pl a te Divergent Boundaries Oceanic Plate Separation Volcanoes and earthquakes concentrate. an c i r e m A th r o e N P la t MidAtlantic Ridge E ur asia n Pl a te Divergent Boundaries Continental Plate Separation East African Rift Valley ate l P an c i r f A Soma l i S ub plate Divergent Boundaries Continental Plate Separation Parallel valleys; volcanoes and earthquakes. East African Rift Valley ate l P an c i r f A Soma l i S ub plate Convergent Boundaries Ocean-Ocean Convergence Mariana Islands e n i p ip Phil e Plat Marianas Trench Pacif ic Pla te Convergent Boundaries Ocean-Ocean Convergence Deep-sea trench; volcanic island arc. Mariana Islands e n i p ip Phil e Plat Marianas Trench Pacif ic Pla te Convergent Boundaries Ocean-Continent Convergence Andes Mountains Peru-Chile Trench te a l P a c Naz South American Plate Convergent Boundaries Ocean-Continent Convergence A volcanic belt of mountains forms. Andes Mountains Peru-Chile Trench te a l P a c Naz South American Plate Convergent Boundaries Continent-Continent Convergence Himalaya te a l P n a i l a r st Indian-Au Tibetan Plateau Main thrust fault Eurasian Plate Convergent Boundaries Continent-Continent Convergence Crust crumbles, creating high mountains and a wide plateau. Himalaya te a l P n a i l a r st Indian-Au Tibetan Plateau Main thrust fault Eurasian Plate Transform-Fault Boundaries Mid-Ocean Ridge Transform Fault Euras ian Pl ate late P n a c i er m A h t r No Transform-Fault Boundaries Mid-Ocean Ridge Transform Fault Spreading centers offset. Euras ian Pl ate late P n a c i er m A h t r No Transform-Fault Boundaries Continental Transform Fault ate l P c i f Paci North Ameri can Pl ate Transform-Fault Boundaries Continental Transform Fault Offset continental crust. ate l P c i f Paci North Ameri can Pl ate The San Andreas fault Figure 2.9 (page 30) Go to next slide to begin As plates move past each other... As plates move past each other... …creek beds are offset As plates move past each other... n Sa A nd re …creek beds are offset San Francisco as fau Los Angeles lt Interactions at plate boundaries depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which of the locations listed below is least associated with a volcanically active plate boundary? A. Mid-ocean ridge B. Deep ocean trench C. Transform fault D. Continental Rift Interactions at plate boundaries depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which of the locations listed below is least associated with a volcanically active plate boundary? A. Mid-ocean ridge B. Deep ocean trench C. Transform fault D. Continental Rift Interactions at plate boundaries depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary B. Convergent Boundary C. Transform-fault Boundary D. All of the above Interactions at plate boundaries depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary B. Convergent Boundary C. Transform-fault Boundary D. All of the above Interactions at plate boundaries depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. At which kind of plate boundary is new oceanic lithosphere formed? A. Oceanic transform boundary B. Oceanic divergent boundary C. Ocean-ocean convergent boundary D. Ocean-continent convergent boundary Interactions at plate boundaries depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. At which kind of plate boundary is new oceanic lithosphere formed? A. Oceanic transform boundary B. Oceanic divergent boundary C. Ocean-ocean convergent boundary D. Ocean-continent convergent boundary Continental rifting, drifting, and collisions assembled and dispersed Pangaea Key Figure 2.13 (pages 38–39) Go to next slide to begin ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA RODINIA Late Proterozoic, 750 Ma ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA RODINIA Late Proterozoic, 750 Ma Formed about 1.1 billion years ago; began to break up about 750 million years ago. ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA Late Proterozoic, 650 Ma ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA Late Proterozoic, 650 Ma The pre-Pangean pattern of continental drift. ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA Middle Ordovician, 458 Ma The pre-Pangean pattern of continental drift. ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA Early Devonian, 390 Ma The pre-Pangean pattern of continental drift. ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA PANGAEA (a) Early Triassic, 237 Ma ASSEMBLY OF PANGAEA PANGAEA (a) Early Triassic, 237 Ma Assembled by 237 Ma. BREAKUP OF PANGAEA (b) Early Jurassic, 195 Ma BREAKUP OF PANGAEA (b) Early Jurassic, 195 Ma Signaled by the opening of rifts from which lava poured; relics can be found today in volcanic rocks from Nova Scotia to North Carolina. BREAKUP OF PANGAEA (c) Late Jurassic, 152 Ma BREAKUP OF PANGAEA (d) Late Cretaceous, Early Tertiary, 66 Ma THE PRESENT-DAY AND FUTURE WORLD (e) PRESENT-DAY WORLD THE PRESENT-DAY AND FUTURE WORLD (e) PRESENT-DAY WORLD The modern world has been produced over the past 65 million years. THE PRESENT-DAY AND FUTURE WORLD (f) 50 million years in the future Continental rifting, drifting, and collisions assembled and dispersed Pangaea According to the reconstructed history of continental movements you just saw, about when did the modernday Atlantic Ocean first begin to form? A. About 750 million years ago B. About 390 million years ago C. About 150 million years ago D. About 50 million years ago Continental rifting, drifting, and collisions assembled and dispersed Pangaea According to the reconstructed history of continental movements you just saw, about when did the modernday Atlantic Ocean first begin to form? A. About 750 million years ago B. About 390 million years ago C. About 150 million years ago D. About 50 million years ago Two competing hypotheses for the mantle convection system. Figure 2.14 (page 40) Go to next slide to begin Whole-mantle convection Mantle Outer core Inner core Upper mantle 700 km Lower mantle 2900 km Outer core Whole-mantle convection Upper mantle 700 km Lower mantle 2900 km Outer core Stratified convection Boundary near 700 km separates the two convection systems. Two competing hypotheses for the mantle convection system. Considering either the whole mantle or stratified mantle convection models, at which kind of plate tectonic boundary is the upper part of the mantle (asthenosphere) rising? A. Divergent boundaries B. Convergent boundaries C. Transform boundaries Two competing hypotheses for the mantle convection system. Considering either the whole mantle or stratified mantle convection models, at which kind of plate tectonic boundary is the upper part of the mantle (asthenosphere) rising? A. Divergent boundaries B. Convergent boundaries C. Transform boundaries Two competing hypotheses for the mantle convection system. Although the exact nature of mantle convection is still a matter of debate, which model for mantle convection is currently favored by most geoscientists? A. Whole-mantle convection B. Stratified-mantle convection Two competing hypotheses for the mantle convection system. Although the exact nature of mantle convection is still a matter of debate, which model for mantle convection is currently favored by most geoscientists? A. Whole-mantle convection B. Stratified-mantle convection Two competing hypotheses for the mantle convection system. Which is the underlying fundamental driving force for mantle convection? A. Magnetism B. Nuclear fusion C. Earth’s rotation D. Gravity Two competing hypotheses for the mantle convection system. Which is the underlying fundamental driving force for mantle convection? A. Magnetism B. Nuclear fusion C. Earth’s rotation D. Gravity Seafloor Spreading Evidence for magnetic reversals has been primarily preserved in: A. metamorphic rocks near convergent plate boundaries B. limestone and shale accumulating in shallow ocean basins C. active dune fields in the arid regions of the world D. extrusive igneous rocks associated with mid-ocean ridges Seafloor Spreading Evidence for magnetic reversals has been primarily preserved in: A. metamorphic rocks near convergent plate boundaries B. limestone and shale accumulating in shallow ocean basins C. active dune fields in the arid regions of the world D. extrusive igneous rocks associated with midocean ridges Seafloor Spreading The idea that igneous rocks can record magnetic anomalies was first observed in: A. pillow basalts near the mid-Atlantic ridge B. basaltic lava flows from successive volcanic eruptions C. welded ash and cinders accumulated after an explosive volcanic eruption D. granitic rocks that have been contact metamorphosed Seafloor Spreading The idea that igneous rocks can record magnetic anomalies was first observed in: A. pillow basalts near the mid-Atlantic ridge B. basaltic lava flows from successive volcanic eruptions C. welded ash and cinders accumulated after an explosive volcanic eruption D. granitic rocks that have been contact metamorphosed Seafloor Spreading Which of the following magnetic reversals are we currently experiencing? A. Gilbert B. Matuyama C. Brunhes D. Gauss Seafloor Spreading Which of the following magnetic reversals are we currently experiencing? A. Gilbert B. Matuyama C. Brunhes D. Gauss Seafloor Spreading Absolute ages obtained from igneous rocks samples recovered from mid-ocean ridges reveal that: A. rocks ages get older with greater distance from the axis of the spreading ridge B. the pattern of rock ages is mirrored on each side of the spreading ridge C. the duration of each magnetic interval is the same across the axis of the spreading ridge D. all of these E. None of these Seafloor Spreading Absolute ages obtained from igneous rocks samples recovered from mid-ocean ridges reveal that: A. rocks ages get older with greater distance from the axis of the spreading ridge B. the pattern of rock ages is mirrored on each side of the spreading ridge C. the duration of each magnetic interval is the same across the axis of the spreading ridge D. all of these E. None of