* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Foldable
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
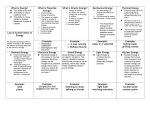
Energy Foldable Types, Forms and Energy Transformations 1. Energy The ability to do work or cause a change. There are 2 types of kinetic Energy:____________ ___________________. and potential A. Kinetic Energy Energy related to the motion of an object, the object is moving. ALSO KNOW AS MECHANICAL ENERGY Examples of Kinetic Energy Examples: Shooting a basketball Skateboard rolling down the hill faster 1. The ______________ something is moving the more kinetic energy it has. mass 2. The more _________ a moving object has, the more kinetic energy it has. B. Potential Energy The energy of position, stored energy, the object is not moving. Examples: A stretched rubber band Or a compressed spring 2 Kinds of Potential Energy 1. Elastic potential energy – stored energy as a result of deformation of an elastic object. 2. Gravitational potential energystored energy that depends on 3 things: the mass, the height, and the acceleration of an object. 2. One of the most familiar forms of energy is thermal energy, which __________ you can sense as heat ___________. 3. All matter is made of particles that small ___________ are constantly in motion __________. 4. If thermal energy is added to matter, the particles move _________, and the faster warmer matter feels _________. 5. If thermal energy is lost, the particles move more _________, and slowly the matter feels _________. colder Chemical energy 6. ___________ is transformed to other forms of energy during a chemical reaction. Examples of Chemical Energy: Food Batteries Examples of Chemical Energy: Candles Photosynthesis 7. A moving electrical charge produces electricity ____________. 8. The energy of these moving particles is electrical energy. ___________ 9. Electrical energy becomes useful when it is ____________ transformed into other forms of energy. Examples of Electrical Energy Electrical Outlets Electrical Wiring Sound energy is 10. ______________ caused by an object’s vibrations. 11. Vibrations that produce sound are transmitted through the air _______. Examples of Sound Energy Tuning Fork Guitar String 12. A familiar form of electromagnetic energy light is ___________ energy. (Also known as radiant energy) microwaves 13. X-rays, __________, TV signals radio and _____ and ultraviolet rays are also forms of electromagnetic energy. 14. When electromagnetic energy interacts with matter it can produce physical ___________ or chemical changes. ___________ Cooking in a Microwave Getting a sunburn 15. _____________ Nuclear energy is energy that can be caused by changes in the nucleus of an atom. 16. Nuclear energy is used to produce electricity in _________ Nuclear power plants __________________. Examples of Nuclear Energy Sun Nuclear fusion/fission 17. Energy Transformation When any form of energy changes into another form of energy. Example of Energy Transformation: A light bulb can transform electrical energy into thermal energy and light (electromagnetic energy) Example of Energy Transformation: A candle burning transforms chemical energy in candle wax to thermal and electromagnetic energy, (heat and light) 18. Law of Conservation of Energy Energy is neither created nor destroyed, it simply just changes form.