* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Michael Barry Michael Barry - Irish Pharmaceutical Healthcare
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence wikipedia , lookup
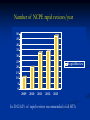
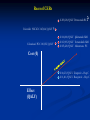
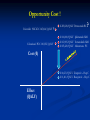
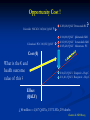
The Value of Innovation Michael Barry 26th November 2013 For discussion • Medicines Management Programme • Pharmacoeconomic Assessment • Value of innovation The Medicines Management Programme Multi-disciplinary Medicines Management Programme (MMP) headed by the National Medicines Information Centre (NMIC) and the National Centre for Pharmacoeconomics (NCPE) in collaboration with the HSE-Primary Care Reimbursement Service (PCRS) Providing sustained national leadership relating to Safe Effective Cost –effective prescribing The MMP ‘preferred drug’ initiative Factors considered in making a recommendation for a ‘preferred drug’ • range of therapeutic indication(s) • clinical evidence base • clinical guidelines ( National & International ) • cost • patient related factors • current prescribing practice The MMP ‘preferred drug’ initiative So remember: Statins : Think SIMVASTATIN PPI: Think LANSOPRAZOLE ACE inhibitor: Think RAMIPRIL ARB: Think CANDESARTAN Next steps for the ‘preferred drug’ initiative Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Serotonin & Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) Respiratory medicines Reference pricing and the MMP Reference pricing begins with the IMB identifying ‘interchangable drugs’ . Atorvastatin (Lipitor) was the first drug and will be followed by esomeprazole (Nexium), rosuvastatin (Crestor) with omeprazole (Losec Mups) and pravastatin (Lipostat) later. It is envisaged that 20 drugs will be identified as interchangable by May 2014. In setting the reference price the following criteria are considered: 1. The ability of suppliers to meet patient demand 2. Value for money afforded by the relevant listed items 3. Equivalent relevant prices in other Member States ( EU 28 ). 4. The relevant prices of therapeutically similar listed items e.g. simvastatin for atorvastatin 5. Resources available to the Executive 6. The terms of any agreements in place with stakeholders e.g. IPHA The new oral anticoagulants Reimbursement approval for new Anticoagulant Over 70% of NOAC prescribing is for patients ≥ 70 years 70-74 years = 17.53% 75 + years = 52.51% Atrial fibrillation accounts for 86.9% of all applications for NOACs The new Reimbursement Approval form for NOACs – enhancing safety The new reimbursement approval form will include information in relation to the following: CHADS ² Score CHA²DS ² - VASc Score HAS - BLED Score Cockcroft -Gault Eqn for GFR (ml/min) Current prescribing of oral anticoagulants – expenditure Growth in NOAC utilisation and expenditure is, in part, related to the issue of INR monitoring in the primary care setting. Over 60% of NOAC prescribing takes place in the South and West of the Country. Which NOAC for AF ? Bayesian mixed treatment comparison (MTC) underway The Medicines Management Programme Under the Medicines Management Programme there is an increased emphasis in obtaining utilisation and expenditure data under the Community Drugs Schemes. HTA is considered part of MMP and may be used where there is concern in relation to value for money Examples of HTAs carried out under the MMP include: Omacor Pregabalin (Lyrica) The Medicines Management Programme An important component of the MMP is communication with our prescribing colleagues. The NMIC has a 20 year record in such communications including our publications ‘NMIC Bulletin’ and ‘Therapeutics Today’. Under the MMP we are now conducting a series of GP meetings around the country with the support of the ICGP and the RCPI. Meetings to date: • Dublin x 2 • Dun Laoghaire • Waterford • Killarney • Donegal Next meetings will be held in Kildare, Dublin, Cork and Galway In 2014 we aim to communicate with GPs through our Pharmacy Advisors National & Regional Prescribing Rates of Preferred Drugs – example NWHB North Western Health Board Region RAMIPRIL as % of all ACE inhibitors = 60% CANDESARTAN as % of all ARBs = 8% LANSOPRAZOLE as % of all PPIs = 30% SIMVASTATIN as % of all Statins = 10% National Prescribing Rates RAMIPRIL as % of all ACE inhibitors = 53% CANDESARTAN as % of all ARBs = 10% LANSOPRAZOLE as % of all PPIs = 23% SIMVASTATIN as % of all Statins = 6% Pharmacoeconomic evaluation Pharmacoeconomic assessment process Pharmaceutical Company HSE - CPU Health