* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction_to_Forces
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
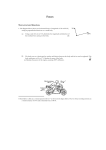
What is a Force? Draw a picture or give a definition. Write a mathematical equation to show what makes a force stronger or weaker. FORCES When you ride a bike, your foot PUSHES against the pedal. The push makes the wheels of the bike move. When you drop something, it is PULLED to the ground by gravity. FORCES A FORCE is a PUSH or PULL in a particular DIRECTION. Sometimes, a force is also a twist! FORCES FORCES AFFECT HOW OBJECTS MOVE. Forces can affect motion in the following ways: They can make objects: BIG SCIENCE IDEA i) START MOVING ii) MOVE FASTER iii) MOVE SLOWER iv) STOP MOVING v) CHANGE DIRECTION vi) CHANGE SHAPE FORCES Since forces cause changes in SPEED or DIRECTION of an object, we can say that…. Forces cause ACCELERATION. There are lots of different types of forces This can be any driving force, it may be a push or pull, but it could be an engine which forces an object forward. This is the force required to raise an object through a fluid This is a force which acts in the air, it can slow objects down when they are moving against it. Or if harnessed could be used to move an object along. This force acts on objects when they are in contact with a surface, such as the ground. It can be reduced by ensuring both surfaces are smooth. This force affects every object on Earth. It is a force which pulls everything to the centre of the earth. This is an upward force which acts against gravity. The reason that you do not fall through the earth is due to this force. Other forces can’t be seen but form fields. Examples of this would be magnetic fields and electromagnetic fields. We use arrows to represent forces on objects. Motive Force (Thrust) 1000 Newtons We always measure forces in Newtons 07/05/2017 Balanced and unbalanced forces Consider a camel standing on a road. What forces are acting on it? Reaction These two forces would be equal – we say that they are BALANCED. The camel doesn’t move anywhere. Weight 07/05/2017 Balanced and unbalanced forces Reaction What would happen if we took the road away? The camel’s weight is no longer balanced by anything, so the camel falls downwards… Weight Group Activity: What forces are acting on this car which is driving along? (label the diagram with arrows showing the direction and type of force) For bonus points: Can you make the size of the arrows proportional to the force(s) acting on the car? Group Activity: What forces are acting on this car which is driving along? This acts against the car, as it moves forward and is acting against the propulsion. This force is always present. It goes towards the centre of the earth, so will always be pointing from the top of the object Thrust This is the most powerful force, this should be your largest arrow, it should be pointing in the direction the car is going … Reaction This force is only present where the car is in contact with the floor, it acts against the propulsion. Balanced and unbalanced forces 07/05/2017 Resultant Forces If the forces on an object are unbalanced we say that a RESULTANT FORCE acts on the object. Resultant force. A resultant force is a single force that can replace all the forces acting on an object Resultant forces cause the object to accelerate or in some cases change shape. If the forces are balanced we can say the resultant force is ZERO and the object will not change its velocity ALSO: forces at right angles to each other (or shape). have no effect on each other. = What is the Resultant Force? 5N The resultant force is 1N to the right 4N What is the Resultant Force? 3N The resultant force is 3N to the left 6N What is the Resultant Force? 5N There is no resultant force 5N What is the Resultant Force? 7N The resultant force is 11N to the right 4N What is the Resultant Force? 8N The resultant force is 5N to the left 3N What are the Resultant Forces? 1N 2N 9N 1N The resultant force is 7N to the right What are the Resultant Forces? 6N 8N 7N 5N The resultant force is 1N to the left and 1N up