* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polarization_1
Fourier optics wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Photoacoustic effect wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
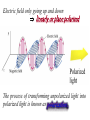
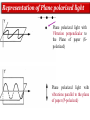
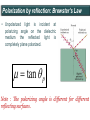
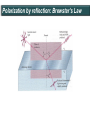
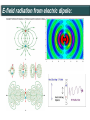
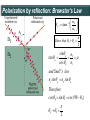
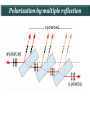
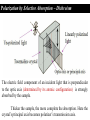
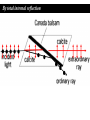
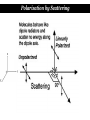
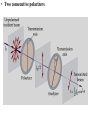
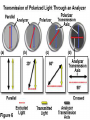
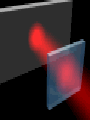
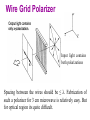
Polarization Interference and Diffraction Wave nature of Light WHY POLARIZATION ? Longitudinal? Transverse? Light is an electromagnetic wave and transverse in nature. Natural light or ordinary light is unpolarized in nature. Vibrations take place symmetrically in all directions in the plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of light. Electric field only going up and down linearly or plane polarized The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as Electric field only going up and down – say it is linearly polarized. Representation of Plane polarized light Plane polarized light with Vibration perpendicular to the Plane of paper (Spolarized) Plane polarized light with vibrations parallel to the plane of paper (P-polarized) Mathematical representation of Plane polarized light Suppose light is propagating in zdirection. Mathematically a plane polarized light can be represented as: E x z, t iE 0x cos kz t or E y z, t jE 0y cos kz t Production of polarized light 1. By Reflection: Brewster’s Law 2. By Refraction: Malus Law 3. By selective absorption: Dichroic material 4. By double refraction: -Nicol Prism - Wave plates Polarization by reflection: Brewster’s Law • Unpolarized light is incident at polarizing angle on the dielectric medium the reflected light is completely plane polarized. tan p Note : The polarizing angle is different for different reflecting surfaces. Polarization by reflection: Brewster’s Law E-field radiation from electric dipole: Polarization by reflection: Brewster’s Law n 2 p tan 1 n 1 n1 n2 Show that 2 p 2 sin p n2 tan p cos p n1 and Snell' s law n1 sin p n2 sin 2 Therefore cos p sin 2 cos( 90 2 ) p 2 2 Polarization by reflection: Brewster’s Law Polarization by reflection: Brewster’s Law For air-water interface, n1 = 1 and n2 = 1.33 (say) then Brewster’s angle is: p = tan-1(1.33) ~ 530 Thus if the sunlight is incident on the sea at an angle close to the polarizing angle, the reflected light is almost polarized. Now if view through the rotation Polaroid, the sea will appear more transparent when the Polaroid blocks the reflected light. Polarization by multiple reflection Use of Polaroid Use of Polaroid Without polarizer With polarizer Use of Polaroid Without polarizer With polarizer Polarization by double refraction Discovered by Dr Dane Erasmus Bartholinus in 1669 When an UPL enters into an anisotropic crystal, it splits into two beams, each of them being characterized by a certain state of polarization. If by some method, we could eliminate one of the beams then we would obtained a LPL. Methods of eliminating one of the beam. 1. By selective absorption - Dichroism. e.g. tourmaline 2. Total Internal Reflection. Polarization by Selective Absorption – Dichroism The electric field component of an incident light that is perpendicular to the optic axis (determined by its atomic configuration) is strongly absorbed by the sample. Thicker the sample, the more complete the absorption. Here the crystal’s principal axis becomes polarizer’s transmission axis. By total internal reflection Polarization by Scattering Law of Malus Law states that intensity of plane polarized light transmitted through the analyzer is directly proportional to the square of the angle between the transmission planes of the polarizer and analyzer. I I 0 cos 2 Intensity of light transmitted through the analyzer I = (E cos)2= E2 cos2 = I0 cos2 When = 00 i.e. pass axis of polarizer and analyzer are parallel I = I0 When = 900 i.e. pass axis of Transmission plane polarizer is perpendicular to Of polarizer transmission plane of analyser E I=0 E sin θ E cos Transmission plane of analyzer Caution: Half rule is applied only when UPL is allowed to fall on polarizer. • Unpolarized light is the superposition of many waves, each with random polarization direction , relative to fixed axis of polarizer. • Each wave is attenuated by factor cos2. • Average attenuation is <cos2> = 1/2 • Two consecutive polarizers. • Two consecutive polarizers. – The first polarizer reduces the intensity by half. – The second polarizer reduces the intensity by another factor of cos2. – The second polarizer projects the electric field onto a new axis, rotated by from the axis of the first polarizer Wire Grid Polarizer Input light contains both polarizations Spacing between the wires should be ≤ λ. Fabrication of such a polarizer for 3 cm microwave is relatively easy. But for optical region its quite difficult. Effect of polarizer on transmitted light 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Un-polarized Light Plane Polarized Light Partially Polarized Light Circularly Polarized Light Elliptically Polarized Light Quest: 22.10 (page-22.38) Optics 4th ed by Ajoy Ghatak (a) Consider two crossed Polaroid's placed in the path of an unpolarized beam of intensity I0. If we place a third Polaroid in between the two then, in general, some light will be transmitted through . Explain this phenomenon. (b) Assuming the pass axis of the third Polaroid to be 450 to the pass axis of either of the Polaroid's, calculate the intensity of the transmitted beam. Assume that all the Polaroid's are perfect. Ans: I0/8 Quest: An unpolarized light passes through a vertically placed polarizer having horizontal polarization axis. Subsequently it passes through a polarizer with its pass axis at 90o with respect to vertical and two polarizers having their polarization axes at an angle 30o and 60o with vertical respectively. What will be the intensity of the emergent light? Ans : (3/32)I0