* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Shanks` Class
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Frontonasal dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
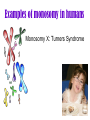
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
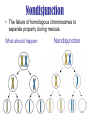
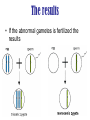
Mistakes in Meiosis Nondisjunction • The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis. What should happen Nondisjunction The results • If the abnormal gametes is fertilized the results Polyploidy • the condition where cells have multiple sets of chromosomes • usually 3-4 sets • Most often found in plants, rare in animals Examples of Polyploidy Diploid & tetraploid many plants Octoploidy strawberries Triploid seedless watermelon Trisomy • The zygote has an extra chromosome • Organisms with an extra chromosome sometimes survive Examples of trisomy in humans • Trisomy 21: Downs Syndrome • Trisomy 18: Edwards syndrome • Trisomy 13: Patau syndrome • XXY: Klinefelter's syndrome Trisomy 21: Downs Syndrome • • • • • • • • • • • • Decreased muscle tone at birth Separated sutures (joints between the bones of the skull) Asymmetrical or odd-shaped skull Round head with flat area at the back of the head (occiput) Small skull (microcephaly) Upward slanting eyes, unusual for ethnic group Small mouth with protruding tongue (see tongue problems) Broad short hands Single crease on the palm Retarded growth and development Delayed mental and social skills (mental retardation) Iris lesion (an abnormality of the colored part of the eye called Brushfield spots) Trisomy 18: Edwards syndrome • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Most children die in the first year of life, some have lived 10 years Growth deficiency Feeding difficulties Breathing difficulties Developmental delays Mental Retardation Undescended testicles in males Prominent back portion of the head Small head (microcephaly) Low-set, malformed ears Abnormally small jaw (micrognathia) Small mouth Cleft lip/palate Upturned nose Narrow eyelid folds (palpebral fissures) Widely-spaced eyes (ocular hypertelorism) Dropping of the upper eyelids (ptosis) Overlapped, flexed fingers Underdeveloped or absent thumbs Underdeveloped nails Webbing of the second and third toes Clubfeet Small pelvis with limited movements of the hips Short breastbone Kidney malformations Structural heart defects at birth (i.e., ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus) Trisomy 13: Patau syndrome • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Mental retardation, severe Seizures Small head (microcephaly) Scalp defects (absent skin) Small eyes (microphthalmia) Cleft lip and/or palate Eyes close set (hypotelorism) -- eyes may actually fuse together into one Iris defects (coloboma) Pinna abnormalities and low set ears Simian crease Extra digits (polydactyly) Hernias: umbilical hernia, inguinal hernia Undescended testicle (cryptorchidism) Hypotonia Micrognathia Skeletal (limb) abnormalities XXY: Klinefelter's syndrome • Klinefelter Syndrome is probably the most common chromosomal variation found in humans. In random surveys, it is found to appear about once in every 500 to one in every 1,000 live born males. • sterility, breast development, incomplete masculine body build, and social and/or school learning problems Monosomy • The zygote is lacking a chromosome • Organisms lacking one or more chromosomes rarely survive Examples of monosomy in humans Monosomy X: Turners Syndrome Monosomy X: Turners Syndrome • • • • • • • • • Short height Webbed neck Drooping eyelids A "shield-shaped", broad, flat chest Absent or incomplete development at puberty, including sparse pubic hair and small breasts Infertility Dry eyes Absent menstruation Absent normal moisture in vagina; painful intercourse Karyotyping • a picture showing the number and type chromosomes in a cell • Chromosomes are arranged in order from largest to smallest • Shows major chromosomal abnormalities • i.e. pieces of chromosomes are missing of extra copies (will not show defective gene) Human Karyotype