* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kawasaki Disease - LSU School of Medicine
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever in Buenos Aires wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
1793 Philadelphia yellow fever epidemic wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
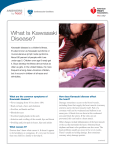
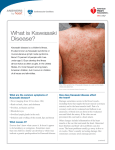
Good Morning Morning Report July 2, 2013 Semantic Qualifiers Symptoms Acute /subacute Chronic Localized Diffuse Single Multiple Static Progressive Constant Intermittent Single Episode Problem Characteristics Ill-appearing/ Toxic Well-appearing/ Non-toxic Recurrent Localized problem Systemic problem Abrupt Gradual Acquired Congenital Severe Mild New problem Recurrence of old problem Painful Nonpainful Bilious Nonbilious Sharp/Stabbing Dull/Vague Illness Script Predisposing Conditions Age, gender, preceding events (trauma, viral illness, etc), medication use, past medical history (diagnoses, surgeries, etc) Pathophysiological Insult What is physically happening in the body, organisms involved, etc. Clinical Manifestations Signs and symptoms Labs and imaging Differential Diagnosis** What other diagnoses would you consider in a patient with suspected Kawasaki Disease? Predisposing Conditions Which country has the highest prevalence of Kawasaki Disease? Japan (10x that of US) In the US, which ethnicity is most commonly affected? Least commonly? Most common in Asians and Pacific Islanders Least common in caucasians Age Median = 2yo 76% of cases in <5yo Male:Female = 3:2 Which seasons are you more likely to see patients present with KD? Seasonal peaks in winter and spring Pathophysiology Complete etiology is unknown, but features suggest an infectious source. Generalized vasculitis Affects all blood vessels throughout the body Which specific vessels are affected in KD? Preferentially involves the coronary arteries Process Initial neutrophil influx Large mononuclear cells w/lymphocytes and plasma cells Active inflammation Progressive fibrosis and scar formation Clinical Manifestations You are seeing a patient with multiple days of fever as well as a rash and some other non-focal symptoms. How many days of fever must be present before diagnosing a patient with KD? What are the other 5 criteria used to diagnose KD? Conjunctivitis** Bilateral bulbar injection No exudate Painless Limbic sparing Shortly after fever starts Rash** Various forms Nonspecific, diffuse with scattered macules & erythematous papules Occasionally scarlatiniform, erythroderma, erythema multiforme, uriticarial, or a fine micropustular eruption Not bullous of vesicular Often involves diaper area Within 5d of fever Adenopathy** Least common feature Anterior cervical triangle Usually unilateral > 1.5 cm Firm, nontender No overlying erythema Strawberry Tongue** Changes of the lips and oral cavity Strawberry tongue Cracked, red, swollen, bleeding lips Diffuse erythema of oral mucosa Oral ulcers and exudates are not seen Hands and Feet** Erythema of palms and soles Firm, sometimes painful induration of the hands and feet Later desquamation that usually begins in periungal region (2-3 weeks after fever onset) Clinical Manifestations** “C R A S H” Other** Arthritis/arthralgias that involve multiple joints In children, what behavioral complaint do parents often give? Irritability*** GI complaints Diarrhea Vomiting Abdominal pain Hepatomegaly and jaundice What abnormal finding may be seen on abdominal imaging (esp. RUQ) Acalculous distension of gallbladder…hydrops of the gallbladder Labs** What would your CBC look like? Leukocytosis Majority with WBC > 15,000 Predominance of immature and mature granulocytes Anemia Thrombocytosis…with platelet counts 500-1000 x 103 Elevated ESR (>40 mm/hr) and CRP (>3mg/dL) Mild to moderate elevation of LFTs Mild hyperbilirubinemia What abnormality could you see on the UA and urine culture? Sterile pyuria…+WBC Negative cultures Aseptic meningitis (if CSF obtained) Treatment** High-dose aspirin (80-100mg/kg/day divided QID) during acute phase of illness 3-5mg/kg/day until no evidence of coronary changes by 6-8 weeks Continued aspirin therapy if coronary changes present IVIG 2g/kg/dose (up to 2-3 doses depending on fever) Children treated with IVIG and ASA had faster resolution of fever and fewer coronary abnormalities than those treated with ASA alone Refractory KD…treatment is controversial Cardiac Complications** Coronary artery aneurysm (identified on echo within 1- 2mo of diagnosis) 20-25% of untreated patients; 5% of treated patients Resolution within 1-2 years in approximately 50% Myocardial infarction Principal cause of death Most occur within 1 year of disease onset but can occur years later Myocarditis Valvulitis Pericarditis with effusion Echocardiogram** When should you obtain an echo on patients with suspected Kawasaki disease? Obtain on all patients with suspected Kawasaki At diagnosis Follow-up…usually at 2 weeks and 6 weeks after diagnosis Follow-Up Atypical Kawasaki Thanks No noon conference today!