* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download English title
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Real bills doctrine wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Okishio's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
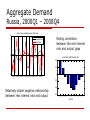
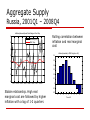
Introduction to a Small Macro Model Jaromir Hurnik Monetary Policy and Business Cycle April 2009 “All models are wrong! Some are useful.” George Box George E.P. Box and Norman R. Draper, “Empirical Model-Building and Response Surfaces” (Wiley 1987), pp. 424. Outline Basic equations Calibration versus estimation Forecast uncertainty The Model A canonical gap model (reduced-form newKeynesian model) Aggregate demand Aggregate supply Uncovered interest rate parity (simple/extended) Policy rule Work horse at many central banks Developed countries: Bank of Canada, Reserve Bank of New Zealand Emerging economies: Czech Republic, Ukraine, Romania, Colombia, Peru, Guatemala, Botswana The Model Distinguishes between the observed value and a trend (≈ steady-state values of the system) Forward-looking Model consistent expectations Inflation Exchange rate Policy analysis Central bank is part of the model Open structure Expert views may be easily incorporated Schematic Transmission Mechanism Transmission Mechanism Inflation expectations LR interest rates SR interest rate RMCI Output gap Inflation Ex rate Shocks hitting the economy Financial shocks: Foreign rates Portfolio changes Demand shocks: Foreign demand Fiscal policy Inflation shocks: Indirect taxes Energy prices Aggregate Demand Relates monetary policy and real economic activity Depends on Own lagged value Monetary policy Nominal interest rate – sticky prices - real interest rate Nominal exchange rate – sticky prices – real exchange rate External developments yˆ t a1 yˆ t 1 a2 mcit a yˆ * 3 t mcit a4 zˆt (1 a4 )rˆt y t Aggregate Demand Real interest rate affects Substitution between consumption today and in the future Investment activity Real exchange rate Substitution between home and foreign goods Aggregate Demand Russia, 2000Q1 – 2008Q4 Output Gap and Real Interest Rate Gap 5 Output Gap RIR Gap Rolling correlation between the real interest rate and output gaps 0 Output Gap<->RIR Gap (time shift) 0.4 0.2 -5 0 2001:1 2002:12003:1 2004:12005:1 2006:12007:1 2008:1 -0.2 Relatively stable negative relationship between real interest rate and output -0.4 -0.6 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 Time shift 2 3 4 Aggregate Demand Russia, 2000Q1 – 2008Q4 Output Gap and Real Exchange Rate Gap 20 15 Output Gap RER Gap Rolling correlation between the real exchange rate and output gaps 10 Output Gap<->RER Gap (time shift) 0.6 5 0.4 0 0.2 0 -5 -0.2 -10 2001:1 2002:1 2003:1 2004:1 2005:1 2006:1 2007:1 2008:1 Counter intuitive relationship between real exchange rate and output in the data. Not surprising. Closed economy and appreciation (depreciation) driven by commodity prices. -0.4 -0.6 -0.8 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 Time shift 2 3 4 Aggregate Supply Relates real economic activity and inflation Monopolistic competition Sticky prices Depends on Expectations Backward- and/or forward-looking Real marginal costs Cost push shocks t b1 t 1 (1 b1 ) e t 1 b2 rmct t Aggregate Supply Output gap approximates domestic inflationary pressure Real marginal cost of domestic producers Real exchange rate gap approximates external inflationary pressure Real marginal cost of importers rmct b3 yˆt (1 b3 ) zˆt Aggregate Supply Russia, 2001Q1 – 2008Q4 Inflation (detrended) and Real Marginal Cost Gap 8 6 Inflation (q-o-q) RMC Gap 4 Rolling correlation between inflation and real marginal cost Inflation (detrended)<->RMC Gap (time shift) 2 0.6 0.5 0 0.4 -2 0.3 0.2 -4 0.1 -6 2001:1 2002:1 2003:1 2004:1 2005:1 2006:1 2007:1 2008:1 