* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy – Where does it come from and why does it produce waste?
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Alternative fuel wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
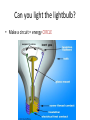
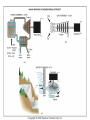
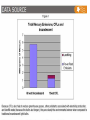
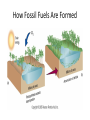
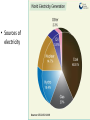
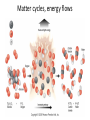
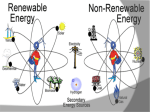
Energy – Where does it come from? ES 302 Objectives • What is energy? • What forms does it come in & how do we use it? • Understand that ALL sources of energy have costs and benefits What is Energy? • Energy “The ability to do work”. • Remember: The amount of energy in the universe is constant, but it flows in a one way path What are the 2 major laws??? - 1st and 2nd Law of thermodynamics What are the 6 major forms? - light, chemical, nuclear, mechanical, electrical, heat Energy Resources • Renewable Energy – – – – – – Hydroelectric Wind Solar Biofuels Hydrogen fuel cell Geothermal • Nonrenewable Energy – – – – Oil Coal Natural gas Nuclear What was the US’s principal energy source… in 1875? In 1910? In 1960? What is your guess? Fossil fuel power Nuclear power Wind / solar power Hydroelectric power 1. Out of the energy sources above, which is used the most worldwide? Least? 2. Guess what percentage each source contributes to the world’s energy supply. 3. Create a graph. Worldwide energy sources 7% 2% 7% fossil fuel nuclear power hydroelectric power wind and solar power 84% Can you make it work? • What is causing the ball to light up? • Where is the power coming from? Can you light the lightbulb? • Make a circuit = energy CIRCLE What is electricity? • The movement of electrons. • Created by moving wires (electrons) through a magnetic field. Energy is needed to make electricity • Where does the supply of electrons come from? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HBu9LZa8Yrk • Can you list the steps to create electricity? Electricity Production • Coal/oil/natural gas fired power plants 1. Burn fossil fuel to make heat. 2. Heat boils water to make steam. 3. High pressured steam turns a turbine. 4. Moving turbine spins a magnet within wires (generator). 5. The magnet creates a flow of electrons = Electricity! 6. Moving electrons sent through wires to houses, schools, etc. What is a watt? • 1 watt = energy to lift 100 g (or 1 Newton) in 1.0 seconds. • It is a measure of energy over time Other Units of Energy • 1 calorie • 1 Btu (British thermal unit) • 1 Q (quad) = 1 quadrillion Btu (very large!) – The U.S. uses ~ 1 quad of energy about every 3.7 days • 1 kWh = one kilowatt of electricity over 1 hour Can you make 2 observations regarding energy and electricity generation? Extra Resources 2nd set of notes on Energy: Usage & Quality Net Energy Energy Quality Energy Efficiency Energy in = Energy Out But the quality is always lower It takes energy to get energy • Before it’s useful… Oil must be 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Found Pumped Transported Refined Transported burned Net energy • Total useful energy available from the resource over its lifetime minus the amount of energy used and wasted • Example: – 10 units of energy in oil in ground – Use 8 units to find, extract, process, transport – How much net energy available? • 2 units Energy Quality • Second Law: In any energy conversion, you will end up with lower quality (less usable) energy than you started with. • QUALITY = The measure of the energy’s ability to be used to produce mechanical or electrical energy • Low temperature heat has the LOWEST quality Energy Efficiency • Amount of energy that gets converted to useful energy. What’s the difference? Light bulb or heat bulb? Two sides to everything. Take old bulbs to Lowe’s or Home Depot! http://www.mnn.com/earth-matters/translating-uncle-sam/stories/cfl-vs-incandescent-battle-of-the-bulb How can changing a light bulb reduce greenhouse gases? Matter Cycles, Energy Flows Global Warming Acid Rain Smog Burning Coal = CO2 + SO + H20 + Ash + (CxHxSxOx) Light + Noise + Heat Example of the Laws of Conservation of Matter and Thermodynamics Cartoon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OqVyRa1iuMc Mini-FBL lesson Discuss the following questions… 1. What is global warming?...climate change? Are they the same? 2. What have you heard about it? 3. Do you think it’s “real?” Climate change vs. Global warming • Climate change - major changes in climate (temperature, rainfall, snow, or wind patterns) lasting for decades or longer. • Global warming - average increase in temperatures near the Earth’s surface and in the lowest layer of the atmosphere. – One form of climate change Global warming • In specific terms, an increase of 1 or more Celsius degrees in a period of 100 – 200 years would be considered global warming. • Over the course of a single century, an increase of even 0.4 degrees Celsius would be significant. Byproducts of electrical generation • Burning coal Air: Mercury, CO2, SO2, NO2, fly ash Water: thermal pollution, acid rain Ground: bottom ash Simple Solutions… What processes involve the transfer of carbon? Carbon Cycle Drawing • Make your own, UNIQUE, drawing of the carbon cycle (both land and ocean). Include the following: – Photosynthesis, decomposition, respiration, combustion, diffusion, (LABEL ALL) – Include yourself somewhere in the cycle – Point out where humans interfere/alter the carbon cycle How Fossil Fuels Are Formed How Fossil Fuels Are Formed Did you beat Mrs. Loch? • You analyzed your (presumed) usage of electricity – That energy is secondary • Primary Energy Resources: The fossil fuels(oil, gas, and coal), nuclear energy, falling water, geothermal, and solar energy. • Secondary Energy Resources: Those sources which are derived from primary resources such as electricity, fuels from coal, (synthetic natural gas and synthetic gasoline), as well as alcohol fuels. Do you have any vampires in your house? What if I left my computer on every night… How much energy would it consume? Assume 14 hours • In “sleep” mode, the computer draws 4 watts/hour How much would it cost the district per day? Per year? • 1 kWh costs $0.15 What if all computers at the school were left on? Energy consumed? Cost to district? • Around 200 computers at UDHS • Sources of electricity http://www.ted.com/initiatives/aws/soccket.html Matter cycles, energy flows What is our best immediate energy option? 1. Cut out unnecessary energy waste by improving energy efficiency 2. Transition to a renewable or solar age – Sun, wind, flowing water, biomass, geothermal, hydrogen gas 3. Burn more coal & synthetic gas/liquids 4. Natural gas 5. Nuclear power No matter what our decision… Ask: • How much will be available in the next 15 years? the next 30 years? longterm? • What is the source’s net energy yield? • How much will it cost to develop, phase in, and use this energy resource? • How will extracting, transporting, and using the energy resource affect the environment? • Can this energy source help us sustain the earth? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xPjESsHwg&feature=related – Very slow explanation of current & voltage. Nice analogy to water (river, lake) • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k7Sz8oT8 ou0 – Cardboard generator constrxn (7:44)