* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Work Power and Energy 0910
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
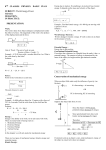
Work, Power & Energy I. Energy A.Energy is… II. Kinetic Energy A.The energy of motion. Kinetic Energy depends on… B.Kinetic energy (KE) – KE = ½ 2 mv III.Potential Energy A.Stored energy due to an objects state or position. The object has the potential to do work. Potential Energy depends on… B.Two kinds of PE… 1.Gravitational PE potential energy created by raising an object above a reference point PEg = weight x height PEg = (mg)h A B C D PEg depends on the reference point or zero level 2.Elastic PE potential energy created by stretching a spring or other elastic material IV.Work A.Work is done on an object when… B.Work – W = Fd (1J = 1N*1m) J – Joule Force and Distance cannot be perpendicular Fa Ff C.Total work equals total force times the distance. Wnet = Fnetd V.‘+’ and ‘-’ Work A.Work is a scalar quantity, but it can still be negative or positive VI.Work and Energy A.Doing work on an object is a transfer of energy B.Work-energy theorem whenever work is done energy changes Wnet = ΔKE -orFnetd = ΔKE • Speed Stacking • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JUYYs1 rDWsc VII.Power A.Power is... B.Power – a quantity that measures the rate at which work is done P = W/t (1W = 1J/1s) W – Watt C.Units of power: SI Unit is Watt (W) English Unit is horsepower (hp) 1 hp = 746 W hp is donkey power VIII.Conservation of E A.Law of Conservation of E –the total amount of energy never changes Total Energy initial = Total Energy final C.Mechanical Energy (ME) – the sum of kinetic energy and all forms of potential energy D.Mechanical energy is conserved when there is no friction Total MEi = Total MEf KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf