* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 2 Geometry Definition Polygon Examples Not Polygons
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
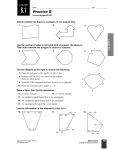
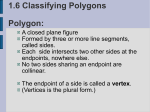
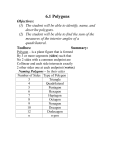
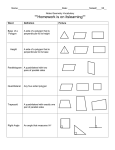
Definition Math 2 Geometry Based on Elementary Geometry, 3rd ed, by Alexander & Koeberlein 2.5 Convex Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure whose sides are line segments that intersect only at the endpoints. In this text only: convex polygons (interior angles measure from 0° to 180°) Examples? Polygon Examples Not Polygons Convex Polygons Concave Polygons Classify by number of sides Triangle (3) Quadrilateral (4) Pentagon (5) Classify by number of sides Hexagon (6) Heptagon (7) Octagon (8) 1 Classify by number of sides Informal Definition A diagonal of a polygon is a line segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices. Nonagon (9) B Decagon (10) A C E D Theorem 2.5.1 The total number of diagonals D in a polygon of n sides is given by the formula: D= n (n − 3) 2 Theorem 2.5.2 The sum S of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is given by: S = (n – 2) 180° • Use the formula to find the number of diagonals of: • a triangle • a quadrilateral • a pentagon D= n (n − 3) 2 Informal Definitions • Equiangular polygon: All angles are congruent. • Equilateral polygon: The measure of all sides are equal. 2 Definition A regular polygon is a polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular. Not Regular Polygons Notice it is possible for Polygons to be either equilateral or equiangular but not both. Notice: A square is a regular quadrilateral. Rectangle Rhombus Corollary 2.5.3 The measure I of each interior angle of a regular polygon of n sides is: I= Corollary 2.5.4 The sum of the four interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360° (n − 2) ⋅180 n Corollary 2.5.5 The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon, one at each vertex, is 360°. Corollary 2.5.6 The measure E of each exterior angle of a regular polygon of n sides is: E= 360 n 3 Informal Definition A polygram is the star-shaped figure that results when the sides of certain polygons are extended. Pentagram Hexagram 4