* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download liquid-crystal display
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
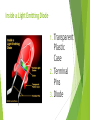
SUKHNANDAN COLLEGE MUNGELI A PRESENTATION ON LED & LCD BY: RAMAKANT CHANDRAKAR What is LED? A light emitting diode (LED) is essentially a PN junction opto-semiconductor device. It emits a monochromatic (single color) light when operated in a forward biased direction. LEDs convert electrical energy into light energy. How Does An Work? a. When sufficient voltage is applied to the chip across the leads of the LED, electrons can move easily in only one direction across the junction between the p and n regions. When a voltage is applied and the current starts to flow, electrons in the n region have sufficient energy to move across the junction into the p region. 3 How Does A LED Work? 1.Each time an electron recombines with a positive charge, electric potential energy is converted into electromagnetic energy. 2.For each recombination of a negative and a positive charge, a quantum of electromagnetic energy is emitted in the form of a photon of light with a frequency characteristic of the semi-conductor material (usually a combination of the chemical elements gallium, arsenic and phosphorus).. 4 Inside a Light Emitting Diode Transparent Plastic Case 2. Terminal Pins 3. Diode 1. Driving LEDs Two type of DRIVING LED Analog LED Drive Circuits Digital LED Drive Circuits 6 Analog LED Drive Circuit 7 Digital LED Drive Circuits 8 Some Types of LEDs Bargraph 7-segment Starburst Dot matrix 9 Advantage of an LED Efficiency Small is high size On/Off time is less . Slow failure Lifetime Applications of an • Sensor Applications • Mobile Applications • Sign Applications • Automative Uses • LED Signals • Indicators 11 Liquid-Crystal (LCD) Displays 1. What’s Liquid Crystals (LC) intermediary substance between a liquid and solid state of matter. e.g. soapy water light passes through liquid crystal changes when it is stimulated by an electrical charge. 13 2. Introduction to Liquid Crystal Displays A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat panel display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly It consists of an array of tiny segments (called pixels) that can be manipulated to present information Using polarization of lights to display objects Common wrist watch and pocket calculator to an advanced VGA(video graphic array) computer screen 14 Different types of LCDs There are Two type of LCDs available 1.Passive Matrix LCDs 2.Active Matrix LCDs 15 Active Matrix V/S Passive Matrix LCDs Passive Matrix LCD Active Matrix LCD Allow high resolution Allow very high resolution It is usually limited to about 50 rows It isn`t limited to about 50 rows Each sub-pixel is individually controlled by an isolated thinfilm transistor (TFT). More use in Laptop & TV Each sub-pixel is not individually controlled by an isolated thinfilm transistor (TFT). Less use in Laptop & TV LCD Display Technology Technology Better Enhancements: color through corrected CCFLs, LEDs Improved Higher black levels (compensating films) Wider contrast (pulsed backlights) Higher viewing angles (compensating films) resolution (1920x1080) Improved LC twist times Advantages Very compact and light. Low power consumption. Very little heat emitted during operation, due to low power consumption. No geometric distortion. Is very thin compared to a CRT monitor, which allows the monitor to be placed farther back from the user, reducing close-focusing related eyestrain. Can be made in almost any size or shape. No theoretical resolution limit. Can be made to large sizes (more than 24 inches) lightly and relatively inexpensively. . Applications Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Alpha-numeric Back For display lighting systems brighter displays Comparison Between LED & LCD LED LCD Power Consumption is less Power Consumption is more Faster response rate time Slower response rate time Sizes Available Sizes Available 17inches and 70inches. 15inches to 65 inches Color Accuracy is less Cannot be extremely slim Color Accuracy is more Can be extremely slim AND THANK YOU FOR YOUR PATIENCE….