* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
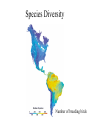
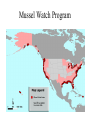
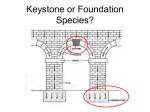
Species Diversity Number of breeding birds Values of species • Instrumental value – a thing is valuable because it is useful to humans • Intrinsic value – a thing is valuable in and of itself – valuable because it exists Economic Values Germplasm storage at Millennium Seed Bank Project, Royal Botanic Garden, Wakehurst Place – outside of London, England The Aurochs – cave paintings Teosinte and Corn New Foods Paca or Mountain Agouti Harvest of Wild Foods Fishing Boats Thailand Digging and Baking Camas Bulbs - Pacific Northwest Medicines Cover of Gerard’s Herbal 1597 Botanic Garden in Padua – 1540’s Rosy Periwinkle Medicine from Live Organisms • Today in US about 41% of medicines have ingredients directly produced by biological organisms - 25% from plants, 13% from microogranisms (penicillin, tetracycline, virtually all other antibiotics, vaccines, hormones, and antibodies) and 3% from animals Epipedobates tricolor – painkiller developed from toxin Clothing, Shelter, Tools, Trinkets, etc. Sisal Fibers Thatch Reeds Thatch Roofing Fuel Gathering firewood - Bolivia Growing willow for biomass fuel Jojoba plant, seeds and oil Sperm whale capture and oil Recreation Biophilia Bird feeding and housing Birding The Big Year Fishing – Winslow Homer Hunting – Winslow Homer Services Pollination Pollinator Loss Native Pollinators – North America Soil Aeration and Decomposition of organic matter Spiritual/Symbolic Values Seagull Monument – Salt Lake City Species as National Symbols River Otter Belted Kingfisher Scientific and Educational Values Jane Goodall And Friend Ecological Values • dominant species - usually the species which constitute a large portion of the biomass in an ecosystem - pines in a pine forest • controller species - species which play major role in movement of energy and nutrients - primary producers and fungal decomposers • keystone species - species which have a larger impact on their environment than we predict based on their abundance Keystone species Strategic Values • Flagship species - the charismatic species that have attracted public attention and won support for conservation - humpback whales, mountain gorillas, tigers, the gray wolf • Umbrella species - species with large home ranges so that by protecting enough habitat to save that species we save many other species as well northern spotted owl, tigers, Pacific salmon • Indicator species - species with narrow ranges of environmental health and tolerance so that the size of their populations is a good indicator of ecosystem health - often these are smaller species - lichens are sensitive to air pollution Northern Spotted Owl Mussel Watch Program Lichens on headstones Uniqueness Values • Uniqueness values: some species are fairly unique from evolutionary standpoint - only members of their lineage - tuatara; duckbilled platypus; gingko; dawn redwood (a living fossil) Tuatara Duck-billed playtpus Gingko Metasequoia – Dawn Redwood Function of Species in Ecosystems – the airplane analogy Function of Species in Ecosystems – the airplane analogy – are species the rivets or the passengers? What happens when we lose too many pieces?