* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Producing Potato Power
Survey
Document related concepts
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
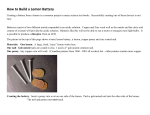
S-6-6-2_Potato Power and KEY Name ___________________________ Date ______________ Producing Potato Power Question: Which materials produce the most electrical current through a potato? Materials: 1 potato about 4 inches of copper wire with insulation stripped 1 steel nail, #6 or 8 1 zinc-plated nail, #6 or 8 voltmeter that can read tenths of a volt Procedure: 1. Carefully push each of the nails into the potato about 1 inch deep, as close as possible without touching at all. These are the battery terminals. 2. Turn on the voltmeter and adjust it to the DC volt setting. 3. Touch one of the voltmeter leads (wires) to each nail. Record the voltage in the data table. 4. Repeat steps 1–3, using the steel nail and the copper wire. 5. Repeat steps 1–3, using the zinc plated nail and the copper wire. Data Table: Terminals Steel nail and zinc-plated nail Steel nail and copper wire Zinc-plated nail and copper wire Voltage (in Volts) S-6-6-2_Potato Power and KEY Questions: 1. What combination of materials produced the highest voltage? 2. Chemical reactions in the potato cell produce an electric current, a flow of charges through the potato. How is the potato cell like a flashlight battery? 3. Cells are devices that convert _____________________ energy into __________________ energy. 4. Draw your experimental set-up in the space below. Label the cell, electrodes, electrolyte, and voltmeter. Use arrows to show the flow of electrical current through the system. Conclusion: How does the potato work as a cell? Write 1–2 sentences, using the terms electrodes, electrolyte, voltage, and electrical current. S-6-6-2_Potato Power and KEY ANSWER KEY Producing Potato Power Data Table: Answers will vary; it is just important that students are able to produce and read a voltage. Terminals Steel nail and zinc-plated nail Voltage (in Volts) Steel nail and copper wire Zinc-plated nail and copper wire Questions: 1. What combination of materials produced the highest voltage? Answers will vary depending on distance between terminals, connection with the leads, and depth that the nails and wire are inserted. In general, the zinc plated nail and copper wire should produce the highest voltage. 2. Chemical reactions in the potato cell produce an electric current, a flow of charges through the potato. How is the potato cell like a flashlight battery? Students should identify that both contain electrolytes that conduct a current 3. Cells are devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. 4. Draw your experimental set-up in the space below. Label the cell, electrodes, and voltmeter. Use arrows to show the flow of electrical current through the system. S-6-6-2_Potato Power and KEY Source: http://www.sullivan-county.com/ele/batteries1_files/05167.png Conclusion: How does the potato work as a cell? Write 1–2 sentences, using the terms electrodes, electrolyte, voltage, and electrical current. The nails and wire are the electrodes. The potato juice is an electrolyte that conducts the electrical current, and the voltage can be measured with a voltmeter.