* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
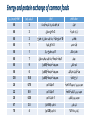
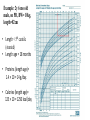
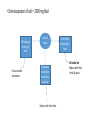
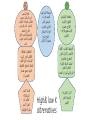
Shrouk Moataz Abdallah Teaching assistant of pediatrics, pedaitric clinical nutrition Malnutrition/short stature in CKD • Strict attention to nutrition is essential to optimise linear growth, wellbeing and survival. • Without early nutritional intervention, losses of as much as 2 height standard deviations may occur in the first 6 months of life (critical phase). • short stature and hypoalbuminemia at the start of dialysis is associated with a 2-fold increased mortality risk Causes of poor growth • A) Many factors, mainly POOR NUTRITIONAL INTAKE: 1-Anorexia due to: • abnormal taste sensation, • frequent oral medications, • preference for water in polyuria 2-Nausea and vomitting 3-Abdominal fullness (PD) 4-GERD and delayed gastric emptying (↑ polypeptide H.) 5-Protein & Volume restrictions with delayed initiation of dialysis • B) Others: protein loss in dialysis, acidosis, chronic inflammation, hormonal foctors..etc. Routes of nutrient delivery Spontaneous oral intake Adequate intake/weight gain? Yes No Supplemental enteral feeding (continous night feeds +/- daytime bolus) Intradialytic enteral nutrition (IDEN) NGT/gastrostomy (PEG) Open or closed system BMI for-height-age? ˂ 5th centile Intradialytic parentral nutrition (IDPN) Nephrotect parentral formula Closed system? Energy • 100% of the estimated average requirement for energy for chronological age. • Inadequate energy from non-protein sources→ -use of dietary protein for energy not growth. -increase in plasma urea and potassium levels. • Volume restriction: use nutrient dense foods (energy enhancers). • Children on PD with glucose-containing dialysate may absorb up 10–12 extra kcal/kg/day Protein • Protein intake must provide at least 100% of the reference nutrient intake (RNI) to prevent growth failure. balance Protein excess Protein malnutrition Targets Albumin: normal Plasma urea: -less than 10 yrs→ ˂ 20 mmol/l -after 10 yrs → ˂ 30 mmol/l • It is suggested to maintain dietary protein intake at : • 100% to 140% of the DRI for ideal body weight in children with CKD stage 3 and at 100% to 120% of the DRI in children with CKD stages 4 to 5. (C) • 100% of the DRI for ideal body weight plus an allowance for dialytic protein and amino acid losses in children with CKD stage 5D. (C) Protein and energy requirements Energy and protein exchange of common foods صنف الطعام المقدار البروتين (جم) الطاقة (سعرحراري) عيش ¼ رغيف بلدي او شريحة توست 3 60 أرز او مكرونة 3مالعق مسلوق 3 60 بطاطس 10اصابع مقلية او ½ كوب مسلوق او مطبوخ 3 80 فول مدمس 3مالعق كبيرة 7 60 خضار مشكل 1كوب مطبوخ مركز 1 50 بيض 1بيضة متوسطة او ¼ كوب بياض مسلوق 7 80 لحم مشفي حجم بيضة متوسطة (50جم) 9 80 جبنة قريش دهن قليل حجم بيضة متوسطة (50جم) 6 50 فراخ مشفية حجم بيضة متوسطة (50جم) 10.5 120 حبوب ريري او سيريالك العادية 1مكيال 5جم 0.75 20 حبوب ريري التركيبة الخاصة 1مكيال 5جم 0.9 22 حبوب ريري فليكس 1مكيال 5جم 0.35 20 لبن بقري ½ كوب (100ملم) 3.5 67 زبادي سادة %1 ½ كوب (120جم) 4 70 • Inadequate oral and/or enteral protein intake should be considered when children with CKD stages 2 to 5 are unable to meet their protein requirements through food with tight volume restriction → use protein supplements to augment 1 scoop (5g)→ 4.5 g aminoacids Ketoacid supplements with low protein diet!! • Compound α-Ketoacid Tablets • Combine with ammonia to form essential aminoacids: 1. ↓ symptoms of uremia. 2. Protect the remaining renal functions 3. Guarantee the patients’ nutrition even with reduced protein intake. 4. Improve the metabolic complications of ureamia. Ketosteril tablets: Indications & dosage • CKD with GFR less than 25ml/min. • Dosage: children aged 3 and older: 1 tab. / 5 kg BW / day or 100 mg / kg / day. 3 times / day with meals. The tablets should be swallowed, without chewing. Tips in protein and Energy calculations • Euvolemic (DRY) weight should be used: -HD→ average weight after hemodilaysis sessions -PD→weight minus dialysis fluid in the peritoneal cavity • Avoid underestimation in stunted patients: use height age (the age at which the child's height would be on the 50th percentile). • Avoid overestimation in obese: use adjusted weight = ideal weight for height + 25% × [actual weight − ideal weight]. Example: 2y 6 mo old male, on PD, BW= 10kg, length=82cm • Length ˂ 5th centile (stunted) • Length age = 18 months • Proteins (length age)= 1.4 × 10 = 14 g/day. • Calories (length age)= 125 × 10 = 1250 kcal/day Daily 14 g protein exchange 1كوب خضار (1جم) ½ كوب بطاطس مسلوقة (3جم) ½ كوب لبن (3.5جم) 1م .كبيرة فول (2.5جم) 2مالعق كبيرة أرز (2جم) 6مكيال حبوب ريري فليكس (2جم) Protein calories: 350 kcal Remaining non-protein calories= 1250-350= 900 kcal Adequate non-protein calories through nutrient dense foods and low protein alternatives = maximium efficacy of protein utilization Rest of calories: non-protein sources الفواكه قليلة البوتاسيوم. الخضروات قليلة البرويتن (مثل البصل ،الباذنجان ،الفاصوليا الخضراء ،الفلفل ،القرنبيط ،البروكلي). العسل االبيض. المربى. الجيلي. الزيوت النباتية. نشا الذرةEnergy enhancers or fortifiers- Fortification of food • 1- Duocal powder: Protein free - Electrolytes free Balanced blend of carbohydrates and fats Included scoop= 1g powder= 5 kcal Dilutuion: gradually added to baby’s formula or enteral feeds (1 g scoop every day) till maximium of 7 scoops/ 100ml → less than 6 months 10 scoops/ 100ml→ 6-12 months In older children can be mixed with food up to 1:3 dilution with keeping osmolarity of 310mosm • 2-Other energy enhancers • At age of weaning (4-6 month) and older we can replace it with a mixture of carbohydrates and fats for natural sources: • Carbohydrate sources: -Cornstarch (1 tbsp= 10g= 35 kcal) -Honey (1 tbsp = 60 kcal) • Fat sources: -Olive oil or any vegetable oil (1 tbsp= 15ml= 135 kcal) Fluids: Tips in restricting oral fluid intake • In orally fed: -Reduce the intake of beverages, foods that are liquid or semiliquid at room temperature (eg, ice, soup, Jell-O, ice cream, yogurt, pudding, and gravy). -Drinking only when thirsty, taking small amounts throughout the day using small cups or glasses. -Sucking on crushed ice, eating cold fruit, chewing gum and avoiding highsodium or very sweet foods. • Formula or nasogastric tude feedings: The free water content of infant formulas (~90% by volume) and enteral feedings (70% to 85%) should be considered when formulating feeding regimens. Sodium • In case of oliguria→ restrict Na 1-2 mmol/kg/day (1 mmol= 23mg) -Na content of Breast milk (0.8mmol/100ml) and standard infant formulas (1-1.5mmol/100ml) are apropriate till 150ml/kg/day -no added salt during food preparation -low Na food alternatives (fresh food, avoid canned& proccessed) -Consider Alkali therapy as part of the daily sodium allowance. • In case of peritoneal dialysis→2-5 mmol/kg/day • In case of polyuria → more liberal use of Na up to supplementing Na if required (1/4 teaspoon of table salt = 17 mmol). • One teaspooon of salt = 2300 mg Nacl 10% naturally occuring in food Choose low Na alternatives Sodium intake 75% added during food Processing & canning Replace with fresh food 5-10% table salt added to food NO added salt Replace with fresh herbs & spices Potassium • In case of oliguria: -restriction to 1 to 3 mmol/kg/d→1mmol=39mg) of K may be reasonable to start. -Breast milk has the lowest K (1.4 mmol/100ml) compared with standard infant formulas (1.8 to 2.5 mmol/100ml)→Volumes of infant formula greater than 165 mL/kg will exceed (3 mmol) K/kg → usually not reached due to volume restriction - Choose low K food alternatives. - Peel, wash and soak vegetables with high K before cooking. منخفضة البوتاسيوم البطيخ ) 1كوب) ،التفاح وعصيره، التوت بجميع انواعه ، الكمثرى متوسطة البوتاسيوم الجريب فروت، اليوسفي ،التين الشوكي ،الليمون، الفراولة ،البرقوق ،الخوخ )ثمرة صغيرة) ،االناناس القرنبيط ،الكرنب ،الفلفل االخضر وااللوان ،الجزر المطبوخ ،الباذنجان، البصل ،البسلة ،الكوسة المقشرة ،الخيار، البروكولي النيء او المجمد االرز ،المكرونة، الشعرية ،الخبز االبيض عالية البوتاسيوم الموز،البرتقال وعصيره، الكنتالوب،الجوافة ،االفوكادو، المشمش ،التين البرشومي الطازج والمجفف (الياميش)،القراصيا ،البلح (5حبات) المانجو ،الكيوي، العنب البطاطس ،البطاطا، القلقاس الجزر النيء، الخرشوف ،قرع العسل، البامية ،السبانخ ،الطماطم، البنجر ،جميع عصائر الخضروات High& low K altrenatives العسل االسود، الشوكوالتة، المكسرات، الخبز االسمر بالردة ،البقوليات محتوى البوتاسيوم بالمليجرامات في مقادير بعض االطعمة الغنية بالبوتاسيوم نوع الطعام فاصوليا بيضاء أفوكادو بطاطس مشوية بالجلد سبانخ مشمش مجفف زبادي منزوع الدسم مانجو بطاطا بالجلد بلح عصير برتقال كوسة بالجلد عيش الغراب موز طماطم مجففة العسل االسود الفول الحراتي جوافة عنب بودرة الكاكاو توابل بابريكا تين برشومي مشمش طازج المقدار 1كوب مطبوخ ثمرة متوسطة ثمرة متوسطة 1كوب مطبوخ ½ كوب 1كوب ثمرة متوسطة ثمرة متوسطة 3ثمرات كبيرة 1كوب 1كوب 1كوب شرائح موزة متوسطة 5ثمرات ملعقة كبيرة 1كوب ثمرة متوسطة 1كوب ملعقة كبيرة ملعقة كبيرة ثمرة متوسطة ثمرة متسطة الوزن (جم) 179 201 173 180 245 336 114 72 248 180 108 118 10 20 110 55 92 5 5 40 35 محتوى البوتاسيوم (مجم) 1004 975 926 839 755 625 564 542 501 496 455 428 422 345 293 230 229 176 172 125 93 91 Phosphorus • Normal Po4 level: → restrict to 100% DRI • High Po4 level: → restrict to 80% DRI • Breast milk is lowest 15mg/100ml • Cow’s milk is highest 85mg/100ml • Avoid high Po4 foods → liver,yoghurt, egg yolk, whole grains, nuts, preservatives. NB: 1mmol of Po4= 32 mg Instead of these higher phosphorus foods: Choose these lower phosphorus foods: Cow’s milk, yogurt Rice milk (unfortified), stage 1 formulas Processed cheese low-fat cottage cheese Ice cream or frozen yogurt Sherbet Soups made with higher phosphorus ingredients (milk, dried peas, beans, lentils) Soups made with lower phosphorus ingredients (water-based) Whole grains, including whole-grain (brown) breads, cereal, rice and pasta Refined grains, including white bread, cereals, rice and pasta Dried peas, beans (black, kidney) or lentils Green peas, green beans Organ meats, sardines Lean muscle meat, poultry, tilapia fish Nuts and seeds Popcorn Peanut butter and other nut butters Jam, jelly or honey Chocolate, chocolate drinks, Colas Plain water, Carob, candy Composition of breast milk and some commercial formulas formula Calories kcal Proteins g Carbs g Fat g Na meq K meq Ca mg Po4 mg Human milk 68 0.9 7.2 3.9 0.8 1.4 35 15 Bebelac 1 67 1.4 7.5 3.5 1 1.8 52 26 Infatrini 100 2.6 10 5.4 1.6 2.5 100 56 Nutrini drink 150 3.4 18.7 6.9 2.9 3.8 84 74 Similac soy isomil 1 Similac soy isomil2 68 1.8 8.9 3.7 1.4 1.9 70 50 69 2.3 8.03 3.07 1.5 2.5 95 66 123 87 Cow milk 64 3.3 4.4 3.7 2.2 3.8 Vitamens and trace elements • Without dialysis→withhold or minimize exposure to these renally regulated micronutrients. • With initiation of dialysis→ water soluble vitamins should be supplemented (table), trace elemnts are not too much affected with routine hemodialysis→ zinc can be supplemented to depleted child (RDA). Recommended doses of water soluble vitamins ASPEN recommendation Enteral dose Parentral dose Thiamine Recommended (grade D) 0.2-1 mg/day 1.2 mg Riboflavin Recommended (grade D) 0.3-1 mg/day 1.4 mg Pyridoxine Recommended (grade D) 6.25-50mg/day 1 mg Folate Recommended (grade D) 0.4-1 mg/day 140 μg Vitamin B12 Recommended(grade D) 0.5- 2.5 μg /day 1 μg *ASPEN guidelines, 2005 Exercise: 3 month old male baby , weighing 4 kgs, UOP=0.7ml/kg/hr, vitally stable, no RRT • Target nutriton plan: -Fluid requirements insensible = 0.24 × 400= 98 ml Urine output= 68 ml Total fluid intake = 165 ml / day = 180ml infant formula -Energy requirement = normal DRI(110) × 1.3 = 140 kcal /kg/day = 560 kcal/day -Protein requirements= 2.2 g/kg/day= 8.5 gm/ day Plan 1 (breast milk) Meal type Total volume No of meals Protein content (g) Calories (Kcal) Breast milk 180 ml 30ml × 6 1.5 120 Cerelac rice 2 scoop/feed Put on milk feeds 7.2 240 Duocal powder Maximum 3 scoops/feed Put on milk feeds Zero 90 Total calories= 450 Missing calories=110 Breast milk 1ml=0.67 kcal Cerelac scoop= 20 kcal, 0.6 g protein Duocal scoop= 5 kcal Plan 2 (high caloric formula) Meal type Total volume No of meals Total proteins (g) Total calories (kcal) Infatrini milk 180 ml 30 ml × 6 4.6 180 Cerelac rice 1 scoop/ feed Put on milk feeds 3.6 120 Duocal powder Maximum 3 scoops/feed Put on milk feeds Zero 90 Total calories= 390 Missing calories=170 Infatrini 1ml=1 kcal Cerelac scoop= 20 kcal, 0.6 g protein Duocal scoop= 5 kcal • االرشادات العامة لمرضى ارتفاع وظائف الكلى • الغسيل الجيد والتقشير والنقع للخضروات الطازجة لمده ساعتين على االقل في ماء دافئ قبل تناولها او طهيها • سلق الخضروات في كمية ماء كبيرة والتخلص من ماء السلق قبل طهيها • يفضل استخدام الشوي او السلق او البخار او الفرن في الطبخ بدال من القلي • الطبخ باستخدام زيوت نباتية فقط ( زيت ذرة ،زيت زيتون ،زيت عباد شمس) • تقليل كميات ملح الطعام المضاف اثناء الطهي مع امكانية استبداله بجميع انواع التوابل والنكهات االخرى (فلفل ،كمون، قرفة ،جنزبيل ،كاري..الخ) • االمتناع عن استخدام المرقة (ماجي) او الصلصات المعلبة في الطبخ أو الشوربات الحتوائها على نسبة عالية من البروتين والدهون واالمالح • االبتعاد عن تناول الخضروات المحفوظة والمعلبات والفواكه المجففة (الياميش) التي تحتوي على كميات كبيرة من االمالح والمواد الحافظة • تناول اللحوم البيضاء منزوعة الجلد او الحمراء قليلة الدهن او بياض البيض مرة اسبوعيا • تجنب صفار البيض والكبدة والمكسرات وبعض انواع المأكوالت البحرية الحتوائها على نسبة عالية من الفسفور • االمتناع عن استخدام اللبن البودرة واستخدام الحليب السائل قليل الدسم او منزوع الدسم قدر االمكان • االبتعاد عن تناول الجبن الدهنية المصنعة عالية االمالح (الرومي ،الشيدر ،الكريمي) واستبدالها بجبن قريش قليلة الدسم. • استخدام عسل النحل في التحلية بدال من السكر ،تقليل العسل االسود الحتوائه على نسبة عالية من البوتاسيوم • منع تناول الحلوى الصناعية والمخبوزات المكيسة (باتيه ،مولتو ،كرواسون) والسماح بتناول حلوى منزلية مرة اسبوعيا • تقليل االطعمة عالية البوتاسيوم (الرجوع لجدول االطعمة) • ممارسة رياضة خفيفة ان امكن References • Pediatric nutrition in practice 2nd edition , Koletzko B., 2015. • NKF KDOQI GUIDELINES, 2008 update. • www.barttersyndromefoundation.org. • ASPEN, 2005.