* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2017 Human Body Test 1 Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
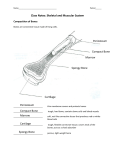
Name ________________________________________________ 2017 Human Body Test 1 Study Guide 1. List the organization of organisms from atoms to organism. Provide an example for each category. atom H molecule H 2O organelle nucleus cell skin cell tissue epithelial organ skin organ system integumentary organism human 2. List the four types of tissue and the function of each. 1. 2. 3. 4. connective – joins, supports, and protects epithelial – covers body surface and lines organs, protection nervous – sends and receives signals/messages muscular – skeletal muscle (movement), smooth muscle (organs & blood vessels), and cardiac muscle (heart muscle) 3. Complete the following body system summary table: Body System respiratory Function inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide digestive breaks down food into nutrients that the body’s cells can absorb integumentary outer protection for body (skin, hair, nails, sweat glands) nervous sends and receives messages circulatory transports materials (nutrients, water, wastes, gases) throughout body (heart = cardiac muscle) protection against disease immune 4. Define homeostasis and provide 2 examples. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a relatively stable (healthy) internal environment. Your body needs to maintain an average temperature of 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit. Your body needs to maintain an appropriate level of oxygen for cells to work properly. other examples: insulin, glucose, heart rate, blood pressure 5. Identify how the body systems listed below would react if you were running outside on a very hot day. Provide details. integumentary – your body would sweat to cool your body temperature respiratory – you would breathe faster to get more oxygen to your cells (for cellular respiration) and to remove carbon dioxide faster circulatory – (blood vessels and heart) – your surface blood vessels would dilate to cool your body and your heart would beat faster to move blood quickly through the body urinary – you would lose less fluid through your urinary system 6. List and explain the main functions of bones: 1. protects organs 2. movement of body 3. produces blood cells 4. structure/support 5. stores minerals/fats 7. Explain the advantage of having: a. small (or short) bones – flexibility, small/precise movement, balance b. long bones - strength/support, large movements c. flat bones – protection of organs 8. Identify the location of the following bones: clavicle, cranium, femur, fibula, humerus, mandible, patella, pelvis, phalanges, radius, ribs, scapula, sternum, tibia, ulna, vertebrae 9. Identify where the following joints are located and their movement. Joint 1. fixed 2. partially fixed Location skull Movement________ none ribs small movements up and down (ribs move up to allow you to inhale; ribs move down as you exhale) 3. ball & socket shoulder/hip 360° (circular) 4. hinge elbow, knee, jaw open/close; bend/extend 5. gliding wrist, ankle multiple 10. What is the name of the tissue that is found on the ends of bones? What is its function? cartilage is a connective tissue that acts as a shock absorber to cushions the ends of bones to prevent them from rubbing against each other 11. How are ligaments and tendons similar? How are they different? Explain. they are both connective tissue ligaments connect bones at skeletal joints; tendons connect muscle to bones 12. What does red marrow produce? red marrow (located in the spongy bone section of long bones, and in flat & irregular bones) produces red and white blood cells 13. Summarize how a human bone heals. Include relevant vocabulary. The injury is flooded with natural painkillers called endorphins, which temporarily block out pain. An injury will swell because the body is sending extra oxygen and nutrients to the injury to begin the healing process. A large hematoma, which is a collection of blood, surrounds the break in the bone. Within four weeks the hematoma will harden around the break, making the injured area extra strong. Over the next several months, osteoclasts will "eat away" the hardened hematoma and the injury will be repaired. Within a year of the injury, the bone will be almost as strong as it was before the break. 14. What are the three types of muscle? Where are they found? 1. skeletal – found throughout body connected to bones; moves bones 2. cardiac – found in heart; pumps blood 3. smooth – found in blood vessels & digestive system; moves materials 15. Identify the muscles in your arm and thigh that allow them to bend and straighten. Which is the flexor? Which is the extensor? Complete the table below. arm thigh flexor bicep hamstring extensor tricep quadricep 16. Explain how muscles work. Do they work alone? Provide details. o muscles work in pairs by pulling on bones o muscles take turns contracting and relaxing o flexors bend bones; extensors straighten bones