* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economic Significance of Microorganisms
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
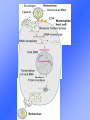
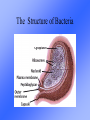
Economic Significance of Microorganisms Microorganisms • Microorganisms are small living things that can only be seen under high power microscope. • Microorganisms include: – – – – – Virus Bacteria Protozoa Microscopic Fungi Microscopic Algae Use of Micro-organisms in environment 1. Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen 2. Decomposition of organic wastes and residues 3. Suppression of soil-borne pathogens 4. Recycling and increased availability of plant nutrients 5. Degradation of toxicants including pesticides 6. Production of antibiotics and other bioactive compounds 7. Production of simple organic molecules for plant uptake 8. Complexation of heavy metals to limit plant uptake 9. Solubilization of insoluble nutrient sources 10. Production of polysaccharides to improve soil aggregation Beneficial Microorganisms • Antibiotics • Food Production • Soil Fertility and Bacteria and Fungi • Combating Pollution Antibiotics • Antibiotic is chemical substance produced by microorganisms that can kill or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms. • Antibiotics kill or inhibit other organisms by interfering the metabolic process in the bacterium that is not found in the host. Penicillin conidia conidiophores phialides Food Production • Fermentation: C2H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + energy • Dairy Products: cheese, yogurt and butter • Wine and bread: yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisaea) Soil Fertility and Bacteria and Fungi • Formation of Humus: – Organic compounds are decomposed by saprophytic bacteria. • Nitrogen Fixation – Nitrogen Ammonia • Nitrifying bacteria – NH4+, NH3 Nitrosomona NO2- nitrobacter NO3- Combating Against Pollution • Sewage Treatment. • Oil spillage: Pseudomonas sp.can digest the oil into harmless forms. Sewage Treatment (1) • Primary treatment – In the sewage treatment plant the solid organic matter is moved from the sewage as sludge which may be treated further to form fertilizer. Sewage Treatment (2) • Secondary treatment: – The organic matter left in solution and suspension are decomposed rapidly by the added microorganisms (e.g. Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Vorticella ) Sewage Treatment (3) • Tertiary treatment: – Finally all the micro-organisms are killed by adding chlorine to the effluent of the treated sewage which can run into the rivers without causing any pollution problems. Water Treatment of HK Microorganism in other productions vaccines amino acid Enzymes (invertase) Vitamins (e.g. B2) Harmful Organisms • Causing Diseases. • Food Spoilage. This orange is covered by fungus. A child infected by mumps. Source from: Microbiology: Essentials and Application (2nd Ed.). Source from : Microbiology: Essentials and Applications. (2nd Ed.) Microorganisms and Diseases • Pathogens are microorganisms that cause disease in animals and crops. • Any organisms that carry pathogen from one living organism to another is called vector. Virus • Virus cause diseases by disturbing the homeostatic condition of the host cells. Viral diseases • Plant virus: Tobacco Mosaic Virus • Human diseases caused by virus: -Small pox -Measles -Influenza -Hepatitis B -AIDS AIDS • Acquire Immune Deficiency Symptom. • It is caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). • Affects T-helper cells, making body defense system unable to combat against disease. • Mainly spread through sexual intercourse and blood transfer. HIV bud from the surface of an infected Helper T cell Hepatitis B Pathogenic Bacteria • Pathogenic bacteria caused diseases by: – destroy the body tissues of the host directly – excrete toxins – release toxin from cell wall after death • Diseases caused by bacteria: – – – – Cholera, Typhoid fever Pneumonia, Whooping cough, Tuberculosis Gonorrhea, Syphilis Food poisoning The Structure of Bacteria E.coli Fungal Diseases -Fungal diseases are called mycoses which affect the skin, nails and hair follicles Methods to control the spread of diseases 1. 2. Prevention Personal and Public hygiene Immunization Treatment Chemotherapy Surgery Food Preservation • Spoilage of food is caused by saprophytic bacteria. • Basic principle of food preservation: – Killing the microorganisms in food; – Stopping or inhibiting their growth. Pickling of Food. Source from: Biology: A Modern approach. (2nd Ed.) Food Preservation Techniques Thermal Processing Refrigeration Drying Food Additives Canning Smoking Thermal Processing Heating Pasteurization Refrigeration Drying Food Additive Canning Smoking