* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII Part I PowerPoint
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Spain during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
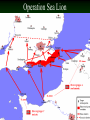
World War II Begins I. Dictators Challenge World Peace A. Japan 1. Wanted an empire equal to western powers 1. They sent Samurai to Western nations to learn about our way of life 2. Japan had very little resources 3. Japan was forced to trade with the United States 4. 1931 – Japan seized Manchuria World War II Begins B. Italy 1. Invaded Ethiopia – 1935 2. Haile Selassie (Ethiopia’s King) asked for help – League of Nations voted sanctions (penalties) against Italy – League had no power to enforce the sanctions – Italy conquered Ethiopia in 1936 3. Italians used poison gas against Ethiopia violating the Treaty of Versailles World War II Begins C. Germany and Hitler 1. Challenged the Treaty of Versailles a. Rearmed Germany b. Returned troops to the Rhineland – 1936 World War II Begins C. Reaction from Western Democracies 1. Appeasement – giving in to the demands of an aggressor in order to keep peace 2. Why appeasement? A. Democracies didn’t want another war B. Germany seen as defense against Soviet Communism C. Great Depression sapped the energies of the western democracies Peace in our time Monty Python - Neville Chamberlain World War II Begins 3. United States A. B. Neutrality Acts passed by U.S. Congress: forbade the sale of arms to any nation at war, outlawed loans to warring powers U.S. policy: avoid involvement in a European war - Isolationism World War II Begins E. Rome – Berlin – Tokyo Axis 1. Agreed to fight Soviet Communism 2. Agreed not to interfere with each other’s plans for expansion World War II Begins II. The Spanish Civil War (1936-1939) A. From Monarchy to Republic 1. 2. King Alfonso XIII forced to leave after public unrest Republic set up with a new, more liberal constitution a. b. Govt. took over some Church lands, ended Church control of education, redistributed some land to peasants, allowed women’s suffrage, reduced size of military Conservatives rejected change (backed by the military) World War II Begins B. Nationalist (conservatives) vs. Loyalists (liberals) – 1936 1. Nationalists led by Francisco Franco a. Supported by Mussolini and Hitler 2. Loyalists – supporters of the republic included communists, socialists, and supporters of democracy Francisco Franco World War II Begins B. A Dress Rehearsal 1. Guernica – 1937 – small Spanish town of no military value – bombed, machine-gunned by Germans testing their new aircraft – 1,600 innocent people killed 2. 1939 – Franco won, created a fascist state (he ruled until 1975) Pablo Picasso’s Guernica World War II Begins III. German Aggression Continued Austria Annexed – 1938 A. 1. 2. 3. Anschluss – union of Germany and Austria Hitler forced Austrian chancellor to appoint Nazis to key govt. posts Hitler sent in German soldiers to Maintain order when the chancellor refused to meet all of Germany’s demands World War II Begins B. The Czech Crisis 1. Hitler demanded the 3 million Germans in Sudetenland (West Czech) be given autonomy (freedom) 2. Later he said this region must be annexed by Germany 3. Munich Conference – Sept. 1938 a. Britain and France chose appeasement b. Gave Hitler the Sudetenland c. Hitler gave his word that Germany had no further plans of expansion World War II Begins 4. “Peace For Our Time” a. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain told his nation he had achieved “peace for our time” b. British politician Winston Churchill – reaction – “They had to choose between war and dishonor. They chose dishonor; they will have war.” World War II Begins IV. Europe Plunges Toward War Czechoslovakia – entire nation conquered by Germany in March 1939 A. 1. 2. Democracies realized that appeasement had failed They now promised to protect Poland if Germany attacked World War II Begins B. Nazi – Soviet Pact – Non Aggression Pact - Aug. 1939 1. Publicly, it bound Hitler to Stalin (Hitler’s enemy) to peaceful relations 2. Secretly, the two agreed (1) not to fight if the other went to war and (2) to divide up Poland and other parts of Eastern Europe 3. Hitler did not want to fight the USSR and Western Democracies at the same time when attacking Poland World War II Begins C. Invasion of Poland 1. Hitler wanted Danzig and Polish Corridor to be part of Germany again 2. If he attacked, war would be declared 3. Sept. 1, 1939 – Germany invaded Poland using Blitzkrieg 4. Sept. 3, 1939 – Britain and France declared war on Germany The Global Conflict: Axis Advances I. The First Onslaught A. Blitzkrieg “lightning war” – 3 stages: 1. German bombers 2. Tanks 3. Infantry a. within one month, Poland fell