Service Executive – Corporate Pharmaceutical Unit (HSE-CPU) NCPE RAPID REVIEW (www.ncpe.ie) National Centre for Pharmacoeconomics (NCPE) Number of NCPE rapid reviews/year 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Rapid Review 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 In 2012 62% of rapid reviews recommended a full HTA ‘Value of Innovation’ Innovation ? • H2 receptor antagonists and PPIs for the treatment of PUD • Protease inhibitors for the treatment of HIV infection • Statins for the prevention of cardiovascular disease • Protease inhibitors for the management of hepatitis C infection • Antibiotic therapy • Antihypertensive & Heart failure therapy with ACE inhibitors • Trastuzumab for the treatment of HER2 positive breast cancer From the HTA perspective innovation is not • a pharmaceutical product with a new mechanism of action but little advantage in terms of health outcomes • a “personalised medicine” or “targeted therapy” that does not work very well • where the primary health outcome is a change in some obscure, meaningless surrogate marker. • a product which demonstrates non inferiority to the current standard of care • a product that is considered unaffordable Innovation – definition ? “a new or existing medicine applied in a way which significantly improves healthcare at a price the HSE can afford” - does not have to be a new product - does have to significantly improve heath outcomes - does have to be affordable there must be added value How do we measure value ? Value may be measured in natural units e.g. life years gained (LYG) or Value may also be determined from a composite of LYG and a measure of utility or well being as assessed using any of the ‘Multi-attribute health status classification systems’ Quality of Well-Being (QWB) Health Utilities Index (HUI) EQ-5D Short Form 6D Mobility Self-care Usual activity Pain/discomfort Anxiety/depression Cost-effectiveness threshold – IPHA 2012 Cost (€) Q4 Q1 Effect (QALY) Q3 Q2 The QALY threshold to be used in the HTA process is € 45,000 Capturing value vs affordability ? Do we value innovation ? Estimating revealed weights for a multi criteria decision analysis approach to Health Technology Assessments: A case study in Ireland Efficiency/Affordability Clinical Utility Consumer demand Criteria assessed Social perspective Economic incentives Modelling issues Cost-effectiveness Gross Budget Impact Safety & Tolerability Process Utility Unmet need Orphan status Disadvantaged population End of life Severe disease Innovation Reversibility Quality of evidence Uncertainty Schmitz S. et al. 2013 Estimating revealed weights for a multi criteria decision analysis approach to Health Technology Assessments: A case study in Ireland The analysis confirms that recommendations for or against reimbursement of technologies are driven by the following: Cost-effectiveness (ICER) Quality of available evidence Safety & Tolerability Innovation Schmitz S. et al. 2013 Are we getting value for money ? Recent ICERs € 203,028/QALY Pertuzumab BC Crizotinib NSCLC € 165,616/QALY Cabazitaxel PC € 110,032/QALY ? ? € 116,000/QALY Ipilimumab MM € 112,905/QALY Vemurafenib MM € 105,420/QALY Abiraterone PC Cost (€) € 16,023/QALY Telaprevir – Hep C € 11,411/QALY Boceprevir – Hep C Effect (QALY) Opportunity Cost ! Crizotinib NSCLC € 165,616/QALY Cabazitaxel PC € 110,032/QALY ? € 203,028/QALY Pertuzumab BC ? € 116,000/QALY Ipilimumab MM € 112,905/QALY Vemurafenib MM € 105,420/QALY Abiraterone PC Cost (€) € 16,023/QALY Telaprevir – Hep C € 11,411/QALY Boceprevir – Hep C Effect (QALY) Opportunity Cost ! Crizotinib NSCLC € 165,616/QALY Cabazitaxel PC € 110,032/QALY ? € 203,028/QALY Pertuzumab BC ? € 116,000/QALY Ipilimumab MM € 112,905/QALY Vemurafenib MM € 105,420/QALY Abiraterone PC Cost (€) What is the € and health outcome value of this ? € 16,023/QALY Telaprevir – Hep C € 11,411/QALY Boceprevir – Hep C Effect (QALY) £ 80 million = 4,367 QALYs, 1337 LYGs, 295 deaths Claxton K. ISPOR 2013 “fair prices and real value” Developments at NCPE • Multi criteria decision analysis (MCDA) and Health Technology Assessment (HTA) • Incorporating Irish values into measurement of Quality of Life • Increasing emphasis on methodological developments around uncertainty and Bayesian approaches in HTA • Enhancing the existing link between the NCPE and academia. “to date assessments in Ireland have been conducted in a pragmatic, timely, transparent and flexible manner and it is important that these features continue to characterise the conduct of future assessments” November 2010 ‘Innovations of Value’ Thank you