0 -0.1 Stable relationship. High real marginal cost are followed by higher inflation with a lag of 1-2 quarters -0.2 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 Time shift 2 3 4 Uncovered Interest Rate Parity Relates domestic and foreign interest rate with the expected change in the exchange rate Domestic interest rate Foreign interest rate Current and expected exchange rate Exchange rate shocks st s e t 1 (i it premt ) / 4 * t s t Uncovered Interest Rate Parity Russia, 1991Q1 – 2006Q4 Exchange Rate (q-o-q) and Money-Market Interest Rate 80 Exchange rate (q-o-q) Interest Rate 60 40 20 0 -20 -40 2001:1 2002:1 2003:1 2004:1 2005:1 2006:1 2007:1 2008:1 Weak relationship between the money market and the exchange rate. Not surprising, because the nominal exchange rate served as the nominal anchor Modified UIP Extension for a more rigid exchange rate regime Smoothness Interventions st e1 stT1 (1 e1 )( ste1 (it* it premt ) / 4) ts where the exchange rate target is defined as stT1 st 1 2 / 4(~ ~* ~ z) Policy Rule Describes behavior of the central bank Reacts when inflation deviates from the price stability Smoothes its reaction to inflation or the output gap (uncertainty about real-time estimates of output gap) Takes into account real economic activity Policy shocks Neutral nominal rate = trend real rate + model-consistent inflation forecast it f1it 1 (1 f1 )(itn f 2 ( te1 T ) f 3 yˆ t ) ti n e ~ i r t t t 1 Policy Rule Russia, 2001Q1 – 2008Q4 Output Gap, Inflation (q-o-q) and Money-Market Interest Rate 30 25 Output Gap Inflation (q-o-q) Interest Rate 20 15 10 5 0 -5 2001:1 2002:1 2003:1 2004:1 2005:1 2006:1 2007:1 2008:1 Interest rate seems to react to both inflation and output, however with a lag only Policy Rule Digression The Taylor-type rule can make policy scenarios difficult to compare One option: replace the rule with a loss function (ála Norges Bank): Min ℓ = var() + l*var(y) Policymaker decides the value of l Model Limitations No explicit modeling of the supply side The choice of the inflation target value does not affect potential output growth No stock and assets equilibria How to model crises? No stock-flow consistency… From gaps back to the levels No explicit modeling of central bank “credibility” Calibration Versus Estimation Estimation Short data sample Changes in economy Policy regime changes Some parameters are difficult to estimate because of endogeneity of policy actions Endogeneity of policy actions (1) The AD equation predicts a negative relationship between r and y Timeline: Expected economic slowdown Policymaker cuts the interest rate The economy still slows down Econometrician observed positive correlation between interest rate and output gap Do rate cuts slow down the economy? Endogeneity of policy actions (2) UIP predicts a positive correlation between E(Δst+1) and r-r* Timeline: Inflation increased Exchange rate depreciated Policymaker hiked the rate to combat inflation Econometrician observed negative correlation between interest rate and exchange rate Do rate cuts appreciate the currency? Calibration Versus Estimation Econometricians reduce our forward-looking model into a backward-looking one: t 1 * t 1 2 * yˆt 1 3 * rt 1 1 * controls ... Such model cannot predict future inflation: Ignores reactions of the policymaker to shocks Coefficients often contradict theory Adaptive expectations of inflation Inflation ≈ past output gaps: yˆ t i 0 t i t i Calibration Versus Estimation Calibration Parameters set on the basis of model properties Restriction from economic theory Responses to typical shocks Adaptive strategy Verification Reactions to shocks Residuals In-sample simulation Data versus model-implied correlations Estimate precision Estimating Versus Calibrating Estimated regression Calibrated model time horizon There are instances to use estimated models, but not for longrun forecasts!