* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I) Inflation
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
2000s commodities boom wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Japanese asset price bubble wikipedia , lookup
Hyperinflation wikipedia , lookup
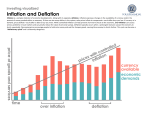
I) Inflation Inflation-A sustained rise in the general level of prices. The value of currency is constantly decreasing. Conversely, prices of all consumer goods are constantly increasing. A) Hyperinflation • Hyperinflation or high inflation can be devastating to an economy• Post WWI Germany (1919-1924) • Printed out money to pay France & UK their war debt rather than taxing. B) Low Inflation • Low inflation can be beneficial to an economy (1-3%) • Indicates moderate growth in the economy c) Inflation leads to speculation • 1) Helps debtors (mortgages decrease in relative value over time) • 2) Hurts creditors & people with fixed income. II) What causes inflation? • A) Demand pull inflationA rise in the general level of prices caused by too high a level of aggregate Shortage demand in relation to E2 aggregate supply. E1 D2 • This is continuously happening because of a constant increase in population and an increase in relative wealth. D1 S P R I C E Quantity b) Cost push inflation S2 S1 P R I E2 Shortage E1 C E D Quantity • A rise in the general level of prices that is caused by increased costs of making and selling goods. • A shortage is created that causes prices to rise when supply is restricted. III) Deflation • A) A decline in the average level of prices • B) Only a problem in Depressions • C) Caused by an overall drop in aggregate demand. S P R I Surplus E1 E2 C E D2 Quantity D1 IV) CPI Consumer Price Index A catalogue of prices of numerous items It’s used to track inflation over the years