* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Themes of Geography
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
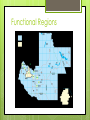
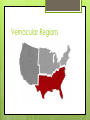
THE 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY THE FIVE THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY Location Place Human-Environment Interaction Movement Regions LOCATION Where are we? Absolute Location A latitude and longitude (global location) or a street address (local location). Paris France is 48o North Latitude and 2o East Longitude. The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave. Relative Location Described by landmarks, time, direction or distance. From one place to another. Go 1 mile west on main street and turn left for 1 block. Map Scale Details are omitted because of space. Level of detail and amount of area covered on a map depend on scale Small scale map: depicts a large area; little detail. Ex: world map Large scale map: depicts a small area; greater details Ex: city map Map Scale Ratio/fraction: numerical ratio btw distance on map and Earth’s surface Ex: 1:24,000 or 1/24,000 (1 is the unit on map=24,000 of the same unit on the ground) Written scale: describes relation btw map and Earth in words Ex: “1 inch equals 1 mile” = 1 inch on map equals 1 mile on surface Graphic scale: bar lone marked to show distance on Earth’s surface Ex: use ruler to measure distance on map and hold against bar ling and read correlating number Projection Method of transferring locations on Earth Advantages and disadvantages of maps and globes? Projection Distortion maps) 1) Shape Map may occur (especially in world appear more elongated or squat 2) Distance Increase or decrease 3) Relative Size One area seems larger than another map but in reality it is small 4) Direction Projection Robinson: pros— useful for oceans; cons—land areas are smaller The West Wing: Why are we changing maps? Mercator: pros— little shape distortion, consistent direction, map rectangular. Cons—heavy distortion at the poles. High latitude appears larger than reality. PLACE What is it like there, what kind of place is it? Human Characteristics What are the main languages, customs, and beliefs. How many people live, work, and visit a place. Physical Characteristics Landforms (mountains, rivers, etc.), climate, vegetation, wildlife, soil, etc. Place Names Toponym: Founder, religious, landscape, physical environment Site: name given to a place Physical character of a place Climate, water sources, topography, soil, vegetation, elevation. Situation: Location of a place relative to other places. Relative location HUMAN-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION How do humans and the environment affect each other? Also known as cultural ecology We depend on it. We modify it. People depend on the Tennessee River for water and transportation. People modify our environment by heating and cooling buildings for comfort. We adapt to it. We adapt to the environment by wearing clothing suitable for summer (shorts) and winter (coats), rain and shine. MOVEMENT How are people, goods, ideas moved from place to place? Human Movement Trucks, Trains, Planes Information Movement Phones, computer (email), mail Idea Movement How do fads move from place to place? TV, Radio, Magazines Movement Diffusion: Process of a characteristic spreading across space. Hearth: where an innovation originates. Relocation diffusion: spread of an idea through physical movement of people. Ex: Spanish speaking culture in Miami, FL. Spread of AIDS across continents. Expansion Diffusion: spread of a feature from one place to another in snowball fashion. Hierarchical diffusion: from person or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places. Ex: hip hop music Contagious diffusion: rapid, widespread diffusion of a characteristic through population. Ex: Ideas on the internet. Stimulus diffusion: spread of principle; characteristic fails to diffuse. Ex: computers sold REGIONS How are Regions similar to and different from other places? Formal Regions (uniform) Regions defined by governmental or administrative boundaries (States, Countries, Cities) Regions defined by similar characteristics (Corn Belt, Rocky Mountain region, Chinatown). Functional Regions (node) Regions defined by a function (newspaper service area, cell phone coverage area). Vernacular Regions Regions (perceptual) defined by peoples perception (middle east, the south, etc.) Formal Regions Functional Regions Vernacular Regions Remembering the 5 themes If you can’t remembering what they are just ask MR. HELP!!! M – Movement R – Regions HE – Human Environment interaction L – Location P - Place Your assignment Describe you and your family using the 5 Themes of Geography. Make sure you use every theme. Type your biography, double space.