these Seafloor Spreading Which of the following components within an igneous rock are most responsive to the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field? A. quartz B. feldspar C. iron D. magnesium Seafloor Spreading Which of the following components within an igneous rock are most responsive to the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field? A. quartz B. feldspar C. iron D. magnesium Transform Boundary Based on the relative motion of the North American and Pacific Plates, the San Andreas Fault is an example of a (an): A. normal fault B. reverse fault C. left-lateral strike-slip fault D. right-lateral strike-slip fault Transform Boundary Based on the relative motion of the North American and Pacific Plates, the San Andreas Fault is an example of a (an): A. normal fault B. reverse fault C. left-lateral strike-slip fault D. right-lateral strike-slip fault Transform Boundary At the present rate motion along the San Andreas Fault, the city of Los Angeles will be a suburb of the city of San Francisco in: A. 9 years B. 9 million years C. 40,000 years D. 2 million years Transform Boundary At the present rate motion along the San Andreas Fault, the city of Los Angeles will be a suburb of the city of San Francisco in: A. 9 years B. 9 million years C. 40,000 years D. 2 million years Transform Boundary Transform boundaries form as a result of ________ stresses in the lithosphere. A. tensional B. compressional C. shear D. random Transform Boundary Transform boundaries form as a result of ________ stresses in the lithosphere. A. tensional B. compressional C. shear D. random Transform Boundary The San Andreas Fault System is composed of: A. a network of parallel transform faults B. a single fault C. a network of perpendicular transform faults D. a zone of both normal and reverse faults Transform Boundary The San Andreas Fault System is composed of: A. a network of parallel transform faults B. a single fault C. a network of perpendicular transform faults D. a zone of both normal and reverse faults Transform Boundary Unlike both convergent and divergent plate boundaries, transform plate boundaries do NOT involve: A. the relative motion between two fault blocks B. the buildup of tectonic stresses C. the creation or destruction of crust D. the generation of earthquakes in response to the release of elastic strain Transform Boundary Unlike both convergent and divergent plate boundaries, transform plate boundaries do NOT involve: A. the relative motion between two fault blocks B. the buildup of tectonic stresses C. the creation or destruction of crust D. the generation of earthquakes in response to the release of elastic strain Plate Tectonics: Subduction Subduction is a tectonic process that happens at which type of plate boundary? A. convergent B. divergent C. transverse D. hot spot Plate Tectonics: Subduction Subduction is a tectonic process that happens at which type of plate boundary? A. convergent B. divergent C. transverse D. hot spot Plate Tectonics: Subduction What causes oceanic crust to subduct when it is confronted by another oncoming plate? A. temperature B. strain C. density D. elasticity Plate Tectonics: Subduction What causes oceanic crust to subduct when it is confronted by another oncoming plate? A. temperature B. strain C. density D. elasticity Plate Tectonics: Subduction Which of the following statements are TRUE? A. All convergent plate boundaries are subduction zones. B. All subduction zones involve the interaction of oceanic and continental crust. C. All subduction zones occur at convergent plate boundaries. D. All convergent plate boundaries involve the process of rifting. Plate Tectonics: Subduction Which of the following statements are TRUE? A. All convergent plate boundaries are subduction zones. B. All subduction zones involve the interaction of oceanic and continental crust. C. All subduction zones occur at convergent plate boundaries. D. All convergent plate boundaries involve the process of rifting. Plate Tectonics: Subduction What factors cause the downgoing plate to melt during the process of subduction? A. pressure and gravity B. gravity and elasticity C. seismicity and pressure D. depth and frictional heating Plate Tectonics: Subduction What factors cause the downgoing plate to melt during the process of subduction? A. pressure and gravity B. gravity and elasticity C. seismicity and pressure D. depth and frictional heating Plate Tectonics: Subduction Where would we go to see the closest convergent plate boundary in North America? A. to the island of Hawaii B. off the coast of Washington State C. to central New Mexico D. all of these E. none of these Plate Tectonics: Subduction Where would we go to see the closest convergent plate boundary in North America? A. to the island of Hawaii B. off the coast of Washington State C. to central New Mexico D. all of these E. none of these Divergent Boundaries The Red Sea is the surface expression of a Continental Rift, or divergent boundary between which two