* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
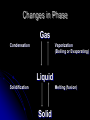
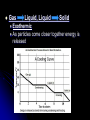
Phases of Matter and Phase Changes Phase . Depends on strength of forces of attraction between particles. Solids Definite shape and volume. Most dense phase Difficult to compress. Exception is water!. Particles vibrate in fixed positions Crystalline lattice structure. Most attraction between particles. Note: Amorphous solids include glass, plastic, wax, and silly putty Liquids Definite volume No definite shape Hard to compress Particles slide past each other Forces of attraction between particles still high Gases No definite shape or volume Expands to fill container Lowest density Density depends on pressure Little attraction between particles “Vapor” = a gaseous state of something that is normally liquid (Ex: water vapor) Phases Applet Short Summary video on phases: (1 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sKvoVzukHo&safe=active Applet: (Excellent) https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/statesof-matter http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/states_ of_matter/ Changes in Phase Gas Condensation Vaporization (Boiling or Evaporating) Liquid Solidification Melting (fusion) Solid Let’s Skip a Phase Sublimation Directly from the solid phase to the gas phase. Happens with substances with weak intermolecular forces of attraction They separate easily! Ex: CO2(s) dry ice, Iodine CO2(s) → CO2 (g) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8tHOVVgGkpk Energy Energy = capacity to do work or produce heat. It can be anything that causes matter to move or change direction. Ex: electrical, atomic, mechanical, chemical Law of Conservation of Energy Energy can’t be created or destroyed, just transferred from one form to another PE vs. KE Potential Energy stored energy Energy can be stored in bonds between atoms Kinetic Energy energy of motion All atoms are moving and vibrating unless at absolute zero Energy and Changes to Matter Exothermic Change: A + B → C + D + energy Energy is released or “ex”its Endothermic Change: A + B + energy → C + D Energy is absorbed or “en”ters Energy During Phase Changes Solid Liquid, Liquid Gas Endothermic Energy is absorbed and overcomes attractive forces between particles Gas Liquid, Liquid Solid Exothermic As particles come closer together energy is released http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/Matter/ HeatingCurve.htm Heat Energy Also called Thermal energy, it makes particles move more as it is added Measured in Joules or calories. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f1eAOygDP5s&safe=active Heat Flow Heat energy travels from an object of higher temp. to one of lower temp. until both reach the same temp. Temperature Measure of the average kinetic energy (motion) of all the particles in a sample. Not a form of energy!!! But if you add heat energy or take it away, it causes particles to move faster or slower and thus changes the temp. Heat vs. Temperature Teacup vs. Bathtub Both at 25˚C Which one contains more heat energy? Which one has the greater average KE? Label This Graph