* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monomior: is a constant variable or a porduct of a constant and one
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
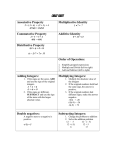
Monomior: is a constant variable or a porduct of a constant and one or more variables, with the variables having only not negative integer exponents Polynomior: is a sum of finite number of monomiors Divisibility: if a, b are positive integers than a is a divisior of b, if there is + integer such that a*q=b Properties: a/a if there a not =b and a/b ->not b/a if a/b b/c -> a/c Proof: a/b -> b=a*q b/c -> c=b*q Prime number: positive integers which has exactly 2 divisor Compostive numbers: positive integers which have more than 2 divisiors Common factorization: every number can be composed as a product of a prime number G.C.D.: of two or more positive integers is the greatest positive integer that is a divisior of all the given integers L.C.M.: of two or more integers is the lowest +integers which has each of the given integers as a factor Relative prims: two or more +integers are called relative prims if GCD is one Algebric fraction: is the quotient of two polynomiors.The denominator can't be a constract term.the domain of the algebric fraction is the set of all real number, but the denominator isn't equal to zero. The locus of points: is the sets of all points and only that point which is satisfy all the conditions.the Locus of point are equidistant Geometrical trasformations: our functions whoose domains and ranges are point sets.A point in the domain of a geometrical transformation whoose image is the point itself its called fixed point. Egybevágósági transf.: distance preserving congurent isometry Distance preserving trans.: is a geometry trans. Ion which the langs of the image of any segment is equal to the original segment Reflection about a line: there is a given line t which will be the axis of of reflection. If P is on the line than its image is point P itself. If Q isn't on the linethan from q we draw a perpendicular line to the axis t. Let the interception point be t. We measure the distance of QP from t on the line on the opposite side of the axis, Q' will be the image of Q P=P' Q Properties: Straight line preserving Segment preserving Angle preserving (fixed point, line) Q' Symmetrical Configuration: The planar configuration is said to be a symmetrical about a line if there is a line(axis) in the plane of the configuration, such that, reflection about a line gives the image of a configuration which is the configuration itself Theorems: The angles on the base of trapesium with non-parallel side are equivalent The angles on the base of isoscales triangle are equivalent The diagonals of the trapesium with non-parallel sides are equivalent The symmetrical axis is a perpendicular bisector of the parallel sides of the trapesium with non-parallel sides A C A' B D B' t Reflection about a point: Let O be a given point it will be the centre of the reflection. If P not=O connect PO measure that distance to the other side of O -> P' P O P' Symmetrical configuration: Configuration has a centre symmetry if there is a point such that reflection about a point gives an image of the configuration which is the configuration itself. Parallelogram is symmetrical about a point. Opposite side of the parallelogram are equal Midpoint of the diagonas is the centre of symetric Opposite angles of the parallelogram are equal Proof: D C=A' o A=C' B Reflect BC about O. (BC)'=AD, C'=A, BC ll AD (distance segment preserving) Theorem: The middline of a paralelogram is equal and parallel to the other two sides. D C p q A B p q is the midpoint of the trapesium.Connect the midpoints of the non-parallel sides (midline) Theorem: The midline of a trapesium is parallel to the parallel sides and the lenghts is half as long as their siedes Proof: D C=B' p q A B=C' AD'A'D parallelogram becouse segment preserving reflect p about q >q' Midline of a triangle: A' pp' is the midline of the new paralelogram pp' ll DA' ll AB pp'=AD'=AB Q is the midpoint of pp' C reflect the triangle about r ABA'C paralelogram (distance preserving) p (B') A r reflect p about r ->p' p is the midpoint of AC, p' is BA' q B (A') A' Theorem: The midline of the triangle is parallel to the side and the lenght is half as long as the lenght of a side. Thalesz theorem: The two endpoint of a diameter of a circle and an arbitraly point on the circle can be connected to form a right triangle the diameter is its hipotanuse. Converse of the Thalesz theorem: The circum centre of the right triangle is the midpoint of the hipotanuse. Proof: B C' C A Construct a rright triangle, find its midpoint of AB=F Reflect about F (AC'BC is a retangle (parallelogra with right angles)) CC' and AB are diagonas and half each other and equals AF=BF=CF=C'F Circumscribed quadrilateral is a convex quadrilateral whoose sides are tangent of a circle. Theorem: In a circumscribed quadrilateral the sums of the lenght of the two pairs of opposite sides are equal. A e B f C h D e,f,g tangency point Ae=Ah=a Be=Bf=b stb. A directed angle: alfa and point o are given in the plain the image of any point p is the point of p' such that the angle p'op is equal to the given angle alfa and the distance of point o is itself and it is the centreof rotation Vectors: is a directed line segement. The lenghts of a line segment is a magnitude of the vector and the direction of a vector is measure by an angle. 2Vectors are equivalnt is they have the same direction magnitude.2 vectors are opposite if they have the same magnitude but opposte direction. If the vectors has zero amgnitude and its direction undefined O Equation:is an equality between two expresson