* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Periodontitis
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Acute pancreatitis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
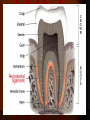
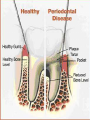
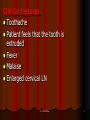
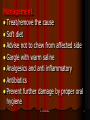
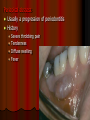
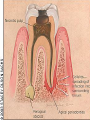
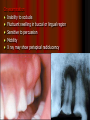
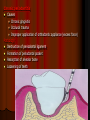
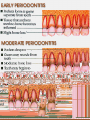
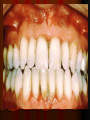
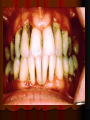
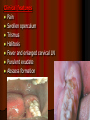
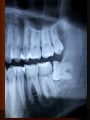
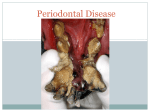
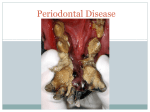
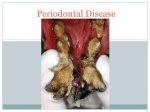
Periodontitis Acute periodontitis Acute inflammation of the perodontal ligament gradually involving the whole periodontium Causes (4I) Injury: trauma due to external force or bite on hard object Infection: Pulpitis, ANUG Irritation due to improper filling Impaction of foreign body (meat bone) Etiological agent – Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Borrelia vincenti Fusiform bacillus Dr S Chakradhar 1 Clinical features Toothache Patient feels that the tooth is extruded Fever Malaise Enlarged cervical LN Dr S Chakradhar 4 Management Treat/remove the cause Soft diet Advise not to chew from affected side Gargle with warm saline Analgesics and anti inflammatory Antibiotics Prevent further damage by proper oral hygiene Dr S Chakradhar 5 Periapical abscess Usually a progression of periodontitis History Severe throbbing pain Tenderness Diffuse swelling Fever On examination Inability to occlude Fluctuant swelling in buccal or lingual region Sensitive to percussion Mobility X ray may show periapical radiolucency Management Incision and drainage Don’t give local infiltration as chances of dissemination of infection is there Antibiotic coverage Analgesic Maintenance of oral hygiene Chronic periodontitis Causes Chronic gingivitis Occlusal trauma Improper application of orthodontic appliance (excess force) Pathology Destruction of periodontal ligament Formation of periodontal pocket Resorption of alveolar bone Loosening of teeth Clinical features Features of chronic gingivitis Swollen, soft, discolored Bleeds on probing Gingival pocket ( >4mm) False pocket if gingiva is elongated towards crown. Recession of gum margin Mobile tooth Halitosis Management Maintain oral hygiene Brushing Mouth Scaling wash to remove plaque and calculi Subgingival curettage of pocket, to allow normal reattachment of gingival and periodontal tissue Mucogingival flap operation: curettage of granulation tissue, dead bone and cementum beneath a flap of gingiva Complications Intraoral and extraoral abscess Maxillary sinusitis Ostemyelitis of jaw Cellulitis of face Dissemination of infection: bacteremia, septicemia Pericoronitis Inflammation of the gingival tissue around an erupting tooth When the eruption is partial, there is an opening through the mucus membrane and rest of the crown is covered by a flap of gum which is known as operculum Commonly occurs in the lower 3rd molar at the age of 18 to 25 yrs But any tooth can be affected Causes Food stagnation and impaction Upper tooth traumatizing lower gum flap Vincent’s infection – acute gingivitis caused by borella vincemtis & fuscobacterium Eruption irritation Immunocompromised host Clinical features Pain Swollen operculum Trismus Halitosis Fever and enlarged cervical LN Purulent exudate Abscess formation Management Clean with 3%H2O2 Nascent O2 is bactericidal Normal saline wash Maintain oral hygiene Brushing Antiseptic mouthwash Chlorhexidine, Betadine, Soft diet Analgesic and anti inflammatory Amoxycillin 500mg tds for 5 to 7 days Or Erythromycin 250mg qid for 5 to 7 days Operculectomy Removal of upper tooth may be necessary