* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download here.
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Antimicrobial surface wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
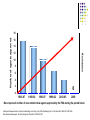
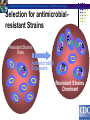
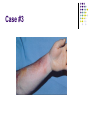
Antibiotics Tamar Barlam Infectious Disease Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Why is antibiotic choice important? Safe, broad-spectrum antibiotics are readily available One can easily cover most common infections with excellent therapeutic results So what’s the big deal? A Changing Landscape for Numbers of Approved Antibacterial Agents 16 14 12 Resistance Number of agents approved 18 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 1983-87 1988-92 1993-97 1998-02 2003-05 2008 Bars represent number of new antimicrobial agents approved by the FDA during the period listed. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Bad Bugs, No Drugs. July 2004; Spellberg B et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1279-1286; New antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:1912 Between 1962 and 2000, no major classes of antibiotics were introduced Fischbach MA and Walsh CT Science 2009 Antibiotic Resistance Antimicrobial-resistant infections can cause worse patient outcomes, longer hospital stays, and higher mortality rates than similar infections with antibioticsusceptible bacteria. Total costs related to AR infections are estimated as high as $30 billion. Inappropriate antibiotic use is believed to be the major contributor to the development and spread of AR bacteria. Studies have demonstrated approximately 30 to 50% of antibiotic treatments are inappropriate. Campaign to Prevent Antimicrobial Resistance in Healthcare Settings Selection for antimicrobialresistant Strains Resistant Strains Rare Antimicrobial Exposure Resistant Strains Dominant Choosing an Antibiotic What is wrong with the patient? Is it an infection? Is it bacterial? How sick is the patient? Host factors that might influence likely pathogens: social history, age, residence, comorbid conditions Host factors that might influence drug choice: allergy, pregnancy, renal/liver function Attributes of the drug What is its spectrum? Gram positive or gram negative? Aerobic or anaerobic or both? Does it reach adequate levels at site of infection? Bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal? Endocarditis Meningitis Osteomyelitis How are they different? Cefazolin Ceftriaxone Cefepime Ampicillin-sulbactam Ertapenem Levofloxacin Ciprofloxacin Ceftriaxone Cefepime Piperacillin-tazobactam Piperacillin-tazobactam Meropenem Ciprofloxacin Cefepime Case #1 54 yo female with poorly controlled diabetes comes to the ED with a buttock abscess with surrounding erythema. The abscess was I&D’d and material sent for culture. Case #1 Patient was placed on clindamycin and discharged home. Case #1 Case #1 Inducible macrolide resistance. Encoded by plasmid-borne gene erm. Constitutive – all test resistant Inducible – clindamycin can test susceptible Bacteria Isolated from Culture of Abscess Material, Deep Tissue Specimens, or Blood. Jenkins T C et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:895-903 © 2010 by the Infectious Diseases Society of America Case #2 23 yo healthy male with tibial fracture after MVA. ORIF performed and patient was discharged after an uneventful hospital course. Pain persisted and after six weeks, there was complete non-union. One month later, a small pustule formed and drained purulent material. Patient was seen by ortho and taken back to OR. What is the patient’s diagnosis? Treatment? Case #2 Case #2 What if these were the culture results? Case #3 47 yo active IVDU, HCV positive, presents with severe left arm pain and swelling. The patient had injected heroin into the veins of that arm 1 day prior. On the morning of admission, he had severe bilateral pleuritic chest pain Case #3 Rest of exam: T103 Other VSS II/VI SEM at LSB, decreased breath sounds R>L base, rales bilaterally No HSM WBC 18,000 w/ 26% B; H/H 13/40, plts 300K other labs wnl Case #3 Case #3 Describe what the patient likely has. What would you do next? Antibiotics? Case #3 Case #3 Antibiotic? Duration? Case #3 What if patient if this was his isolate: