* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
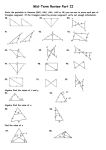
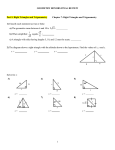
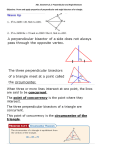
Chapter 8 Introduction to Geometry Chapter 8 Form 1 Mathematics Introduction to Geometry F.1 ( )_______________________( ) Worksheet 2 1. In the spaces below, draw (a) an acute-angled triangle, (b) a right-angled triangle. (c) an obtuse-angled triangle. P D A 2. C E B Q F R In the above figures, ABC is a ____________________ triangle, DEF is an ____________________ triangle, PQR is an ____________________ triangle. The sum of the three angles of a triangle is _______________. 3. A B Figure (a) Figure (b) Figure (c) In the above, Figure (a) shows a quadrilateral, Figure (b) shows a polygon with 5 sides which is called a polygon with 6 sides which is called a The line segment AB is a and Figure (c) shows a . of the polygon. Draw another diagonal in Figure (c). P. 1 Chapter 8 Introduction to Geometry Form 1 Mathematics 4. Figure (a) Figure (b) Figure (c) In Figure (a), the polygon with all sides equal is called an polygon. In Figure (b), the polygon with all angles equal is called an polygon. In Figure (c), the polygon with all sides and all angles equal is called a 5. 3-D stands for . 6. In the figure, the object that occupies space is called a The surface of the figure is called a . The line segment AB in the figure is an A and B are the 7. . . of the object. If the object shown on the right is cut along its length by the plane, then the figure obtained is called a . Draw the cross-section when the solid is cut along the plane ABCD. A B C P. 2 polygon. Chapter 8 Introduction to Geometry 8. Form 1 Mathematics If the cross-sections that we obtain from a solid are all the same, then the cross-sections are called 9. . In the figure, the surfaces of the objects are all polygons. These objects are called 10. The figure below shows some . which can be folded to form a 3-D figure. Try to draw the 3-D figures in the spaces below. Which ones are polyhedron? Why? P. 3 Chapter 8 Introduction to Geometry Exercise: Form 1 Mathematics B A G F C D E Refer to the polygon above. The polygon ABCDEF is a ___________________________________. The polygon AGEF is a ______________________________________. AFG is a __________________ triangle as AF = FG = GA. Draw a diagonal from C to E. CDE is an ____________________ triangle as CD = DE ≠ CE. It is also an _____________________ triangle as ∠CDE is greater than 90°. CEF is a ____________________ triangle as CE ≠ EF ≠ FC. Challenging question. Can you find ∠FAB ? P. 4 Chapter 8 Introduction to Geometry Form 1 Mathematics Glossary diagonal face acute-angled triangle vertex / vertices right-angled triangle cross-section obtuse-angled triangle uniform cross-section polyhedron / polyhedra scalene triangle isosceles triangle net equilateral triangle quadrilateral pentagon hexagon equilateral polygon equiangular polygon regular polygon three dimensional figure solid edge P. 5