to Germany and the USSR The Global Conflict: Axis Advances B. Baltic States 1. Stalin’s armies took over Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and part of Finland The Global Conflict: Axis Advances C. Early Axis Triumphs 1. “Phony War” – Britain, France waited behind the Maginot Line no attack occurred 2. Norway + Denmark Fall – April 1940 3.Netherlands + Belgium Fall – April/May 1940 The Global Conflict: Axis Advances D. Miracle at Dunkirk – May 1940 1. Allied forces trapped in France between Germans and the English Channel 2. Hundreds of British ships/boats came to rescue 300,000 troops across the Channel The Global Conflict: Axis Advances E. France Falls 1. Germany attacked from North, Italy from the South 2. June 22nd, 1940 – Hitler forced France to surrender – Germany occupied the north, S. France became Vichy France (a puppet state that collaborated with the Nazis) The Global Conflict: Axis Advances II. The Battle of Britain A. The Battle Begins 1. Aug. 12, 1940 – German bombers attacked England’s southern coast 2. Royal Air Force (RAF) battled the German Air Force (Luftwaffe) The Global Conflict: Axis Advances B. The London Blitz 1. Sept. 7, 1940 – German began bombing of London a. continued for 57 nights – much of the city destroyed, 15,000 killed b. London + other cities bombed off and on until June 1941 The Global Conflict: Axis Advances c. Hitler hoped to break the will of the British, but morale remained high d. Operation Sea Lion (invasion of Britain) was postponed, Hitler shifted his focus to Russia Operation Sea Lion The Global Conflict: Axis Advances III. North Africa A. Italy attempted to invade Egypt (British Colony), failed 1. Germans sent in General Erwin Rommel 2. Rommel “Desert Fox” pushed the British back to Cairo, Egypt 3. British worried Germans would capture the Suez Canal The Global Conflict: Axis Advances IV. The Balkans A. Italian forces invaded Greece 1. Germans came to the rescue again, Greece + Yugoslavia added to Axis control 2. Bulgaria + Hungary joined Axis alliance The Global Conflict: Axis Advances V. Operation Barbarossa – conquest of Soviet Union (June 1941) A. Reasons for attack 1. Living space for Germany (lebensraum) 2. Gain raw materials 3. Desire to crush communism + Stalin Timeline • Place Events in Order • Pages 770 – 780 • Event at the top, date at the bottom, colored illustration in the middle Timeline – Place Events in Order Pages 770 – 780 • Denmark and Norway Fall - April • Battle of Britain – Aug. • Troops into the Rhineland - March • Nazi-Soviet Pact • Atlantic Charter • Italy invades Ethiopia – October 1935 • France Falls • • • • • • • • Attack on Pearl Harbor Spanish Civil War Operation Barbarossa Austria Annexed Guernica Miracle at Dunkirk Munich Conference Netherlands and Belgium Falls – April/May • Invasion of Poland The Global Conflict: Axis Advances B. German Advance (June 1941) 1. Stalin unprepared because of the Great Purge 2. 2.5 million Russian soldiers killed trying to fend off the invaders 3. Russians burned everything as they retreated (scorched earth) 4. Most Germans believed victory would come soon but the winter weather stalled German advance The Global Conflict: Axis Advances C. Siege of Leningrad (Sept. 1941) 1. 2 ½ years of fighting, food was scarce, 1 million residents of the city died 2. Stalin wanted Britain to open second front in W. Europe to relieve pressure The Global Conflict: Axis Advances VI. Growing American Involvement A. “The Arsenal of Democracy” 1. Lend-Lease Act – allowed FDR to send or lend equipment to any nation whose defense was vital to U.S. national security The Global Conflict: Axis Advances B. Atlantic Charter (Aug. 1941) 1. Roosevelt + Churchill met secretly in the Atlantic 2. Charter set goals for the war: a. destroy the Nazi regime b. people of all nations should choose their own govt. (selfdetermination) c. permanent system of general security (United Nations) The Global Conflict: Axis Advances VII. Japan Attacks (Dec 7th, 1941) A. Growing Tensions 1. Japan seized territory in the Pacific 2. To stop Japan, U.S. banned the sale of war materials to Japan 3. Japan + U.S. held talks to ease tension 4. General Hideki Tojo (military leader and Prime Minister of Japan) did not want peace The Global Conflict: Axis Advances B. Attack on Pearl Harbor (Dec 7th, 1941) 1. General Tojo ordered surprise attack on the American fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii 2. 19 ships destroyed or damaged, 2,400 killed 3. FDR asked Congress to declare war The Global Conflict: Axis Advances C. Japanese Victories 1. Seized American colonies (Philippines) 2. Overran British Colonies 3. Japanese empire stretched from Southeast Asia to the Western Pacific 4. High point of Axis success (summer 1942)