* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Muscles of facial expression
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
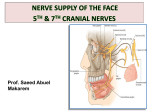
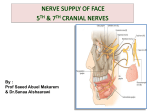
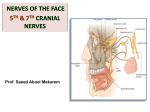
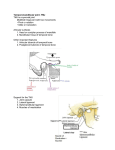
Muscles of facial expression Located in scalp, face, neck No deep fascia in face -> skin moves with muscle, in body, skin moves over muscle. o Muslces originate on bone and insert on skin, or other muscle -> NO TENDONS 1° fxn of face muscles = sphincters and dilators of face orifices, expression = 2° Orbital -> closes eyelids, oral -> lips and mouth shape, nasal -> dilate nostrils, epicranial -> wrinkle forehead, auricular -> animals for ear cocking Cranial Nerves Muslces of face expression -> ALL 2ND PHARYNGEAL ARCH o Supplied by CN VII o CN VII -> 5 of 7 nerves types o Primary root -> cell bodies in facial nucleus SVE (branchial motor) (muscles of face expression) o Intermediate nerve motor -> cell bodies in superior salivatory nucleus GVE (to salivary glands) Sensory -> cell bodies in geniculate ganglion SVA (ant. 2/3 of tongue) GVA (nasal cavity and soft palate) GSA (parts of ear) o primary root and intermediate root enter internal acoustic meatus separate, and merge w/i meatus. Three branches b/f exiting the stylomastoid foramen greater petrosal n. -> GVE to lacimal and nasal glands nerve to stapedius -> SVE to stapedius muscle nerve to chorda tympani -> SVA from tongue, and GVE to submandibular and sublingual glands facial nerve exits stylomastoid foramen -> parotid gland -> parotid plexus (hand thing on neighbor) o temporal o zygomatic o buccal o marginal mandibular o cervical Parotid Gland largest of 3 salivary glands, has parotid sheath sensory inn. = (auriculotemporal n.) V3 and great auricular n. (C2, C3) motor (GVE) = CN IX (via auriculotemporal n.) (hitch a ride) Bell Palsy – CN VII = unilat. Paralysis of face expression mm. UMN and LMN o upper part of facial nucleus -> upper face = bilat. Input from corticonuclear fibers o lower part of facial nucleus -> lower face = only contralat. Input temporal bone fx -> damage to ANY level = FACIAL MUSCLE PARALYSIS o level 1: internal acoustic meatus -> loss of hearing, balance, taste, and salivation o level 2: loss of taste, lacrimation, salivation o level 3 and 4: loss in taste and salivation o level 5: loss in facial muscles only Select Facial Muscles Orbicularis oculi -> around orbit o Orbital part -> circles eye o Palpebral part -> covers eyelids, closes eye gently o LOF -> ptosis, fluid drips out, corneal ulcers Orbicularis oris -> rims the lips, has 4 parts w/ stem at modiolus = hub at mouth corner o Crossing fibers creates philtrum o Whistling, kissing, pout Buccinator -> forms substance of cheek. o keeps cheeks taught. Prevents biting and keeps food together. Expels air. Smiles. o LOF = drooping of mouth corner. Food and saliva dribbles out. Keeps food out of vestibule. Zygmaticus Major -> elevates labial commissures. Smile and sneer. Arteries and Veins and Lymphatics Blushing and blanching. From internal and external carotid. facial artery -> from external carotid o termiantes as angular artery alongside nose o can take pulse with it. Anterior to masseter. o Also temporal pulse Facial vein = main vein of face Triangular danger zone = facial veins to dural venous sinuses Superficial drainage of face = pericervical collar of nodes Deep drainage = deep cervical nodes along jugular Muscles of Mastication They act on the TMJ joint, located in the temporal and infratemporal fossae TMJ = synovial joint. Articulation b/t head of mandible and mandibular/glenoid articular fossa. Articular surfaces = lined with fibrocartilage rather than hyaline. Withstands shear stress, but more susceptible to hormonal fluctuations -> deterioration. Superior articular and inferior articular cavities divided by articular disc o A.d. attached to joint capsule, condyle, and muscle Mod. Hinge joint -> gliding, hinge act, and pivot o Upper jt capsule = loose (gliding) o Lower jt capsule = tight (hinge and some pivot) Chewing involves elevation/depression, protraction/retraction, and medial/lateral excursion Closed mouth to 15 degrees = only hinge action at inferior jt capsule Open mouth >15 degrees = combined gliding of mandibular heads o Involves depression and protraction Grinding movements o resting condyle -> pivots or rotates horizontally o swinging condyle -> swings/glides anteriorly There is a physiologic normal dislocation Dislocation could be pathologic as well TMJ Muscles Masseter = primary mashing, some protrusion Temporalis = along cranium. Drives lower jaw into upper jaw. Up and back pull. Retrusion. Pterygoids, medial and lateral plates o Protrusion, eleveation, side to side movement o Lateral -> lateral direction Upper -> insert on TMJ capsule Lower -> insert on condylar process o Medial -> creates sling w/ masseter two heads, deep and superficial o bilateral action -> elevates mandible o unilateral action -> smaller grinding movements Depression of mandible -> gravity, suprahyoid, infrahyoid, platysma, and lat. Pterygoid CN V Trigeminal nerve. 4 fiber types. GSA SVE Pathway… for SVA (taste on tongue via lingual n.) Pathway…for GVE (salivary glands via lingual n.) Emerges from Pons as o Sensory root Mesencephalic nucleus = proprioception Principal/pontine sensory nucleus = touch Spinal nucleus = pain, temps, touch o Motor root -> cell bodies in trigeminal motor nucleus Most of trigeminal ganglion = sensory nuclei o Housed in trigeminal cave o 3 peripheral processes of trigeminal ganglion = 3 divisions V1 -> out sup. Orbital fissure, somatic sensory to orbit Branch exits supraorbital notch V2 -> out foramen rotundum, somatic sensory to upper jaw Branch exits infraorbital notch V3 -> out foramen ovale, somatic sensory to lower jaw Motor to muscles of mastication Branch exits mental foramen Trigeminal nerve = nerve of 1st pharyngeal arch o Muscles of mastication (V3) V3 branches include Lingual n. Mandibular n. Buccal n. Blood Supply Maxillary artery -> from external carotid. Three parts: 1 -> 2 -> 3 o 1) Mandibular inferior alveolar middle meningeal o 2) Pterygoid buccal artery deep temporal branches o 3) pterygopalantine







![[SENSORY LANGUAGE WRITING TOOL]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014348242_1-6458abd974b03da267bcaa1c7b2177cc-150x150.png)