plates? A. Pacific and Indian Plates B. North American and Pacific Plates C. African and North American Plates D. Arabian and African Plates Divergent Boundaries The Red Sea is the surface expression of a Continental Rift, or divergent boundary between which two plates? A. Pacific and Indian Plates B. North American and Pacific Plates C. African and North American Plates D. Arabian and African Plates Divergent Boundaries A divergent plate boundary like the East African Rift is a result of ________ stresses within the crust. A. compressional B. tensional C. shear D. none of these Divergent Boundaries A divergent plate boundary like the East African Rift is a result of ________ stresses within the crust. A. compressional B. tensional C. shear D. none of these Divergent Boundaries Which of the following statements are TRUE? A. All divergent plate boundaries are mid-ocean ridges. B. All continental rift boundaries will become mid-ocean ridges (tricky). C. All mid-ocean ridges boundaries began as continental rifts. D. All divergent plate boundaries involve the process of subduction. Divergent Boundaries Which of the following statements are TRUE? A. All divergent plate boundaries are mid-ocean ridges. B. All continental rift boundaries will become mid-ocean ridges (tricky). C. All mid-ocean ridges boundaries began as continental rifts. D. All divergent plate boundaries involve the process of subduction. Divergent Boundaries Why is molten magma rising to the surface at divergent plate boundaries? A. because it is more dense than the hotter rock around it B. because it is affected by anti-gravity C. because it is less dense than the cooler rock surrounding it D. it is pure chance that magma rises at these boundaries Divergent Boundaries Why is molten magma rising to the surface at divergent plate boundaries? A. because it is more dense than the hotter rock around it B. because it is affected by anti-gravity C. because it is less dense than the cooler rock surrounding it D. it is pure chance that magma rises at these boundaries Divergent Boundaries Where would we go to see the closest divergent plate boundary in North America? A. off the coast of Washington State B. to central New Mexico C. to the island of Hawaii D. all of these E. none of these Divergent Boundaries Where would we go to see the closest divergent plate boundary in North America? A. off the coast of Washington State B. to central New Mexico C. to the island of Hawaii D. all of these E. none of these Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea Which continental landmass was assembled first? A. Pangea B. Australia C. Gondwana D. Rodinia Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea Which continental landmass was assembled first? A. Pangea B. Australia C. Gondwana D. Rodinia Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea How long did it take to form the modern continental arrangement since the breakup of Pangaea? A. 750 Ma B. 200 Ma C. 500 Ma D. 50 Ma Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea How long did it take to form the modern continental arrangement since the breakup of Pangaea? A. 750 Ma B. 200 Ma C. 500 Ma D. 50 Ma Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea Based on the present directions of plate motions, which of the following should occur over the next 50 million years? A. North America will separate from South America. B. Australia will collide with Antarctica. C. Africa will collide with Eurasia. D. The Atlantic Ocean Basin will close. Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea Based on the present directions of plate motions, which of the following should occur over the next 50 million years? A. North America will separate from South America. B. Australia will collide with Antarctica. C. Africa will collide with Eurasia. D. The Atlantic Ocean Basin will close. Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea The bolide impact that is hypothesized to have led to the extinction of the dinosaurs impacted the Earth’s surface __________ about __________ years ago. A. in the Australian Outback; 200 million B. in Northern Siberia; 25 million C. off the Yucatan Peninsula; 65 million D. near the North Pole; 5 million Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea The bolide impact that is hypothesized to have led to the extinction of the dinosaurs impacted the Earth’s surface __________ about __________ years ago. A. in the Australian Outback; 200 million B. in Northern Siberia; 25 million C. off the Yucatan Peninsula; 65 million D. near the North Pole; 5 million Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea Which of the following ocean basins are no longer present due to plate motions over the past 750 Ma? A. Rheic Ocean B. Iapetus Ocean C. Tethys Ocean D. all of these E. none of these Assembly and Breakup of Pangaea Which of the following ocean basins are no longer present due to plate motions over the past 750 Ma? A. Rheic Ocean B. Iapetus Ocean C. Tethys Ocean D. all of these E. none of these