* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 8 Unit Notes 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
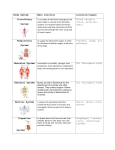
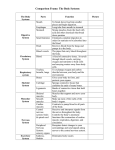
Topic 8 Notes – Human Body Systems The human body is a collection of organ systems working to function together. Remember, organelles cells tissue organ organ system organism. T-CHART THE FOLLOWING NOTES: SYSTEM NAME | SYSTEM FUNCTION/DESCRIPTION | ORGANS Circulatory System uses the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) and blood to transport oxygen, food, waste and nutrients to and from the body. Blood serves as the system of transport, and it connects to all other body systems. White blood cells defend the body from disease. The heart is the pump that keeps this transport system moving through veins, arteries and capillaries. Respiratory System uses the nose, mouth, trachea, diaphragm, bronchi and lungs to transport oxygen to the blood and carbon dioxide from the body. When we breathe, the body takes in the oxygen that it needs (through your lungs and then red blood cells) and removes the carbon dioxide that it doesn't need from your blood (see circulatory system). Skeletal System provides structure and protection using bones and ligaments. The Skeletal System has three major jobs: It protects our vital organs such as the brain, the heart, and the lungs. It gives us the shape that we have. It allows us to move, using our joints and bones. Because muscles are attached to bones, when muscles move, they move the bones and the body moves. Muscular System allows movement using skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. The Muscular System is made up of more than 600 muscles. These muscles work with your skeletal system to provide a movable frame of support and protection. You control some of your muscles with your nervous system and others, like your heart, do their jobs without you thinking about them at all. Muscles are all made of the same material, a type of elastic tissue. Integumentary System (integument = “ a covering”) protects our body with the skin, hair, and nails. The integumentary system is all about protection. The system protects your body from disease by providing a barrier to viruses and bacteria. The system protects your body from physical damage by offering a thick barrier that both contains your internal organs and stops large objects, like a rock from entering your body. Digestive System The digestive system is made up of organs like the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and large & small intestines, liver, gall bladder and pancreas, that break down food into particles of glucose, proteins, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, and fats, which the body needs for energy, growth, and repair. The circulatory system moves food to cells that need energy and removes wastes. Excretory System (excrete = “to get rid of”) gets rid of body chemical and gaseous waste using your kidneys, bladder, lungs, skin, liver, urethra and ureter. Urine is the result of the excretory system balancing the amount of water and salts in your body after your digestive system gets through doing it’s job. Your kidneys are the core organs and act as a blood filter (circulatory system). Once the urine passes through your urethra, it leaves your body. Reproductive System produces offspring, and is responsible for reproduction and survival of the human species. Reproduction creates a genetically unique child. Organs include the ovaries (women) and ova (female gamete) and testes/testicles (men) and sperm (male gamete). Nervous System coordinates and controls the actions of all organs and organ systems and sends and receives signals throughout the body using organs such as the brain, spinal cord, nerves and sense organs (5 senses). The Nervous System is made up of the brain and the spinal cord, as well as thousands of nerves. The primary organ of this system is the brain and spinal cord. The system also detects, process and responds to environmental stimuli in or out of your body. Endocrine System regulates and controls the body using hormones produced and secreted (released) in the glands. The endocrine system is made up of a group of glands that produce the body's long-distance messengers, or hormones. Hormones are chemicals that control body functions, such as metabolism, growth, and sexual development. The glands, which include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, thymus gland, pineal body, pancreas, ovaries, and testes, release hormones directly into the bloodstream, which slowly transports the hormones to organs and tissues throughout the body. Compared to the nervous system’s control, this is a lot slower. The Immune System is our body's defense system against infections and diseases. Organs, tissues, cells, nodes, and white blood cells work together to respond to dangerous organisms (like bacteria/viruses) and substances that may enter the body from the environment.