* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.7 Slope-Intercept Form
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Exact solutions in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
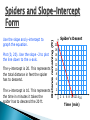
Learn to use slopes and intercepts to graph linear equations. X-intercept - the x- coordinate of the point where the line intersects the x-axis. The ycoordinate of this point is always 0 (3,0). Y-intercept – the y-coordinate of the point where the line intersects the y-axis. The xcoordinate of this point is always 0 (0,5). Slope-intercept form – when a linear equation is written as y = mx + b. m is the slope and b is the y-intercept of the line. Finding Intercepts Find the x-intercept and y-intercept. y A. The line intersects the x-axis at (2,0). 4 2 x –4 –2 –2 –4 0 2 4 The x-intercept is 2. The line intersects the x-axis at (–4). The y-intercept is –4. Finding Intercepts Find the x-intercept and y-intercept. y B. The line intersects the x-axis at (4,0). 4 2 x –4 –2 –2 –4 0 2 4 The x-intercept is 4. The line intersects the x-axis at (0, 1). The y-intercept is 1. Slope-Intercept Form The linear equation y = mx + b is written in slope-intercept form, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept of the line. y = mx + b Slope y-intercept Graphing w/Slope-Intercept Form Graph the equation. 1 y= x+1 3 Step 1: Find m and b. y= 1x+1 3 Step 2: Plot (0, 1) m=1 3 b= 1 1 Step 3: Use the slope to plot at least 1 3 more point on the line. Graphing w/Slope-Intercept Form Graph the equation. 1 y= x+1 3 y 4 2 x –4 –2 –2 0 2 4 –4 Step 4: Draw a line through the points. Not Slope-Intercept Form? Graph the equation. B. 3x + y = 5 Step 1: Find m and b. 3x + y = 5 – 3x = – 3x y = 5 – 3x y = –3x + 5 m = –3 b=5 Now Graph It! Step 2: Plot (0, 5) Step 3: Use the slope –3 to plot at least 1 more point on the line. Step 4: Draw a line through the points. What To Do, What To Do… Graph the equation. 2x + y = 4 Step 1: Find m and b. 2x + y = 4 – 2x = – 2x y = 4 – 2x y = –2x + 4 m = –2 b=4 And the Graph… Step 2: Plot (0, 4) Step 3: Use the slope –2 to plot at least 1 more point on the line. Step 4: Draw a line through the points. Write the Equation Write the equation of the line in slope-intercept form. The line rises from right to left so the slope is negative. m = rise = - 2 5 run The line intersects the y-axis at (0, -4), so the y-intercept is -4. b = –4 Substitute for m and b. x–4 y= 2 5 And Another One… Write the equation of the line in slope-intercept form. The line rises from left to right so the slope is positive. m = rise = run 1 2 The line intersects the y-axis at (0, 2), so the y-intercept is 2. b=2 Substitute for m and b. x+2 y= 1 2 Spiders and Slope-Intercept Form A spider descends a 20-foot drainpipe at a rate of 2 feet per minute. The linear equation y = – 2x + 20 represents the distance y the spider has left to descend after x minutes. Graph the equation, and then identify the x- and yintercepts and describe their meaning. Use the slope and y-intercept to graph the equation. Plot (0, 20). Use the slope -2 to plot the line down to the x-axis. The y-intercept is 20. This represents the total distance in feet the spider has to descend. The x-intercept is 10. This represents the time in minutes it takes the spider has to descend the 20 ft. Distance remaining (ft) Spiders and Slope-Intercept Form Spider's Decent 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Time (min) Exit Ticket 3 1. Graph y = x – 3. Identify the x- and y8 intercepts. y 8 4 x –8 –4 –4 0 4 8 –8 x-int. = 8, y-int. = –3