* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT - UCLA Health
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
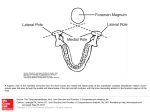
Cummings Ch 127: T-Bone and Ear Anatomy Sameer Ahmed 9/25/2013 The temporal bone consists of four embryologically distinct components: Squamous, mastoid, petrous, and tympanic parts A horizontal ridge known as the temporal line is formed along the most inferior insertion by the temporalis muscle Aligned with the zygomatic process, Surface landmark that estimates the location of the middle fossa floor (Tegmen) “The middle fossa dural plate (MFD) is located on average 5 mm above the LTI (linea tempralis inferior)” “This study confirms that the mastoid antrum is located 15 mm deep to the lateral surface of the mastoid bone” Facial Nerve Course Cisternal segment/intracranial segment Meatal segment → 8mm Porus acoustics: Medial IAC Fundus: Lateral IAC Labyrinthine segment → 5mm Brainstem to IAC --> 16 -24 mm Fundus to geniculate ganglion(1st genu) Tympanic segment → 8-11mm Geniculate to 2nd genu Courses above oval window; dehisc 50% of time 2nd genu is just anteroinferior to the horizontal SCC Vertical segment → 10-14mm 2nd genu to stylomastoid foramen At the fundus (lateral IAC) Bill's Bar separates CN 7 anteriorly from SVN “Jail Bar” Falciform cr. separates CN 7 from cochlear n.; SVN from IVN Anatomic relationship changes closer to the brainstem Jugular foramen: Pars nervosa: CN X, CN XI, Arnold's nerve, jugular bulb, and posterior meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery Pars venosa: CN IX, Jacobson nerve, and venous return from inferior petrosal sinus Inferior limit for a translab approach to IAC Cochlear aqueduct The cochlear aqueduct eventually opens into the scala tympani at the cochlear base Keel: Ridge of bone between Jugular bulb and ICA EAC: Lateral cartilaginous: 1/3rd Medial bony: 2/3rd Think skin; continuous with TM epithelium Bony-cartilaginous junction in EAC Lateral canal skin thicker, more sebaceous units Site of granulation tissue in malignant OE Routes of tumor/infxn spread Foramen of Hushke Incomplete ossification of bony anterior EAC; medial Fissures of Santorini Defects in cartilaginous EAC 1st and 2nd branchial arches → external ear 6 Hillocks of His 1st branchial arch: 1-3 hillocks (tragus, superior helix) 2nd branchial arch: 4-6 hillocks (antihelix, antitragus, lobule, and inferior helix) External ear blood supply Posterior auricular & Superficial temporal art. Tympanic Membrane Outer layer: epidermal/squamous (ectoderm) Middle layer: fibrous (mesoderm) Can be subdivided into radial outer and circular inner Inner layer: mucosal (endoderm) Fibrous annulus: thickened pars tensa forming a fibrous outler ring for the attachement to the TBone; lies within tympanic sulcus except superiorly where it is deficient at the Notch of Rivinus Pars flaccida = Shrapnell's Membrane Eustachain Tube Medial 1/3rd → Bony Lateral 2/3rd → Cartilaginous Collapsed at rest Tensor veli palatini intermittenly enlarges ET during yawning or swallowing Bony cartilaginous jnxn of ET is the narrowest portion of the ET Carotid artery is just medial to ET Middle Ear Relative to tympanic annulus Epitympanum: above annulus Mesotympanum: confined by the annulus Hypotympanum: below annulus Mestoympanum Anterior limit: ET Posterior limit: Facial nerve Medial wall: Cochlear promontory Postero-superior: Oval window Postero-inferior: Round window Sinus tympani: posterior to both windows and medial to vertical division of FN Pyramidal eminence: anterior to 2nd genu Hypotympanum Limited inferiorly by the jugular bulb Epitymapnum Superior-medial wall of bony EAC (scutum) forms the lateral wall of the epitympanum Epitympanum divided into 3 spaces: Prussak's space, just medial to pars flaccida and lateral to the head and neck of the malleus; The compartment anterior to the malleus The posterior compartment, which communicates with the antrum Attic Cholesteatomas can spread postero-superiorly into the antrum or postero-inferiorly into posterior mesotympanum Ossicles Malleus Manubrium (handle; tip is the umbo) Lateral/short process Anterior process Head Neck Tensor tympani attaches to malleus neck and manubrium by a tendon originating from the cochleariform process Incus Body Short process Long process Lenticular process Diarthrodial joints (for malleus-incus and incus-stapes connections) Stapes Head (capitulum) Anterior and posterior crus Footplate (base) Stapes footplate attaches to bony margin of oval window via an annular ligament (syndesmosis joint)